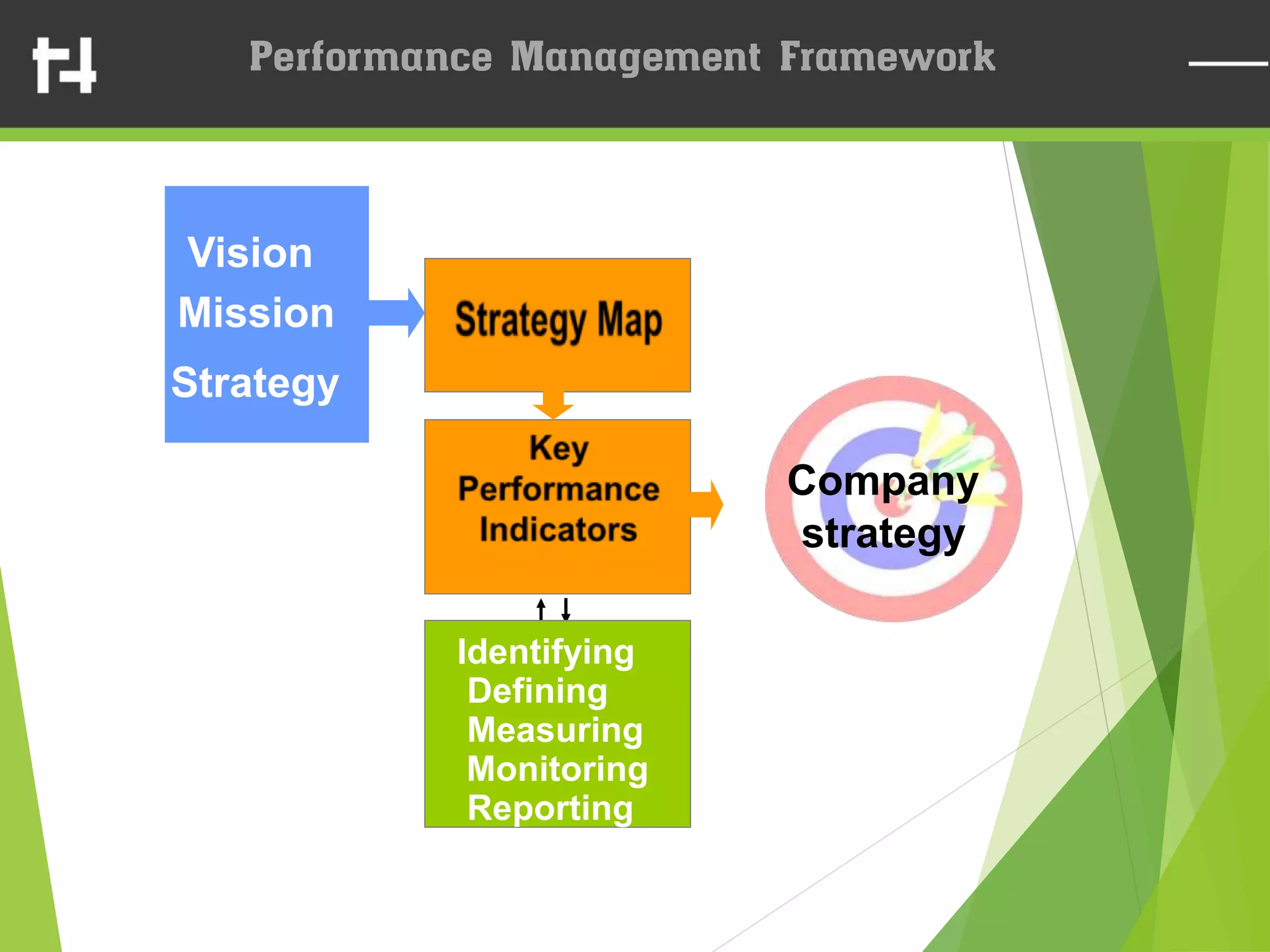
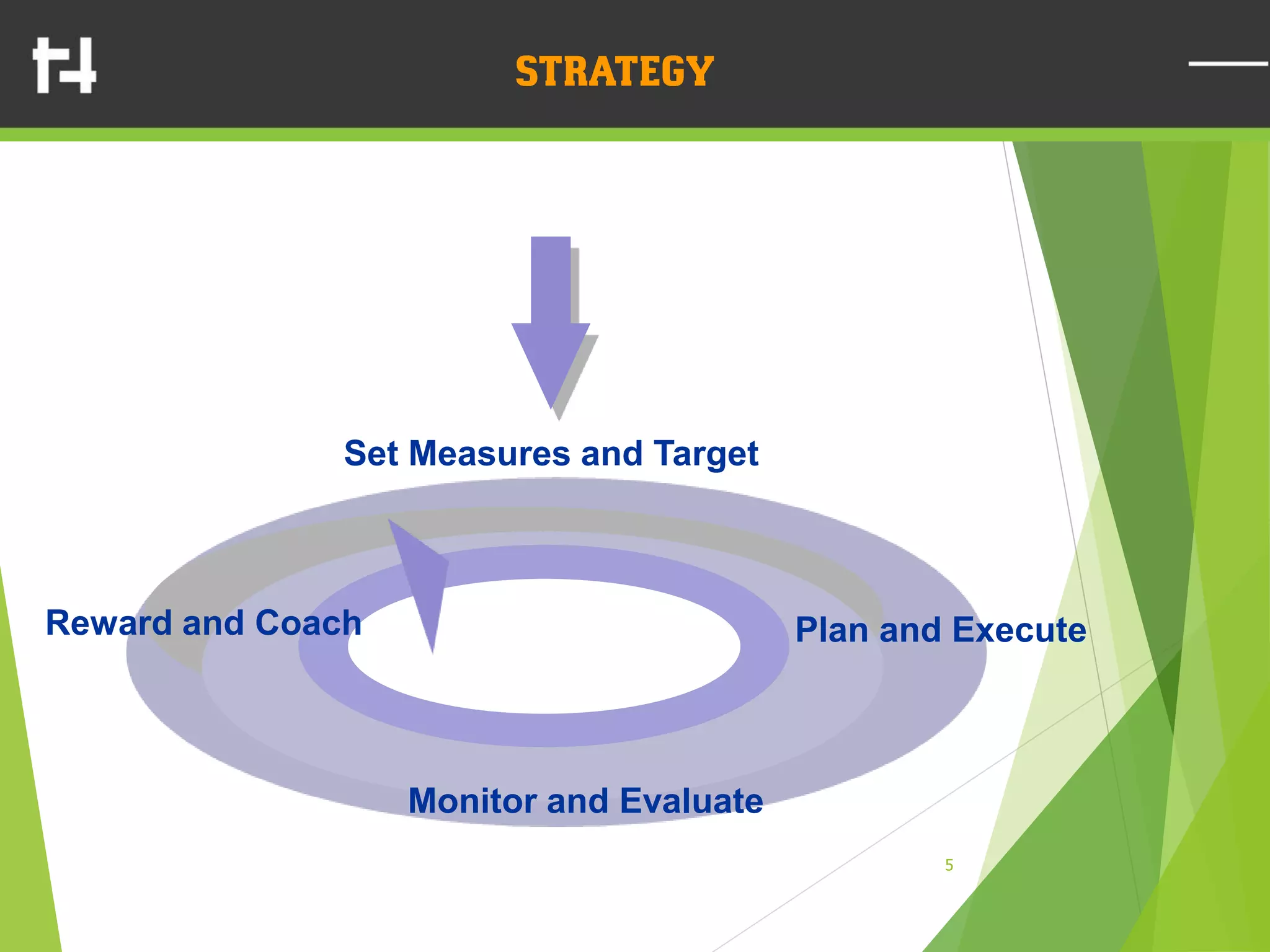
