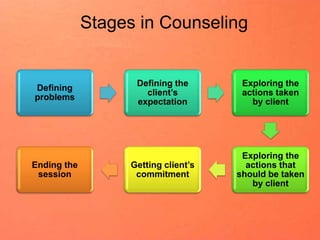
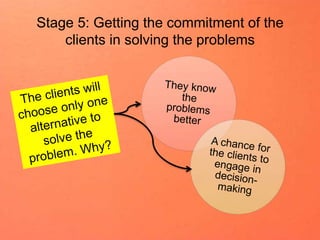
Counseling involves 6 stages: (1) defining problems by building rapport and having clients share their objectives; (2) defining client expectations; (3) exploring actions clients have taken; (4) exploring new actions; (5) getting a commitment; (6) ending by summarizing decisions made. Effective listening skills include attending fully, using silence, not interrupting, reflecting emotions, paraphrasing, asking open questions and for clarification. The goal is to understand clients without judgment and get them to openly share their perspectives and feelings.