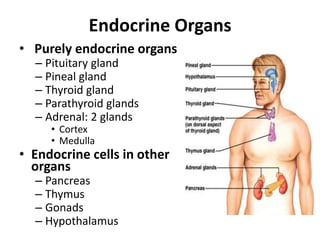
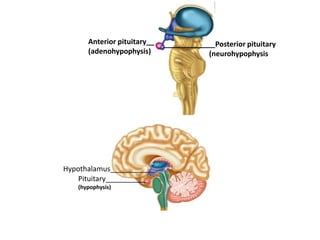
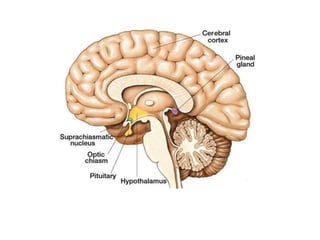
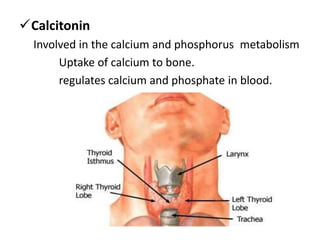
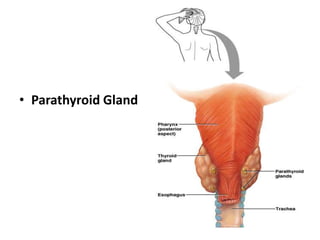
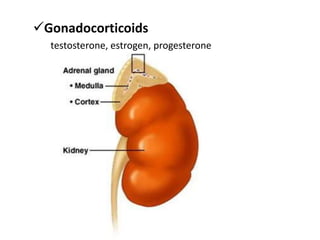
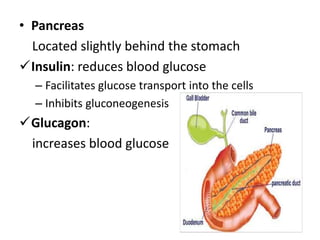
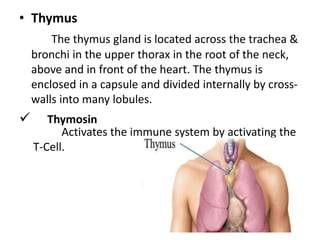
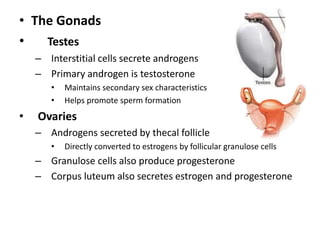
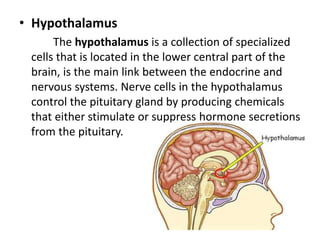
This document provides an overview of the endocrine system and its glands. It defines endocrine glands as glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream rather than through ducts. It then describes the key endocrine glands including the pituitary gland, pineal gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, pancreas, thymus, gonads, hypothalamus, and the hormones they secrete. These hormones regulate metabolism, growth and development, tissue function, sexual function, reproduction, sleep, and mood. The hypothalamus controls the pituitary gland which acts as the master endocrine gland.