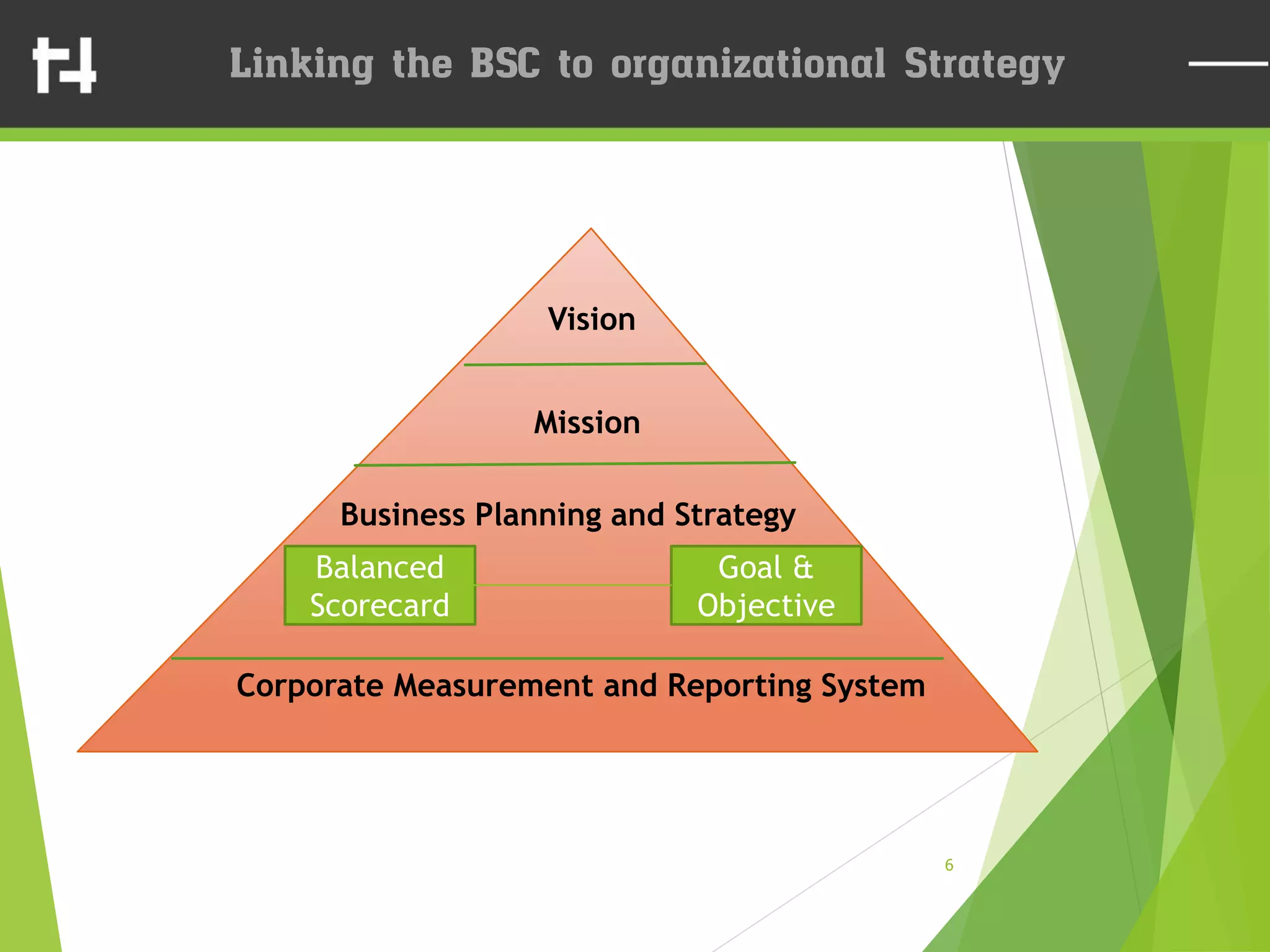
