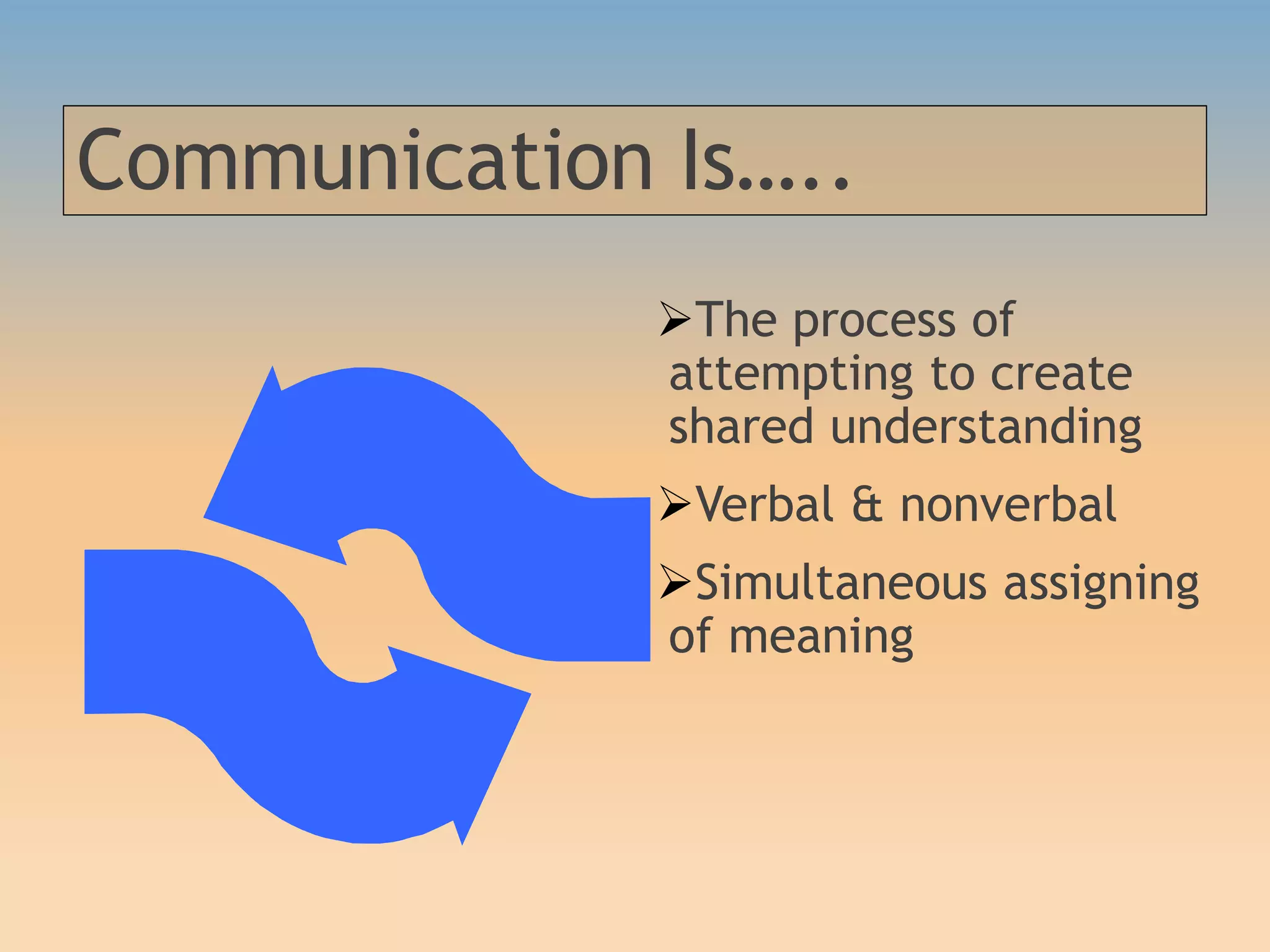
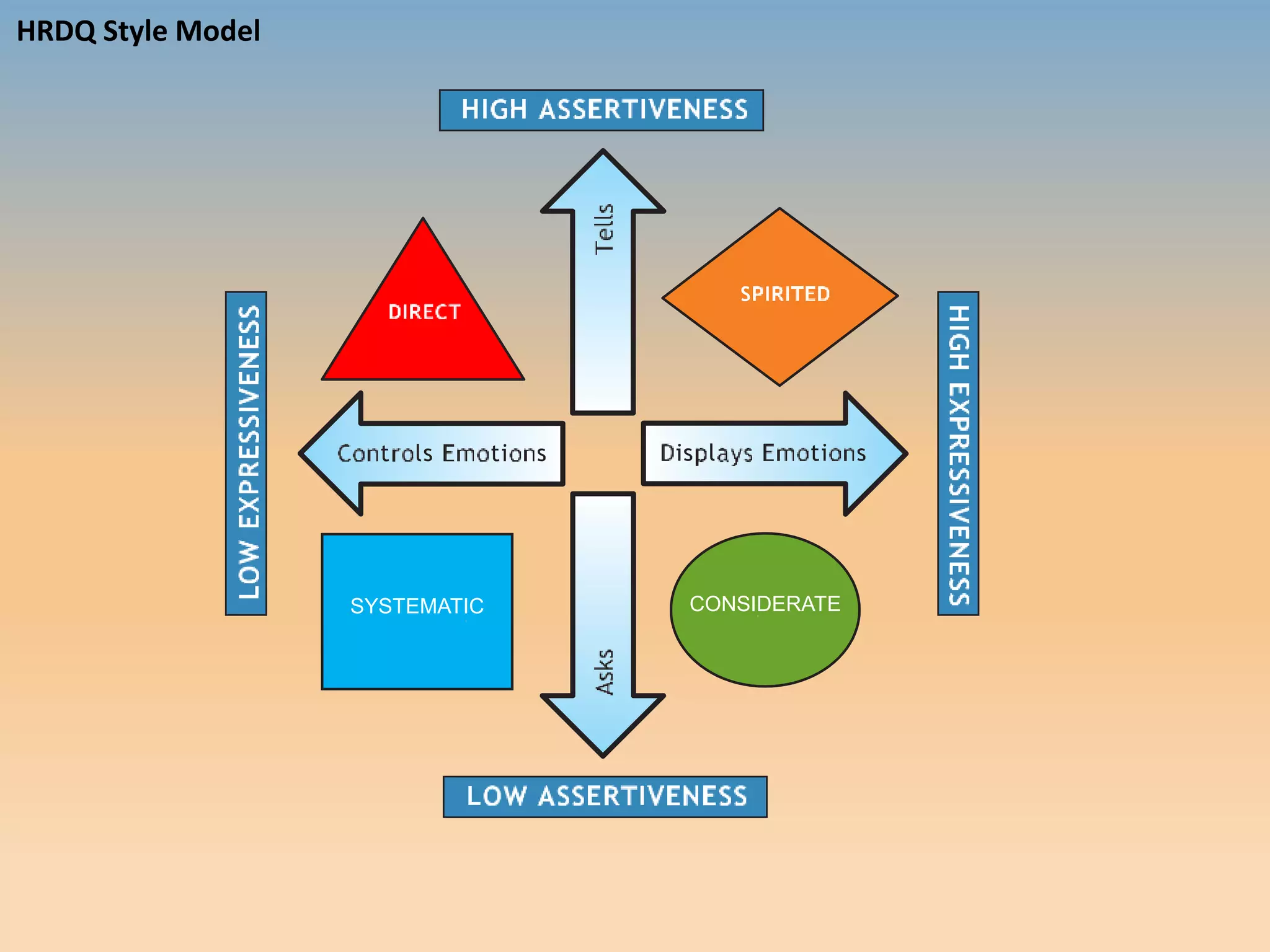
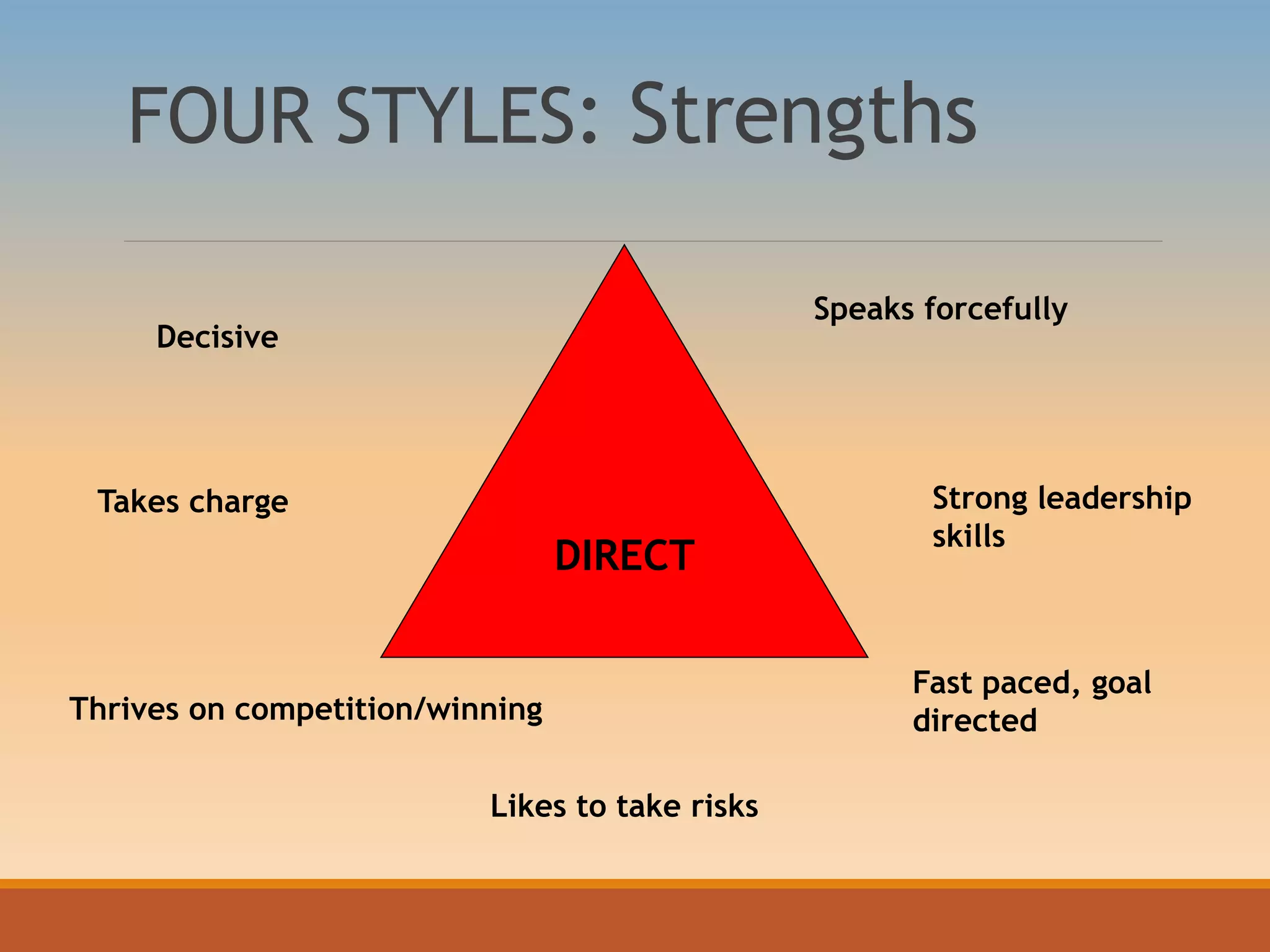
