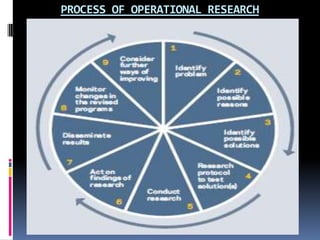
Operational research is the scientific study of operations aimed at improving decision-making. It originated from military planning in World War II and has since expanded to various industries. In public health, operational research uses analytical methods to identify health program problems, potential solutions, and test solutions to inform evidence-based decisions around programs. It involves interdisciplinary teams that study issues like disease screening, outbreak response, and health behavior programs. Societies like IFORS and journals promote the field. Overall, operational research integrates data analysis into program management to enhance monitoring and evaluation.