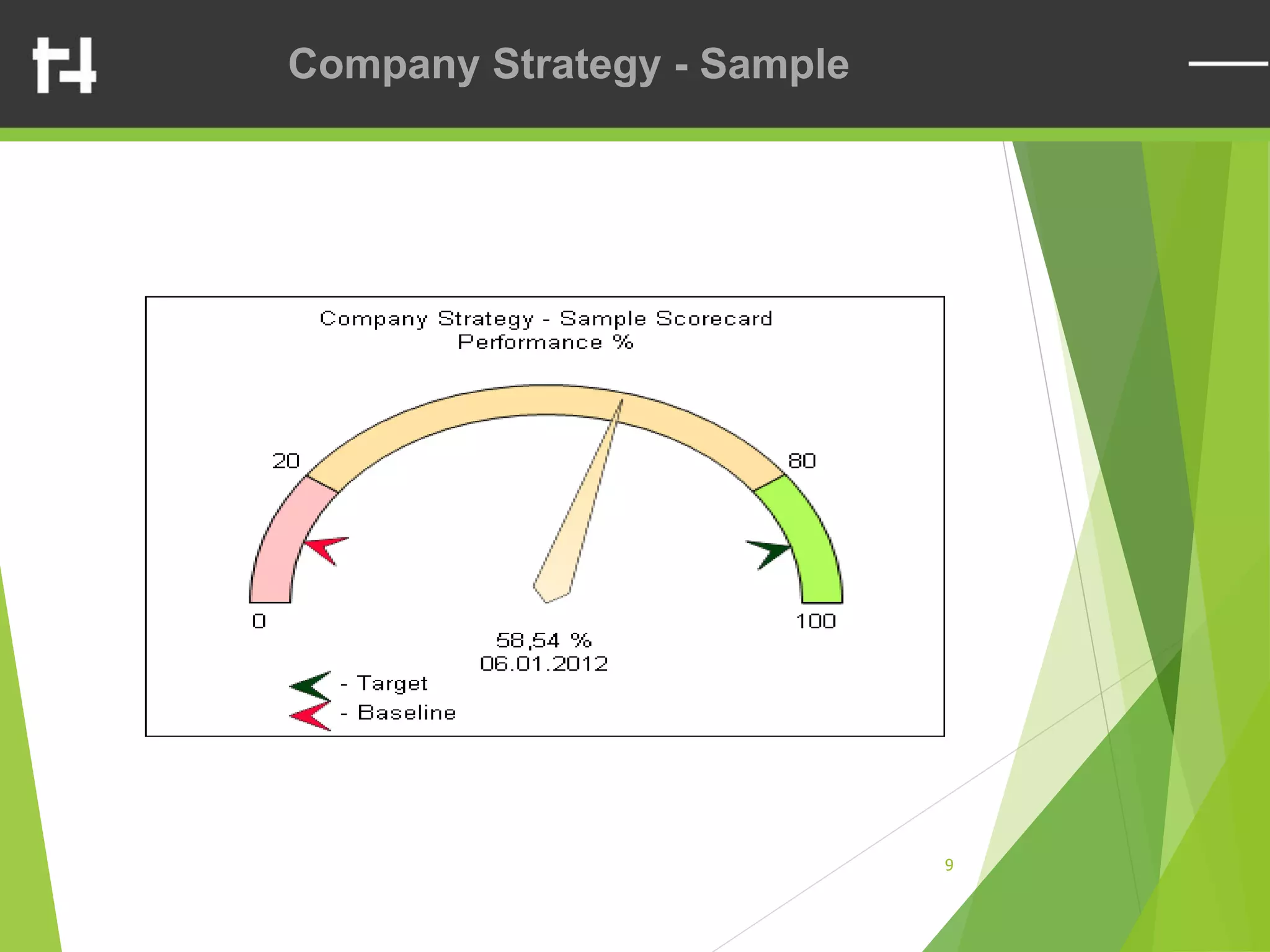
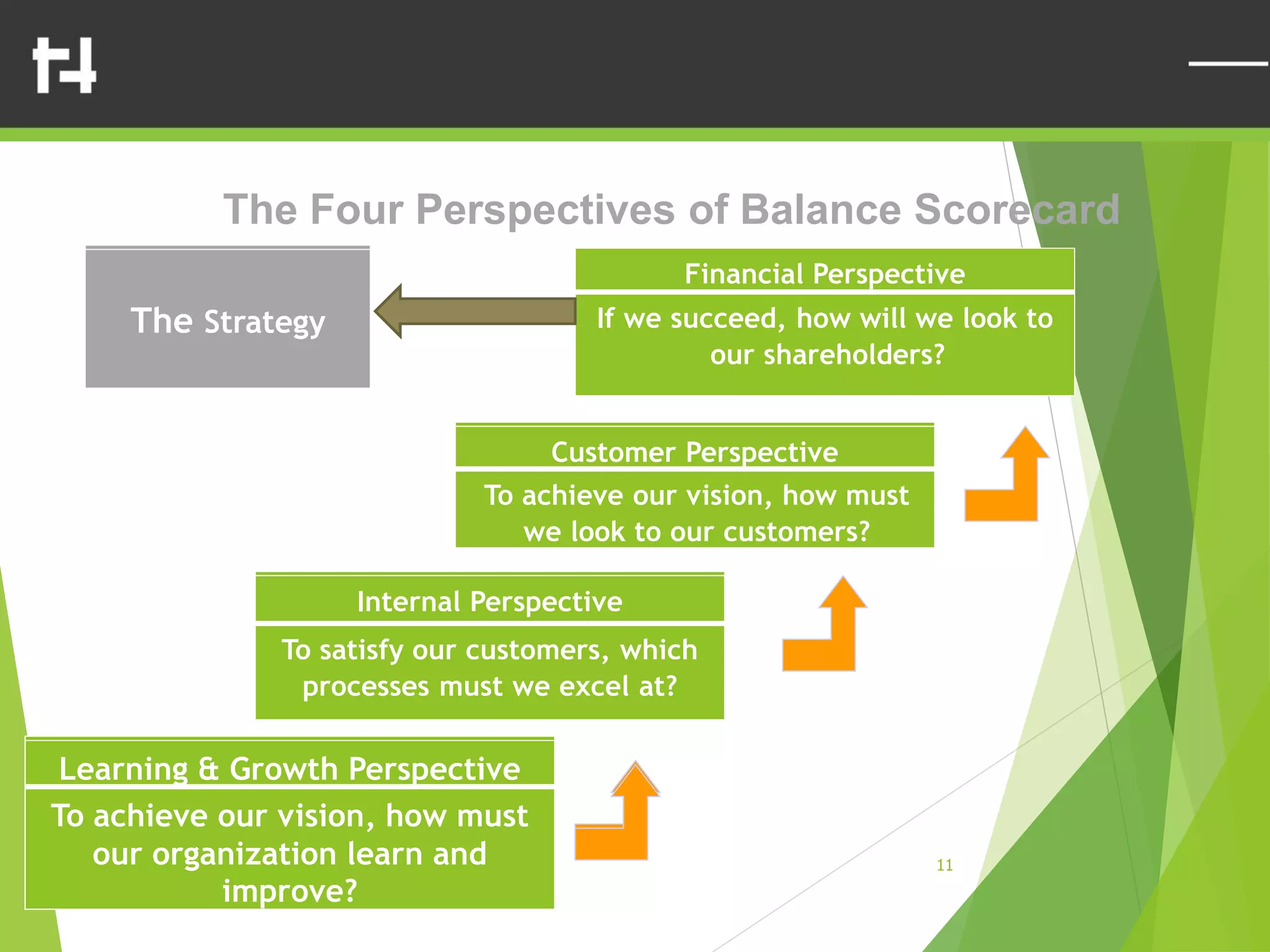
