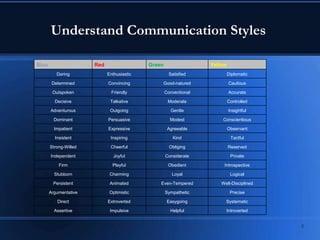
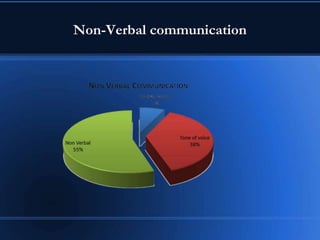
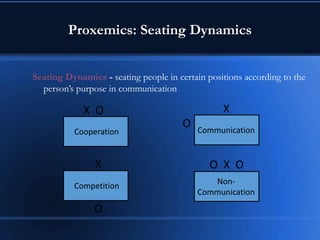
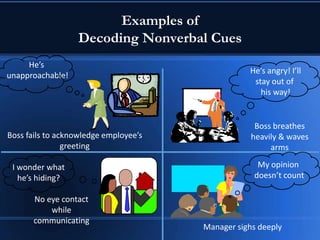
This document discusses communication skills and styles. It defines communication as a two-way process of exchanging information through verbal and non-verbal messages. Effective communication leads to productive relationships, while barriers like assumptions and poor listening skills can interfere. The document outlines the communication process and essential elements like eye contact and active listening. It also describes different communication styles and strategies for interacting with each style effectively.