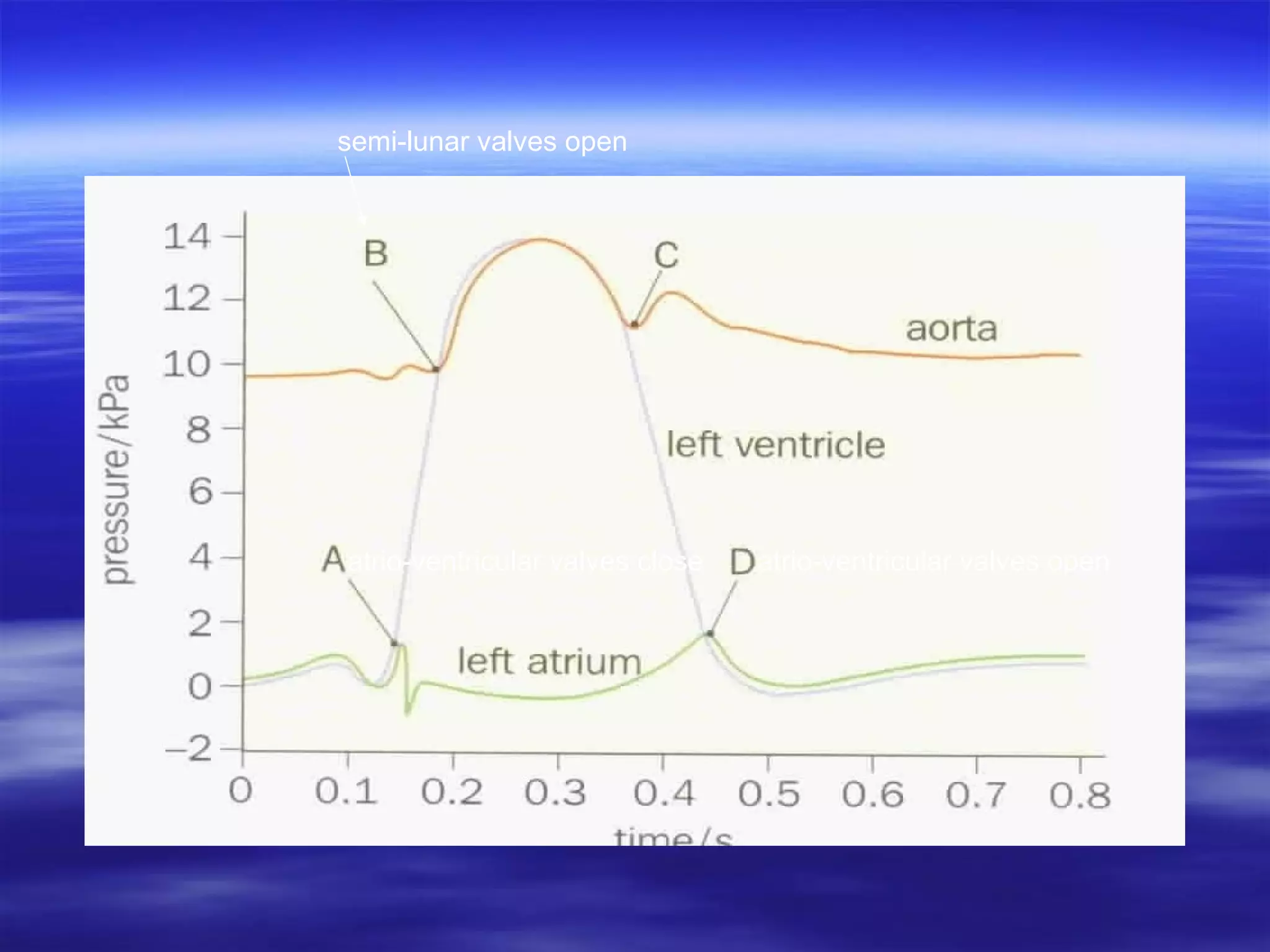
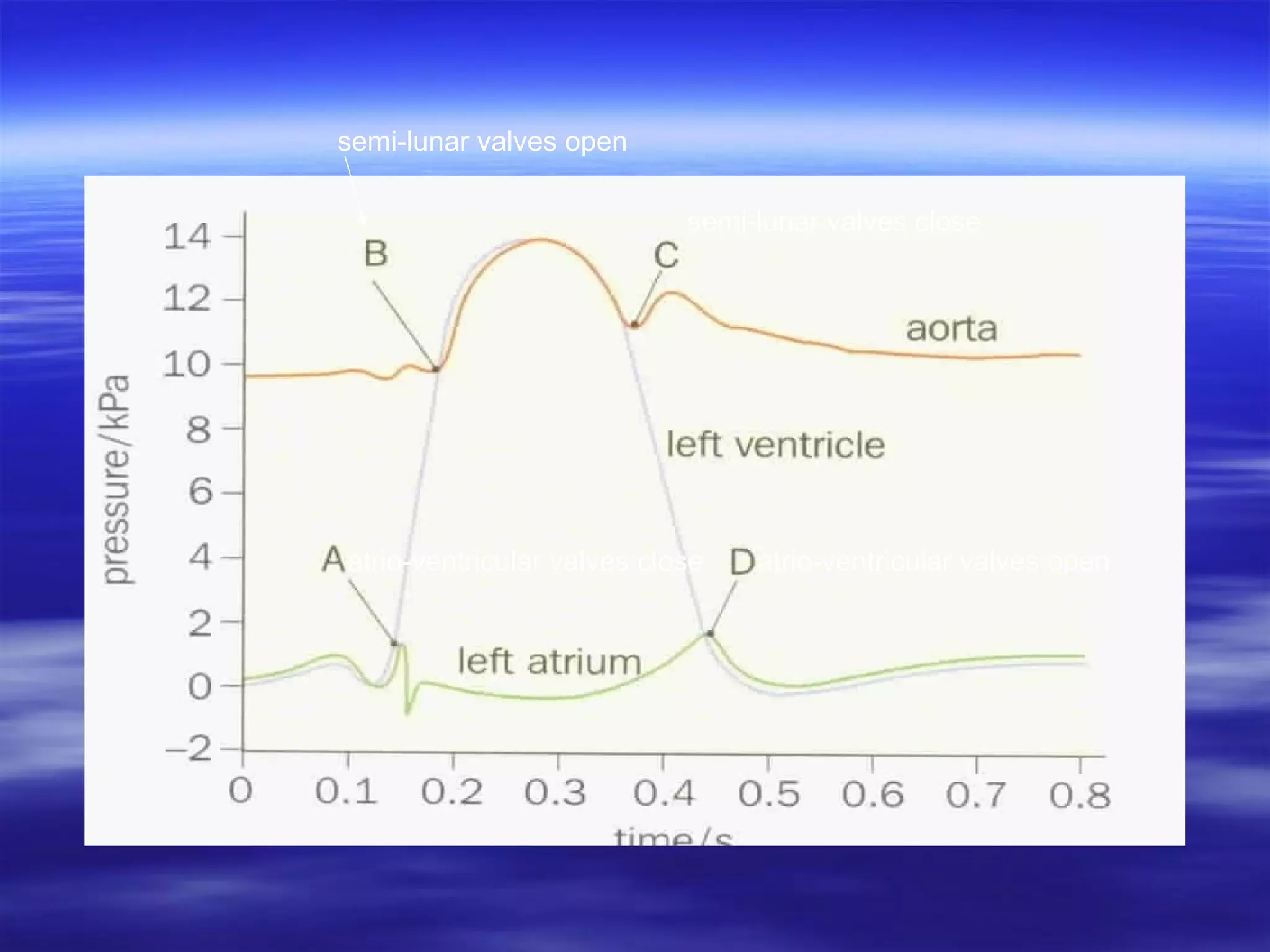
The document describes the cardiac cycle, which is the sequence of events in one heartbeat. It defines systole as the period of ventricular contraction and diastole as the period of ventricular relaxation. The cycle begins with atrial systole, where the atria contract and blood passes to the relaxed ventricles. This is followed by ventricular systole, where the ventricles contract and force blood out through the arteries. Finally, during diastole the ventricles relax and refill with blood from the veins, completing the cycle.