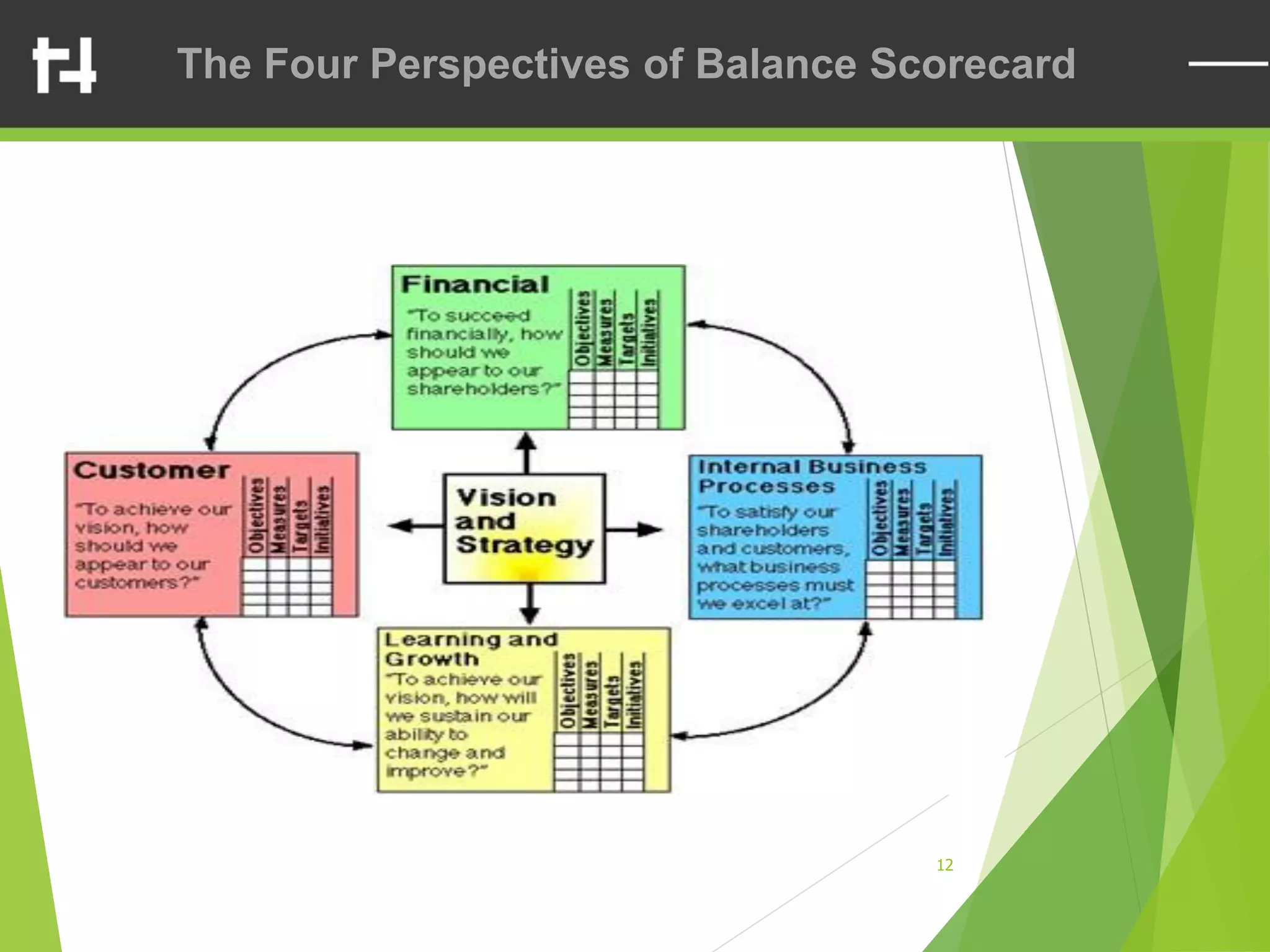
