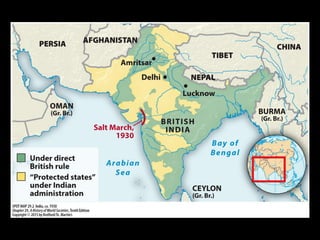
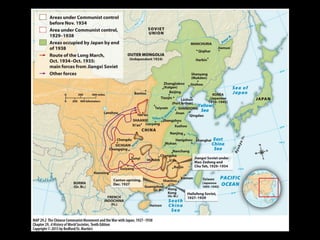
Nationalism arose in Asia between World War I and II for several reasons. The promises of self-rule during WWI raised nationalist aspirations that went unfulfilled. The mandate system and Treaty of Versailles failed to grant independence, fueling further nationalist sentiments. Figures like Ataturk, Gandhi, and early Chinese and Japanese nationalists led independence movements using various tactics from westernization and modernization to non-violent resistance and militant action. However, tensions between groups seeking independence often led to conflicts, as nationalist aspirations did not always align, while European colonial powers also resisted full independence.