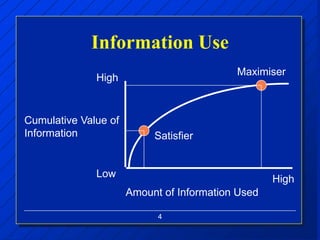
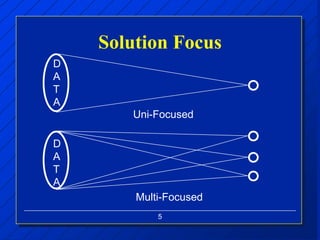
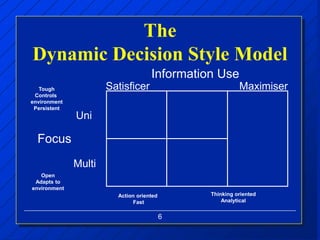
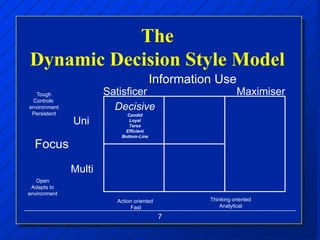
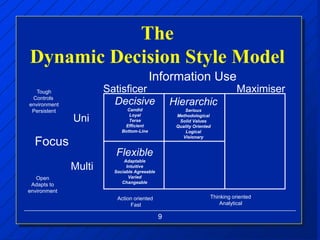
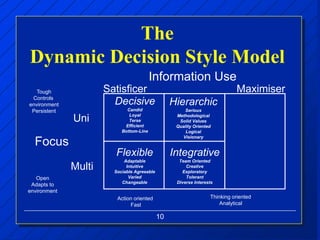
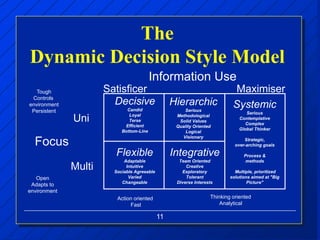
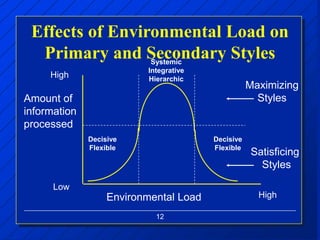
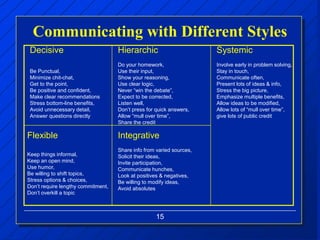
The document discusses decision making styles, which are learned habits of thinking influenced by culture and experience. There are two key elements of decision styles - information use, which refers to the amount of information considered when making decisions, and solution focus, which refers to the number of alternatives generated. The Dynamic Decision Style Model categorizes styles based on whether they focus on a single or multiple solutions and use a high or low amount of information. Each style has strengths and weaknesses that are suited to different environments and situations. The document also provides tips for communicating effectively with individuals of different decision making styles.