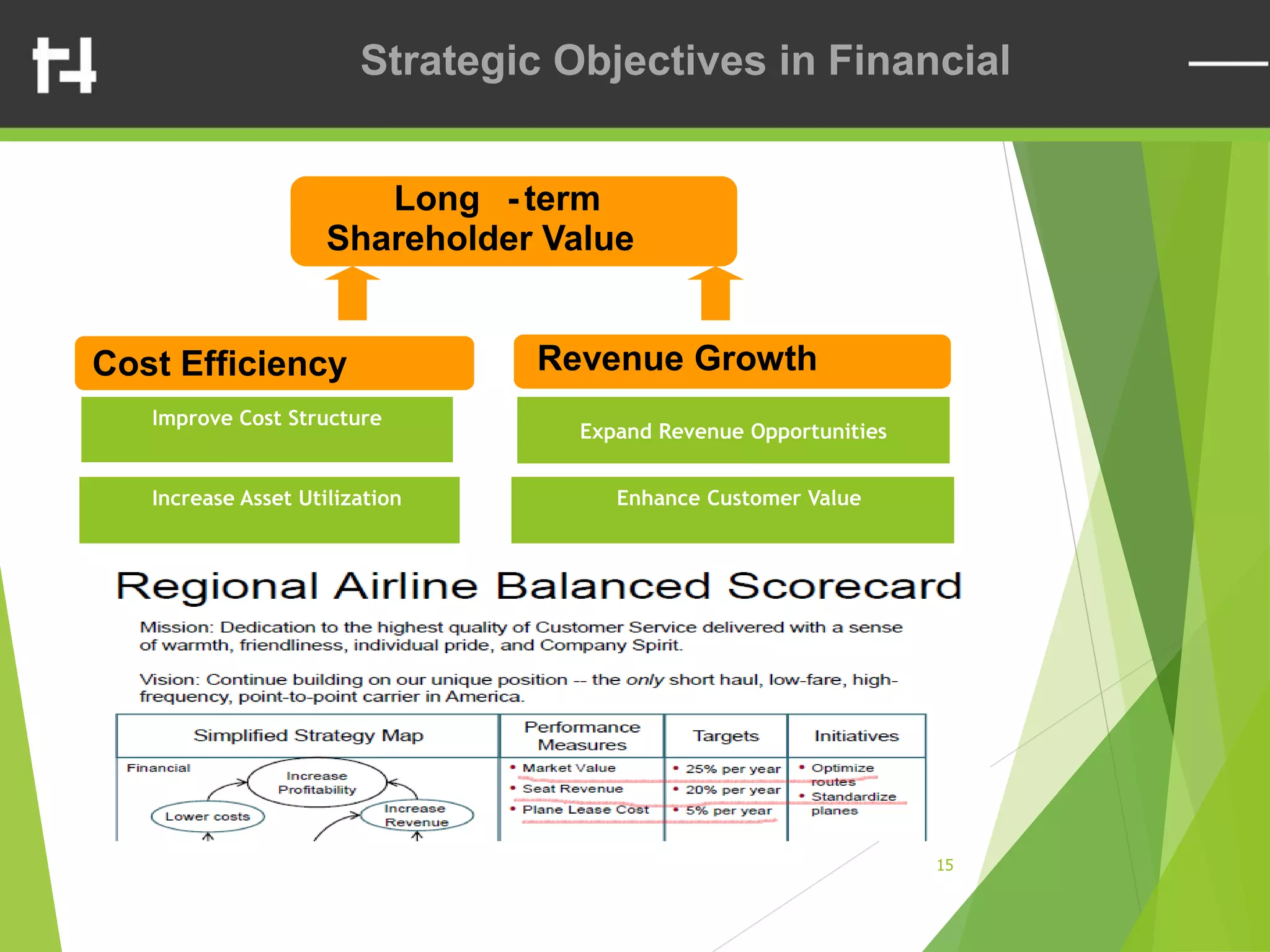
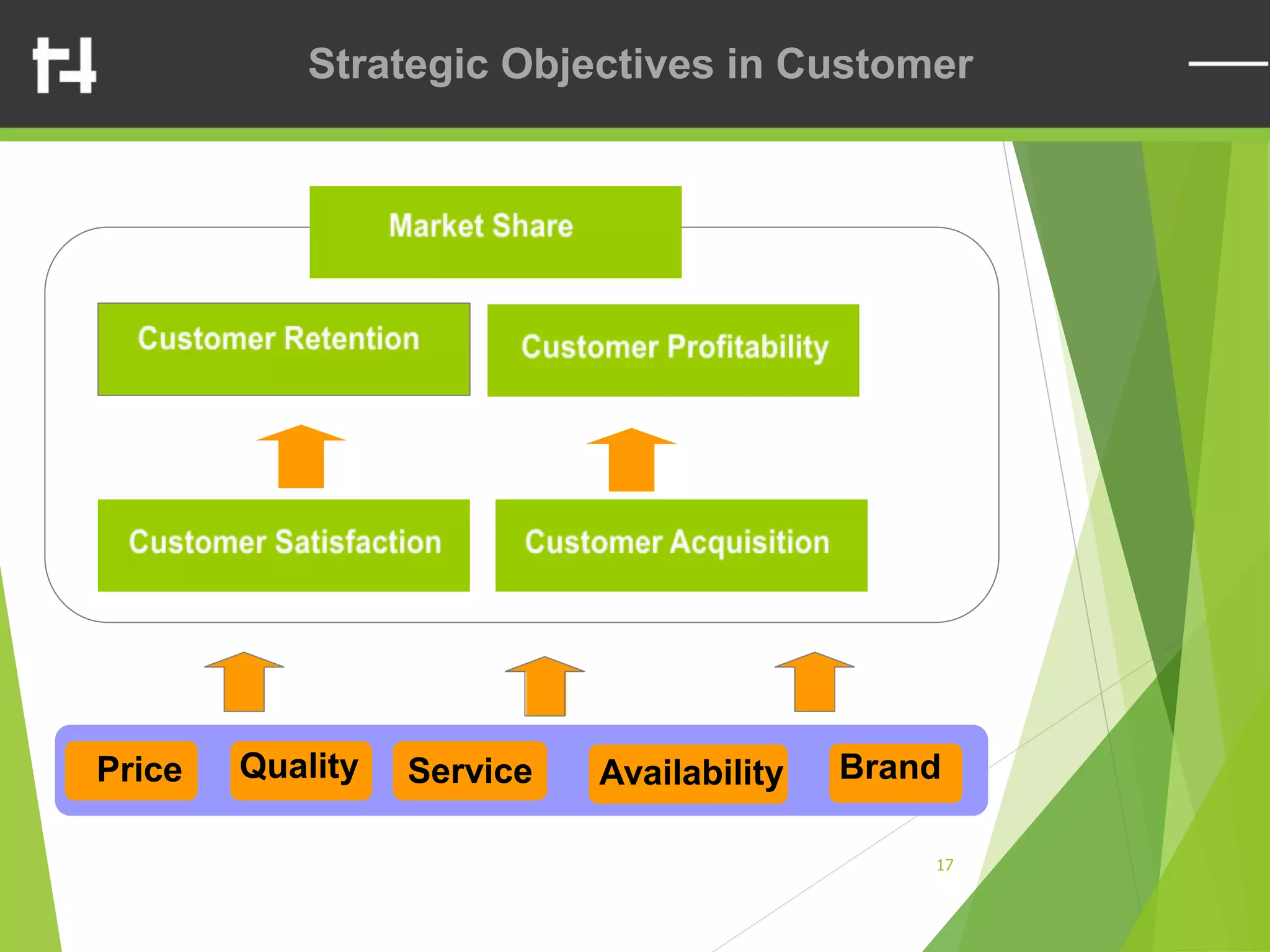
