The document summarizes major developments in Europe between 500-1200 CE:
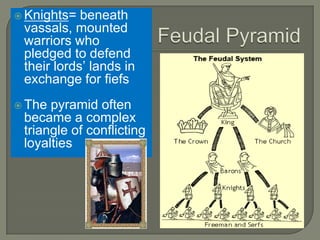
1) The decline of the Western Roman Empire led to the emergence of the Middle Ages and new political systems like feudalism replaced Roman traditions. 2) Germanic invasions disrupted trade, depopulated cities, and shifted populations to rural areas in Western Europe. 3) New languages like French and Spanish developed from Latin as Germanic peoples mixed with Romans. 4) The Catholic Church survived the fall of Rome and became a unifying institution across Europe during the Middle Ages. 5) Feudalism established a pyramid-like hierarchy of lords, vassals, and knights in which land was exchanged for military service.