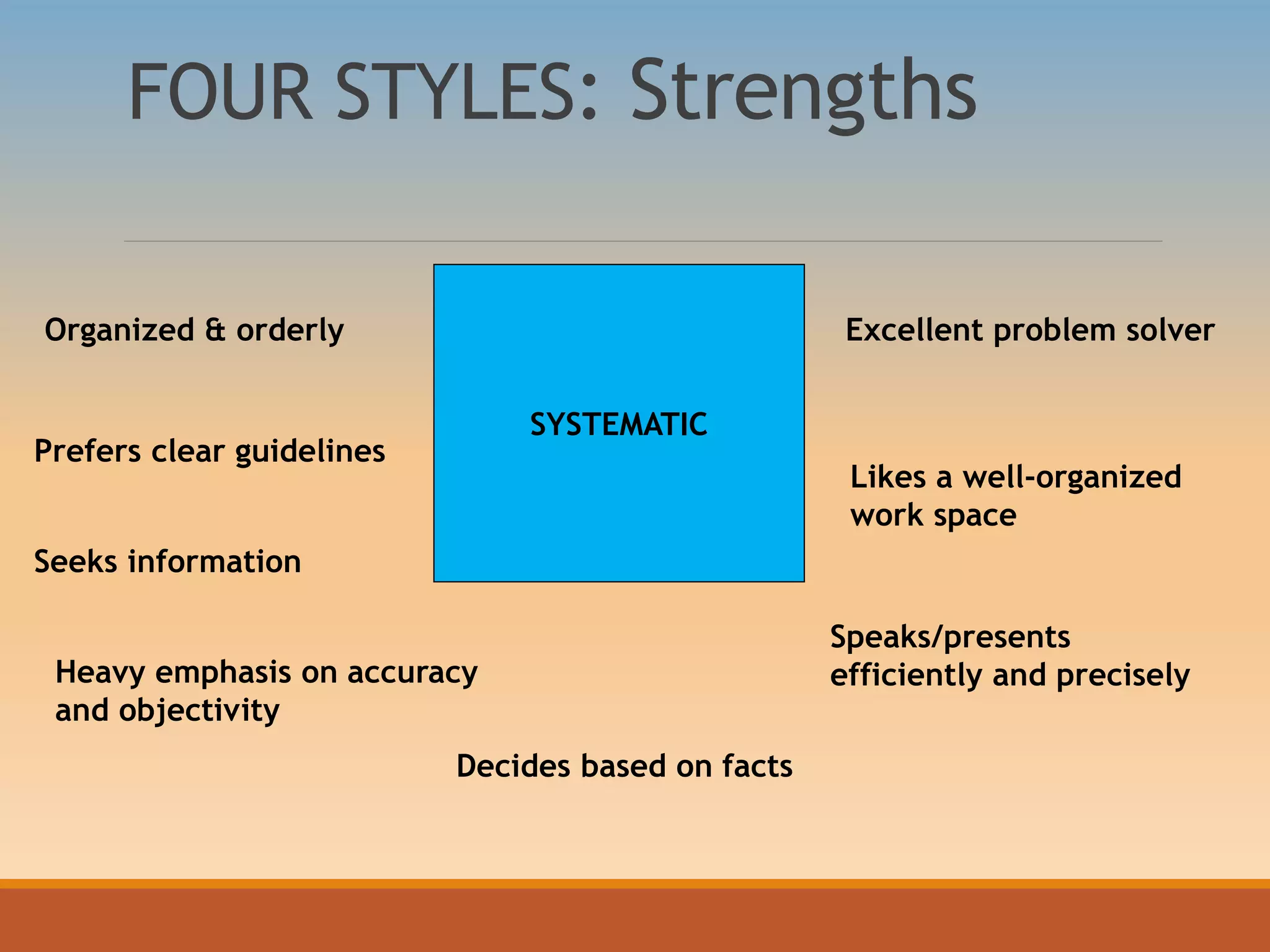
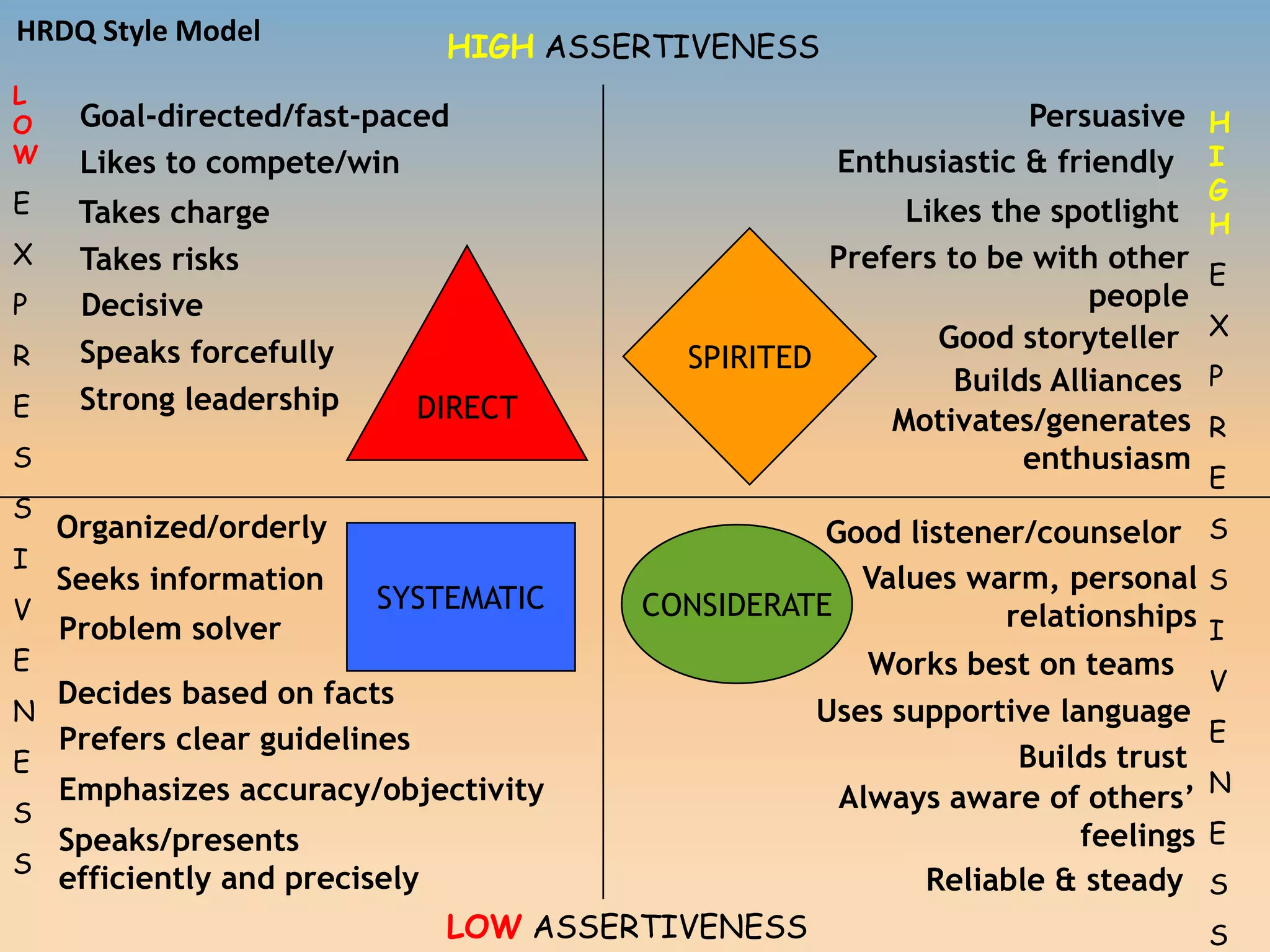
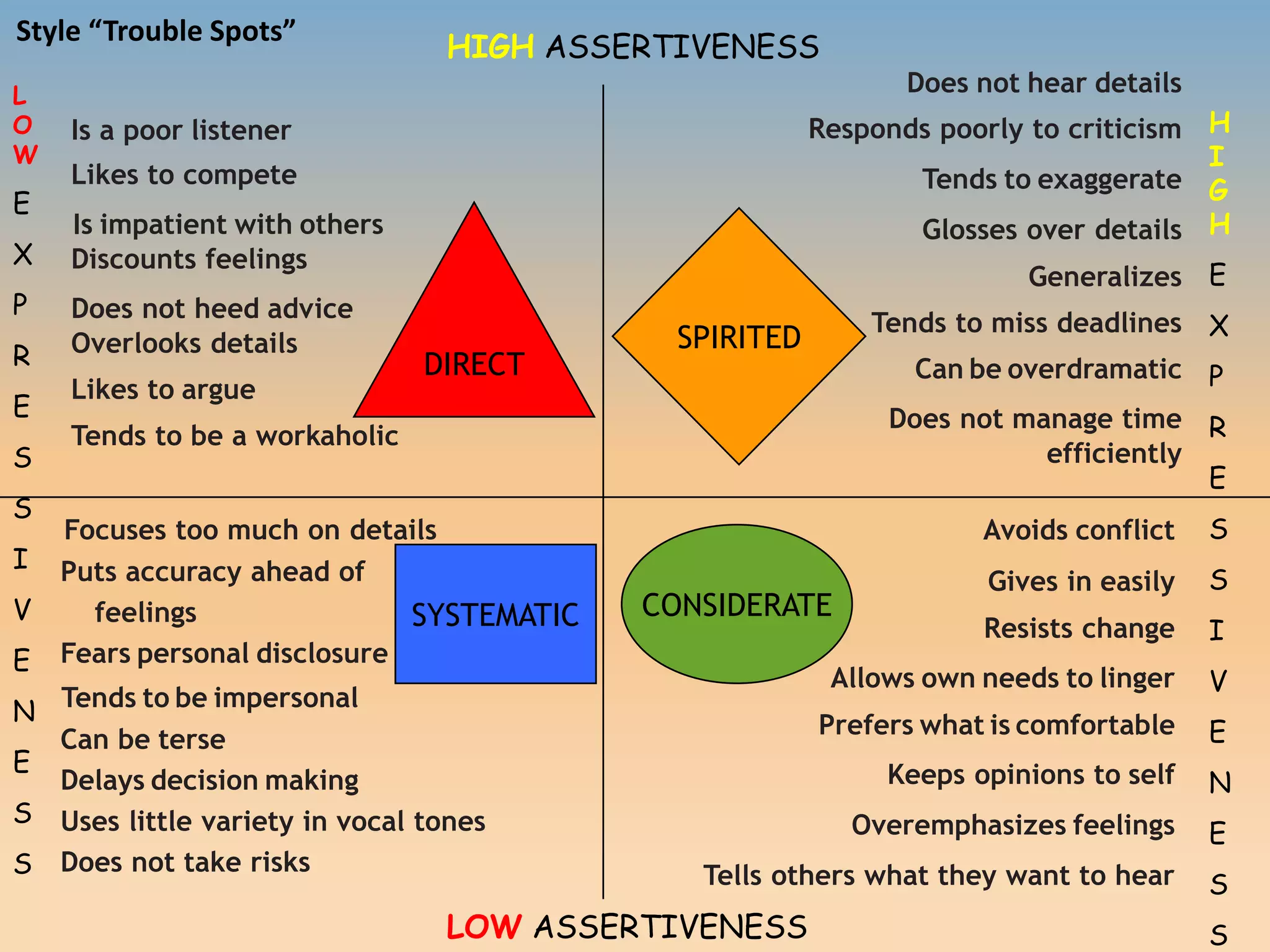