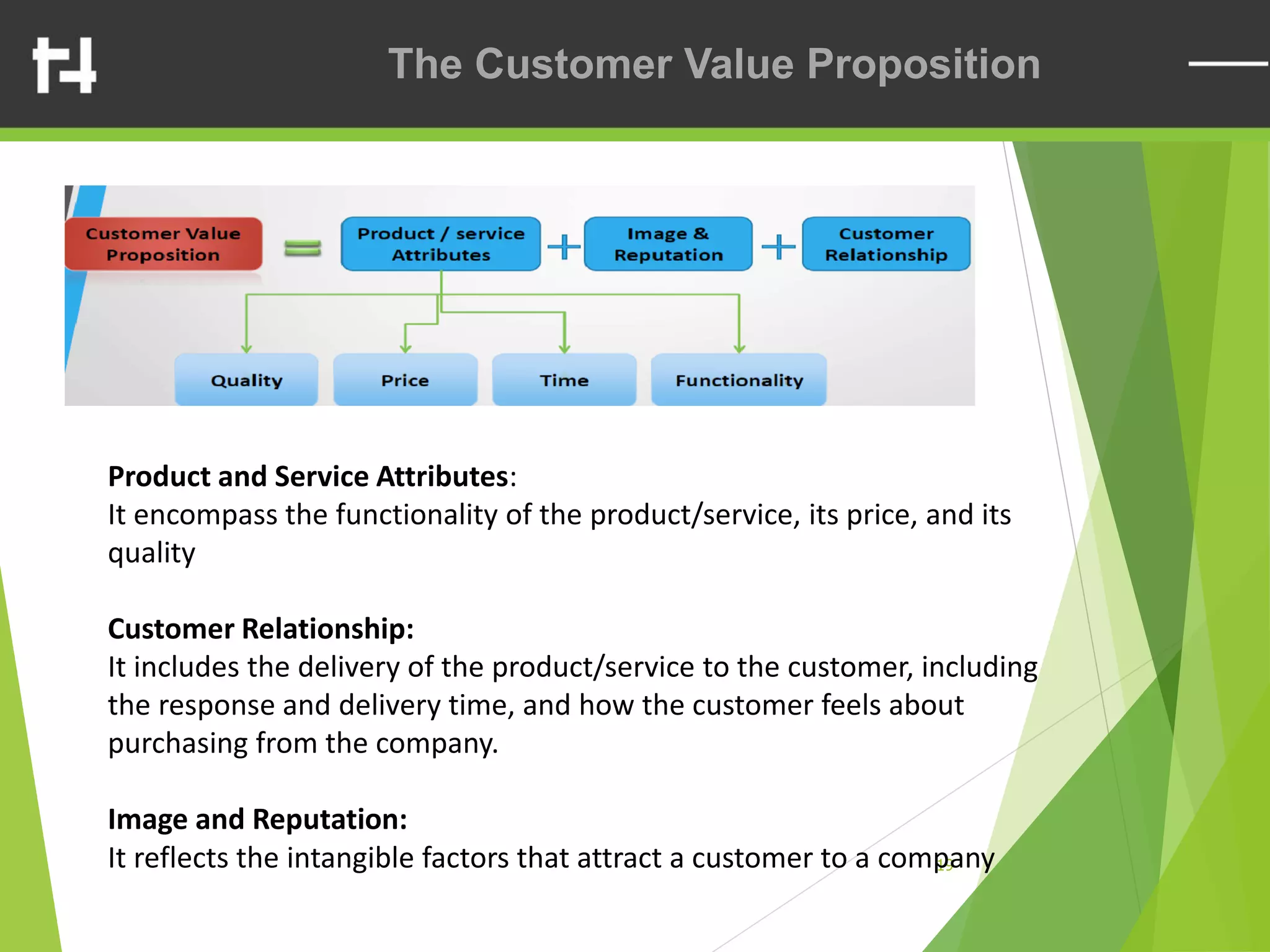
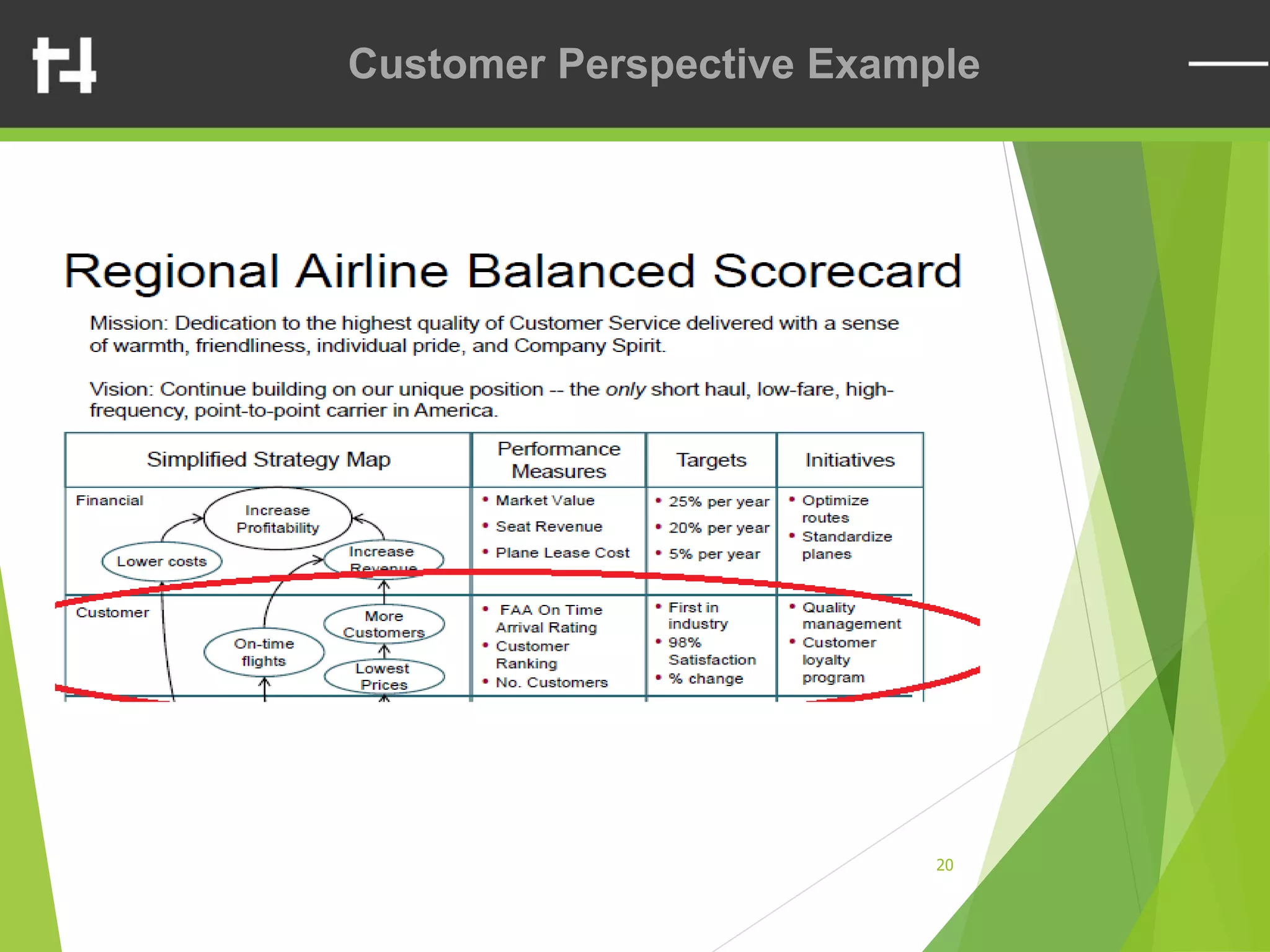
