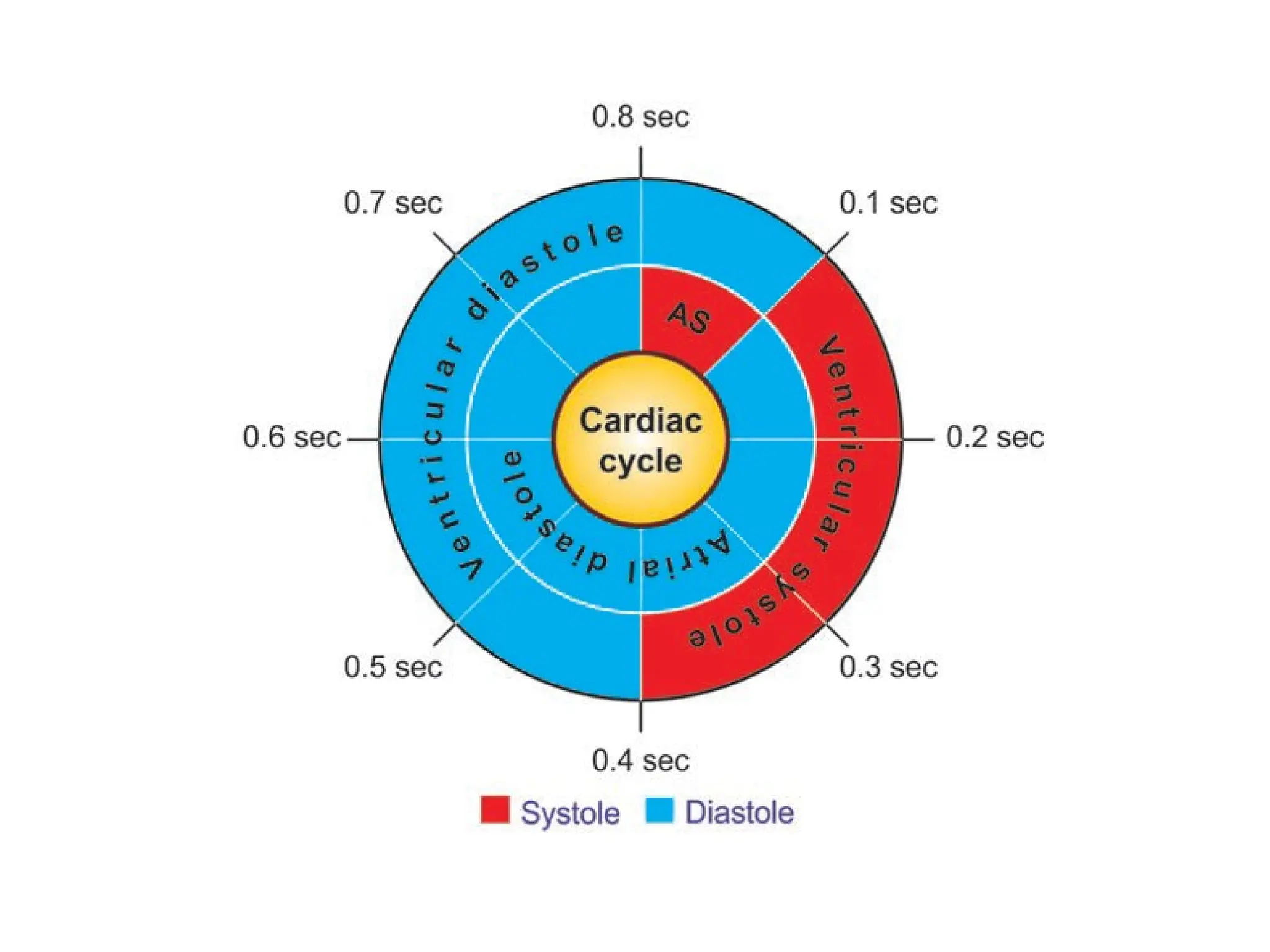
The cardiac cycle is the sequence of events occurring in the heart during each beat, consisting of atrial and ventricular events with specific durations for systole and diastole. Key phases include isometric contraction, ejection period, rapid and slow filling, with heart sounds attributed to various valve closures and blood movements. Heart rate averages 72 beats per minute with each cycle lasting approximately 0.8 seconds.