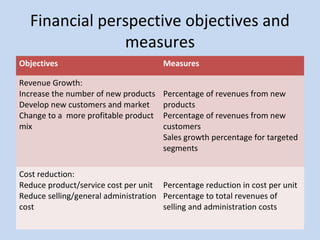
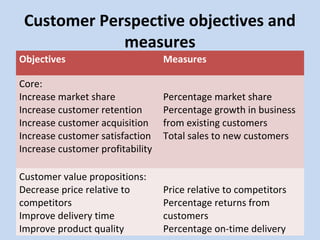
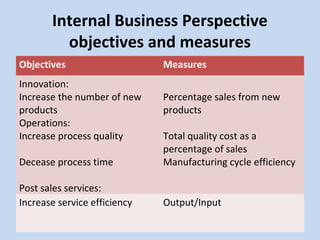
The document outlines the balanced scorecard concept, developed by Kaplan and Norton in 1992, emphasizing the integration of financial and non-financial performance measures across four perspectives: financial, customer, internal business, and learning and growth. It describes strategic objectives for each perspective, such as revenue growth, customer satisfaction, and innovation processes, aimed at aligning organizational strategy with operational performance. Additionally, it highlights the importance of continuous learning and investment to maintain competitive advantage and achieve long-term value.