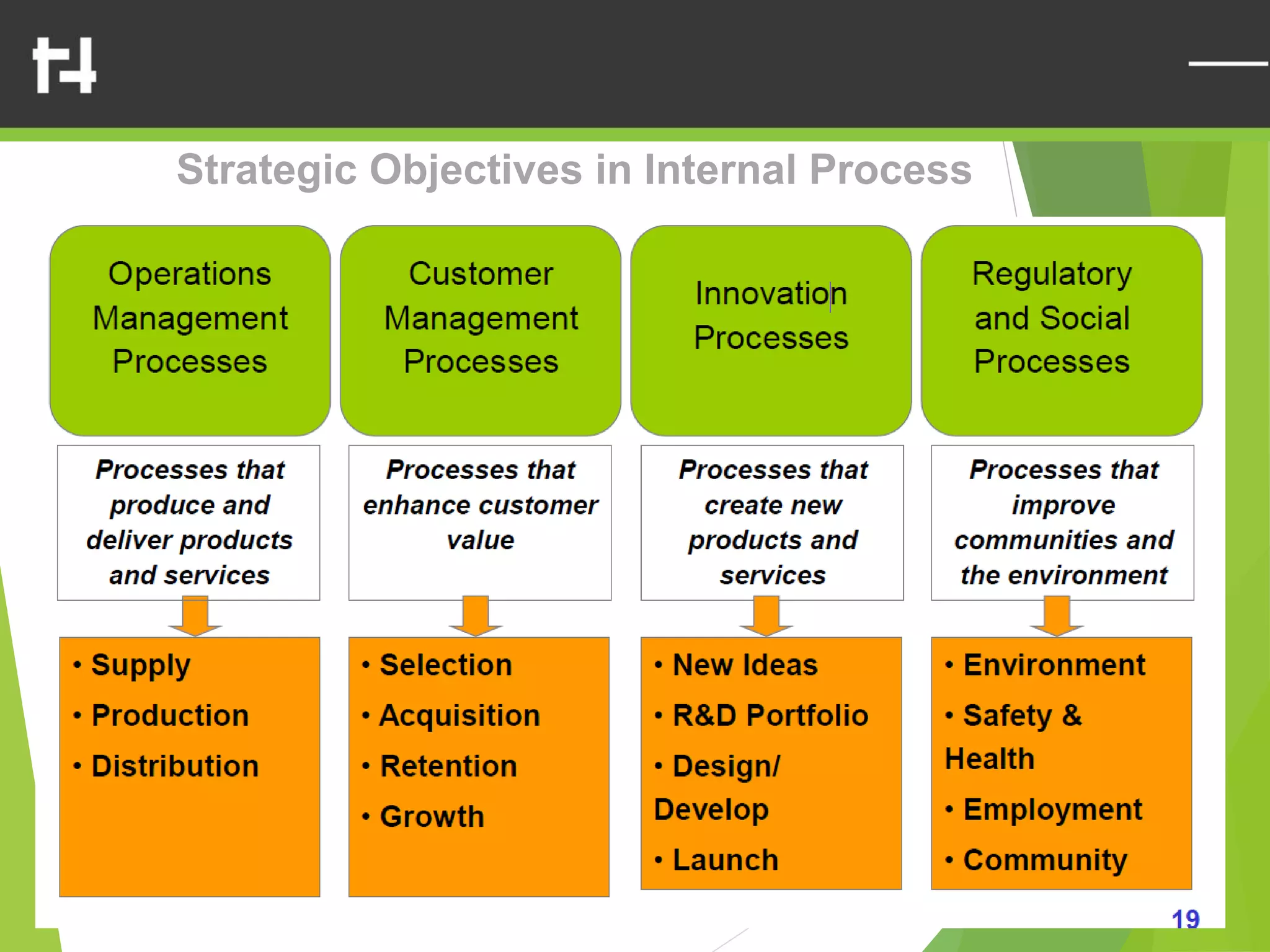