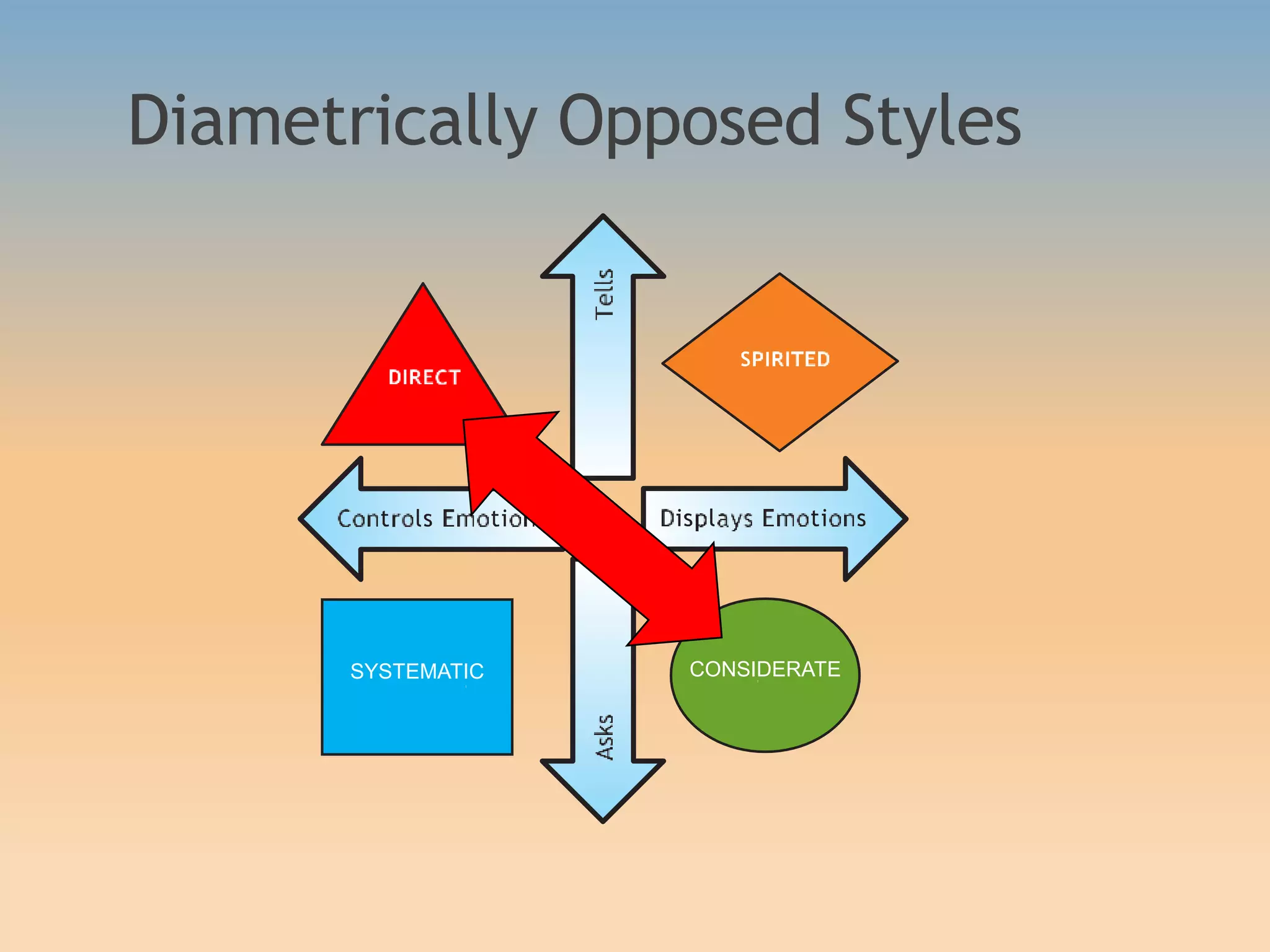
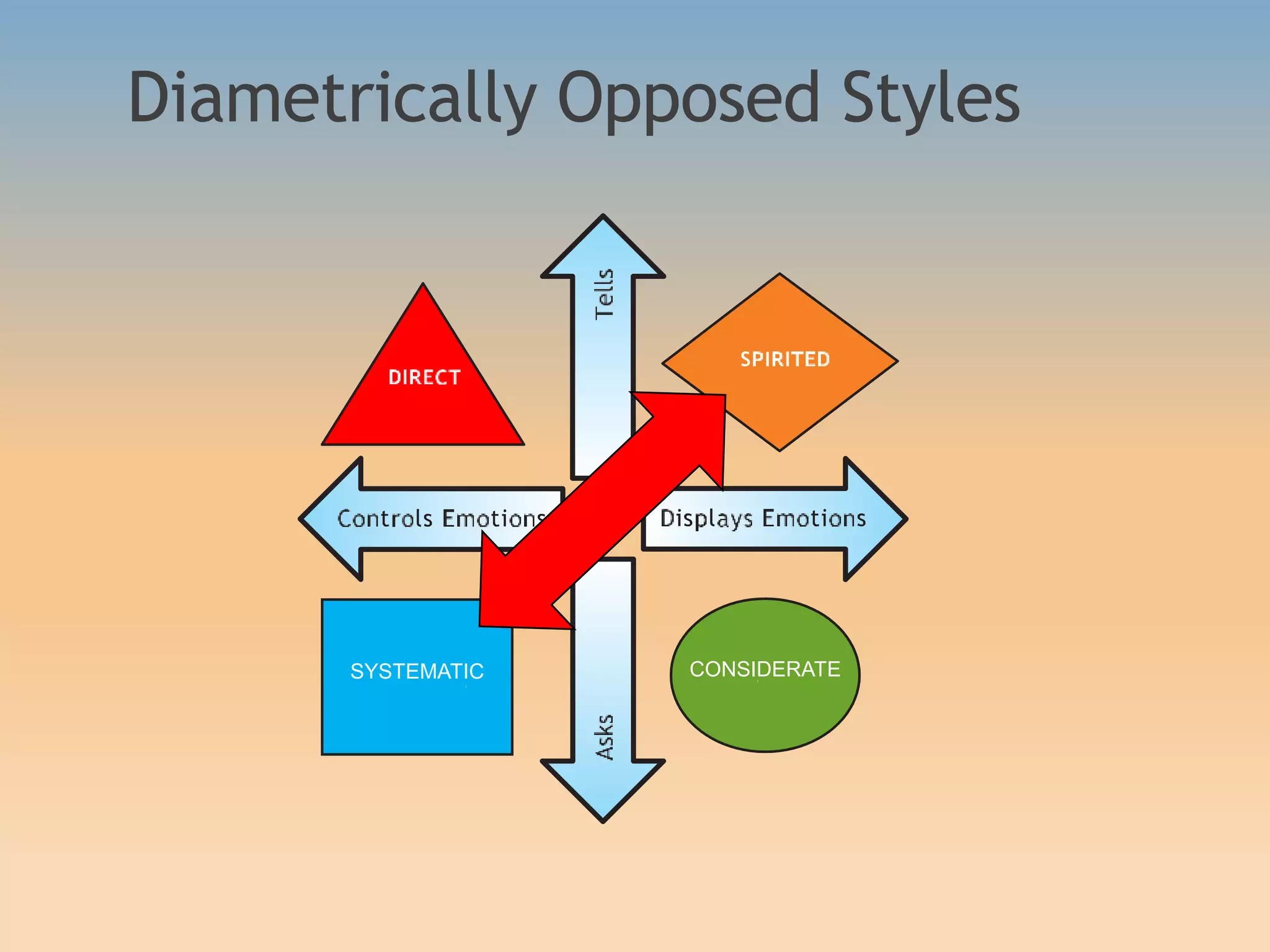
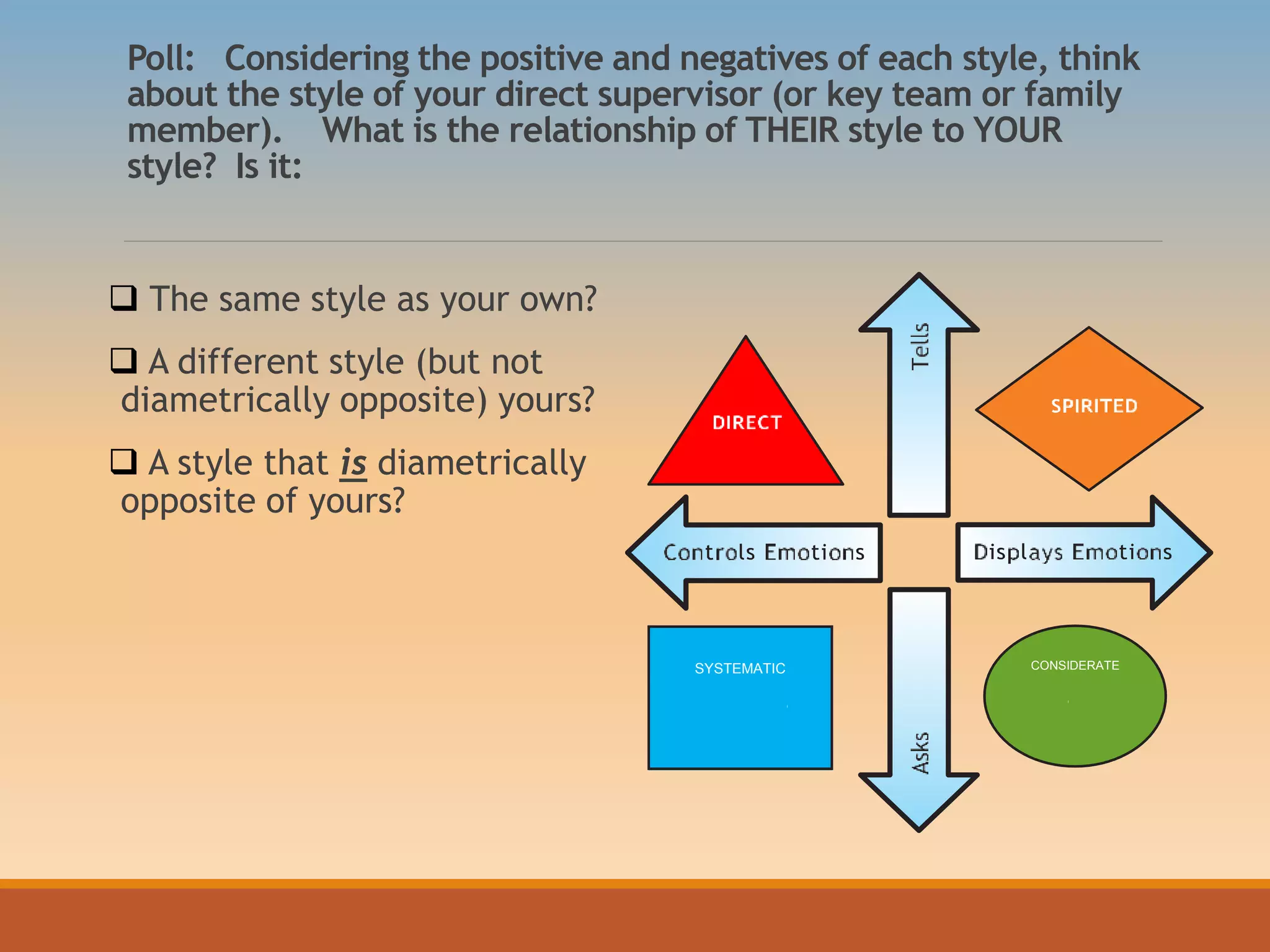
