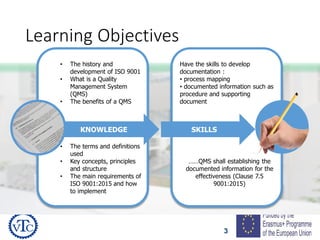
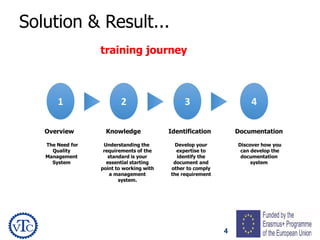
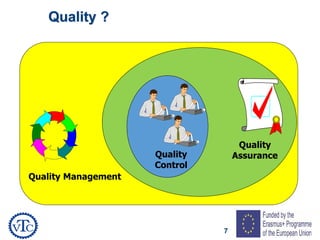
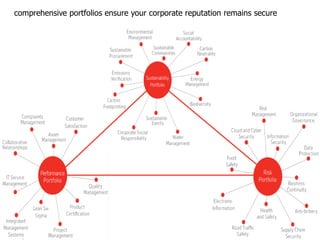
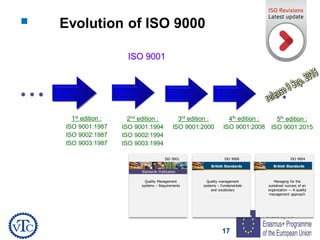
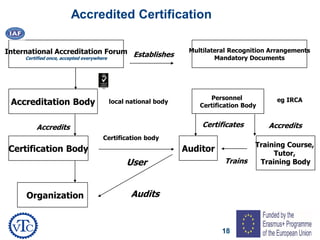
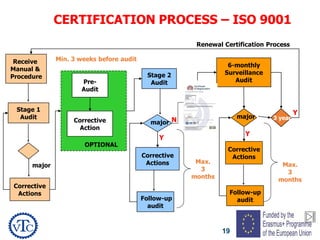
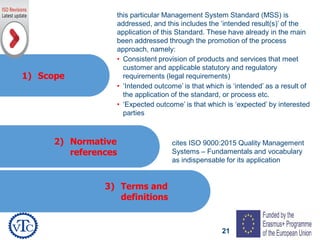
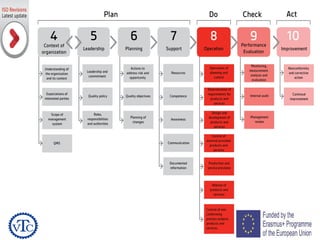
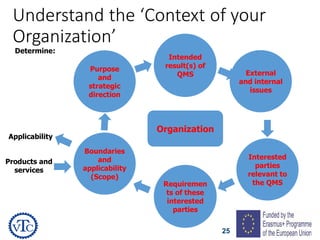
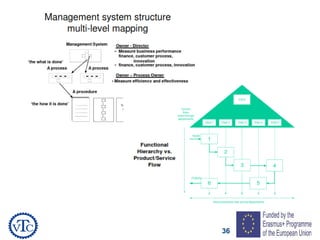
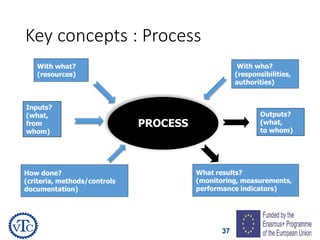
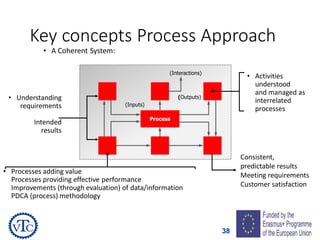
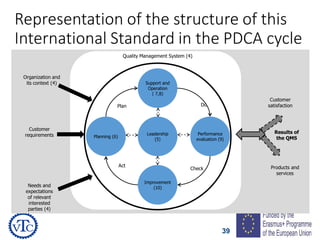
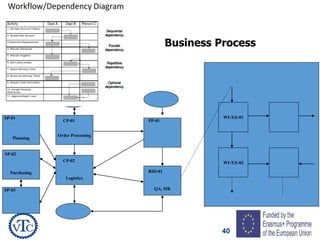
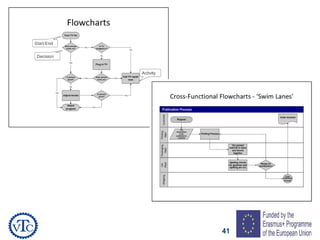
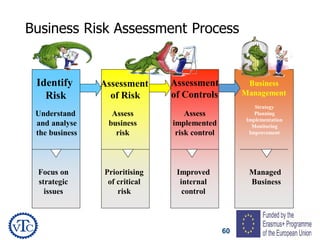
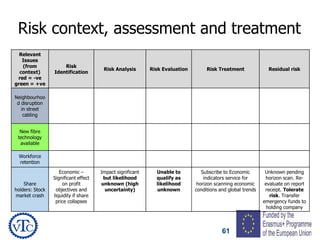
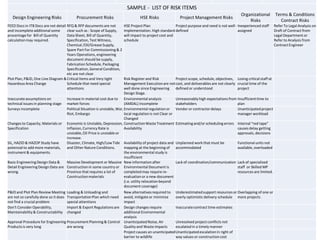
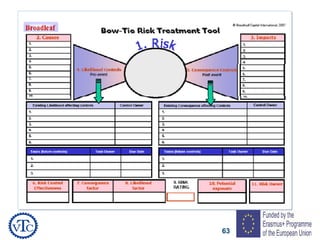
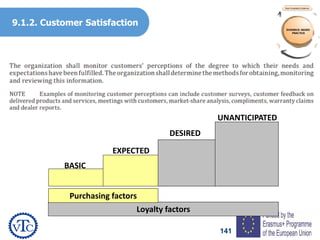
1) The document discusses leadership requirements in ISO 9001:2015, including demonstrating leadership commitment, establishing a quality policy, and defining organizational roles and responsibilities.
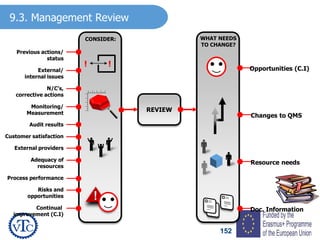
2) Top management must ensure the quality management system is effective and integrated, that resources are available, and that quality objectives align with strategic goals. Customer focus and satisfaction must also be promoted.
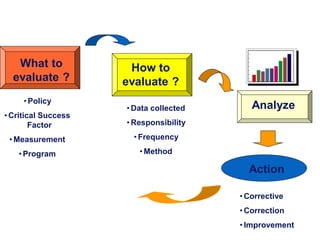
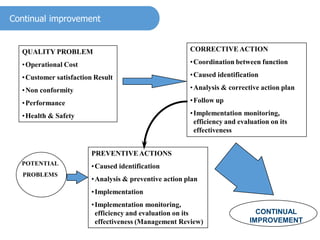
3) The quality policy provides a framework for quality objectives and commits the organization to satisfying requirements and continual improvement. It must be communicated and available as documented information.