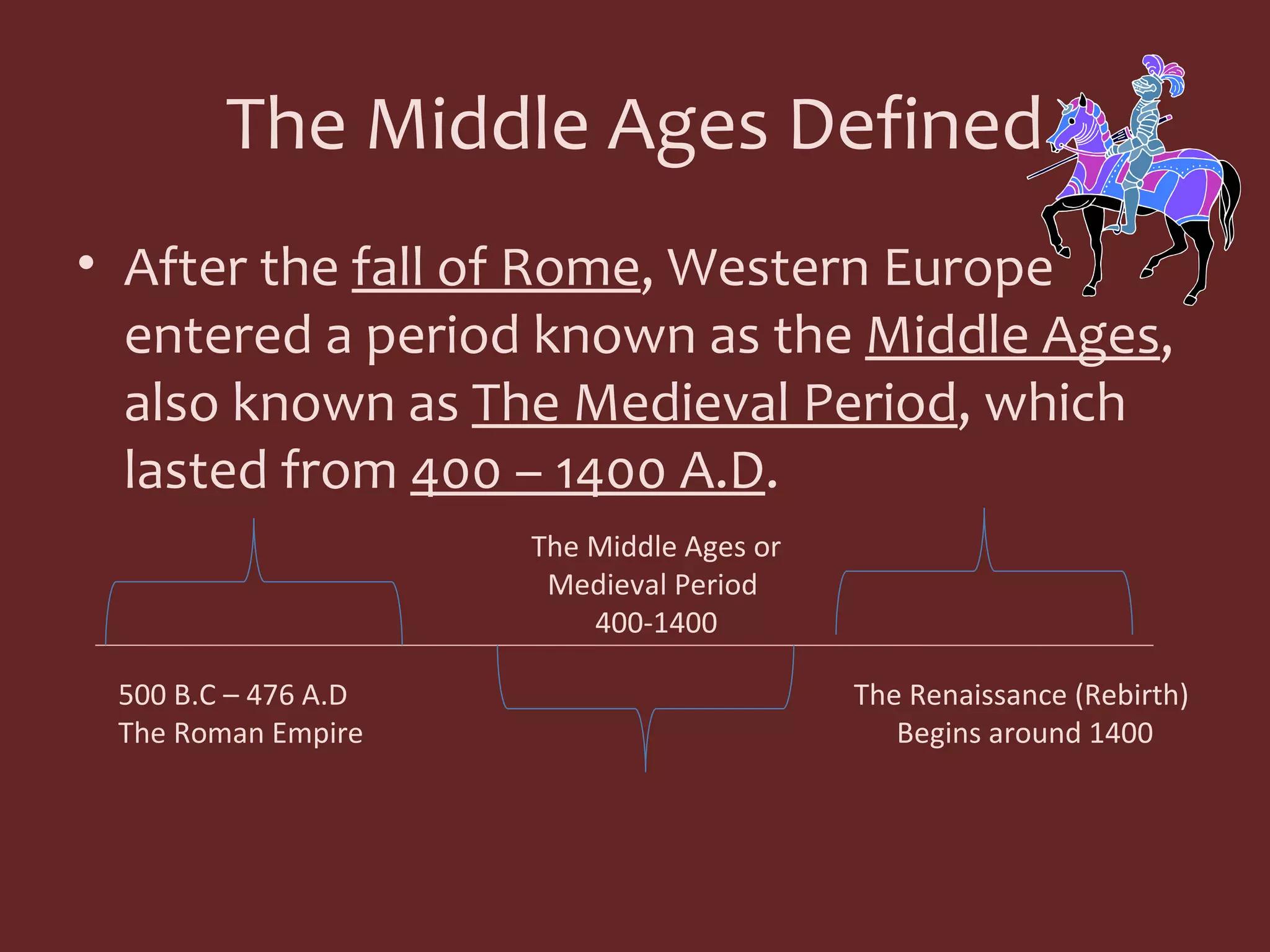
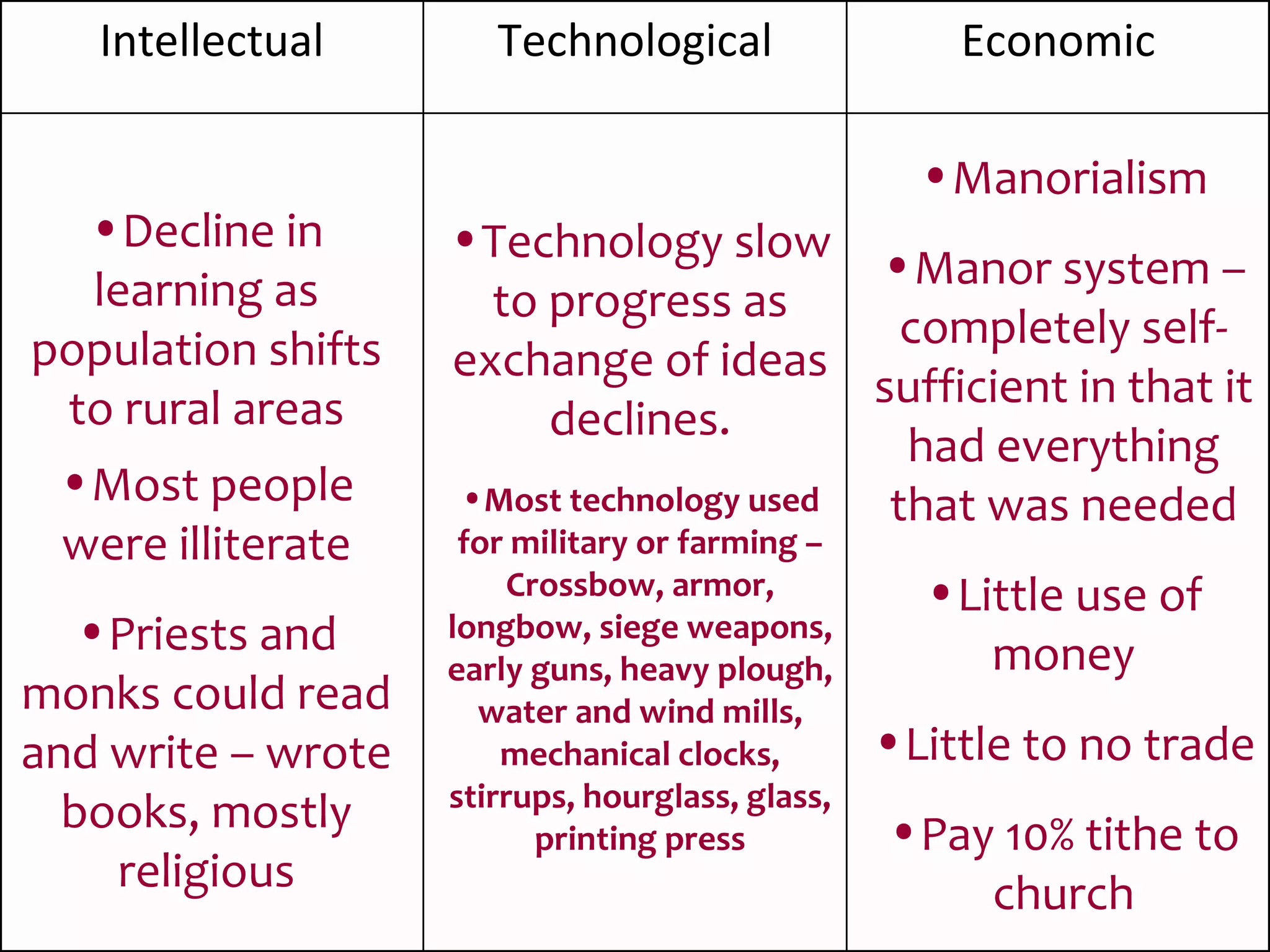
After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, Western Europe entered a period known as the Middle Ages from 400-1400 AD. During this time, feudalism developed as a political and social system out of necessity. Under feudalism, kings granted land to nobles who then protected their territory, and nobles granted land to knights and peasants in exchange for loyalty and labor. This hierarchical system helped bring order but also led to a decentralized power structure and a decline in trade, learning, and technology development over the Middle Ages.