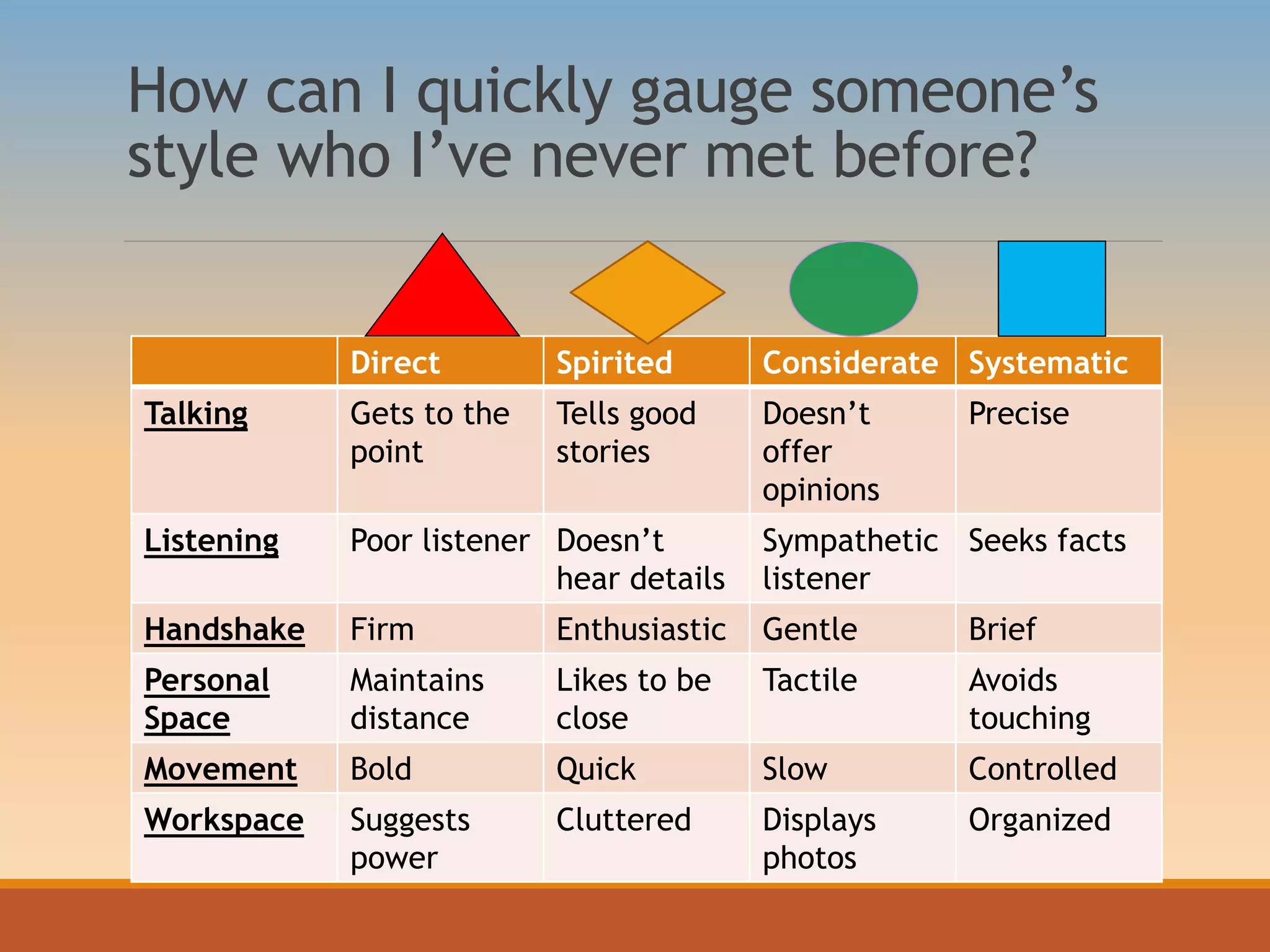
The document discusses various communication styles, emphasizing the importance of understanding one's own style and the styles of others to improve interpersonal interactions. It identifies four main communication styles: direct, spirited, systematic, and considerate, each with its strengths and potential trouble spots. The session aims to help individuals recognize their communication style preferences, gauge the styles of others, and learn to adapt their communication for better effectiveness in personal and professional relationships.