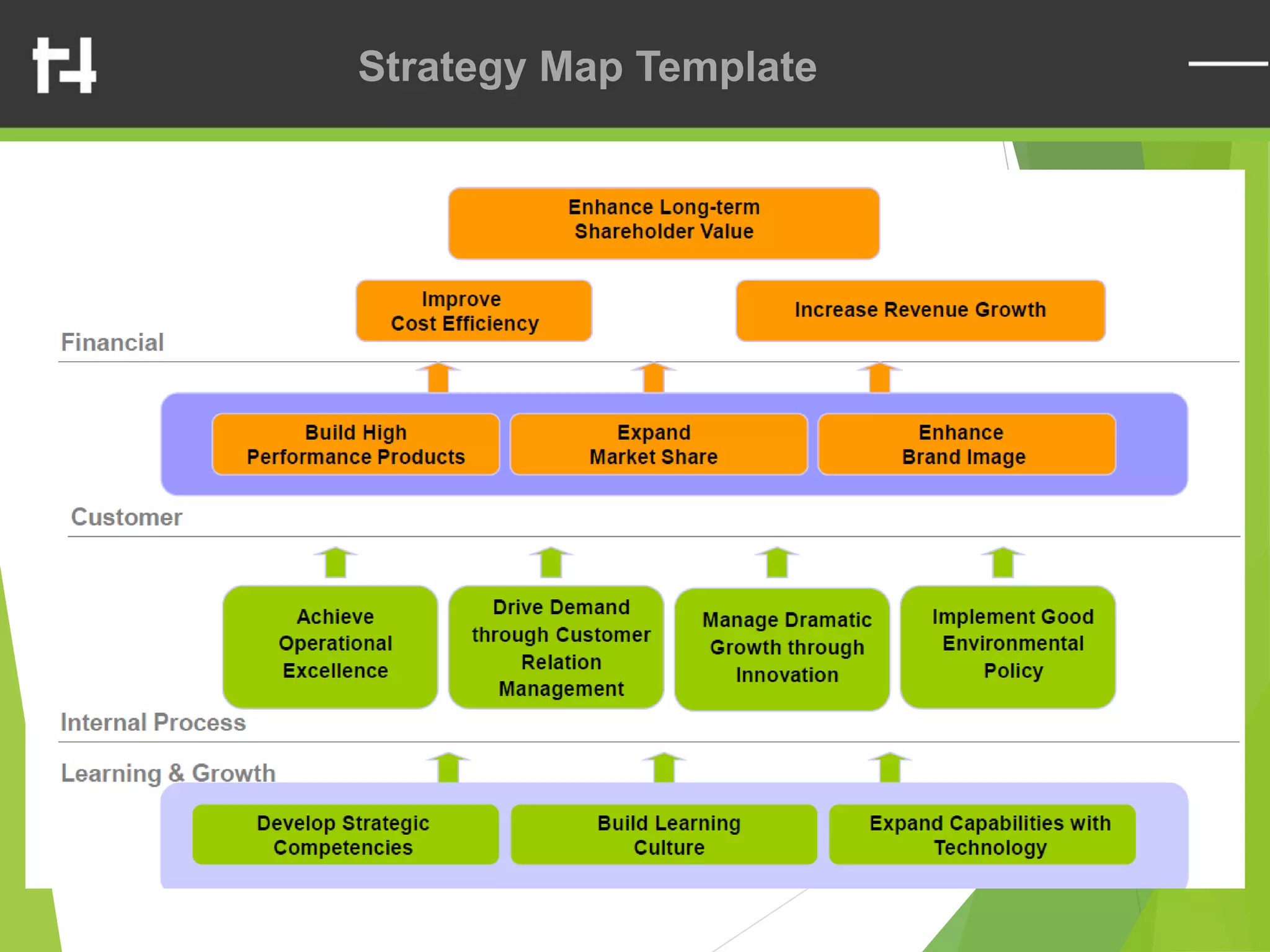
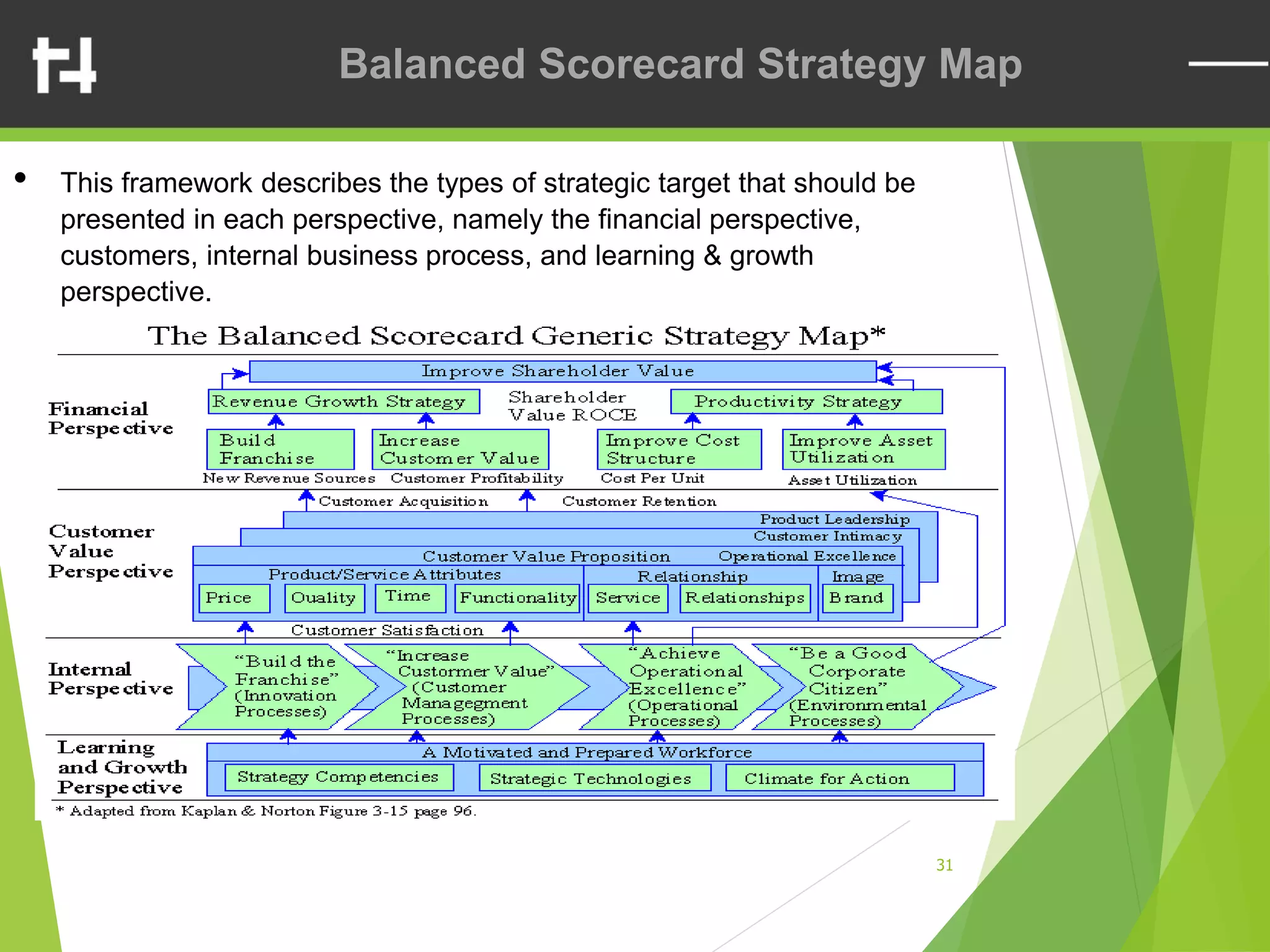
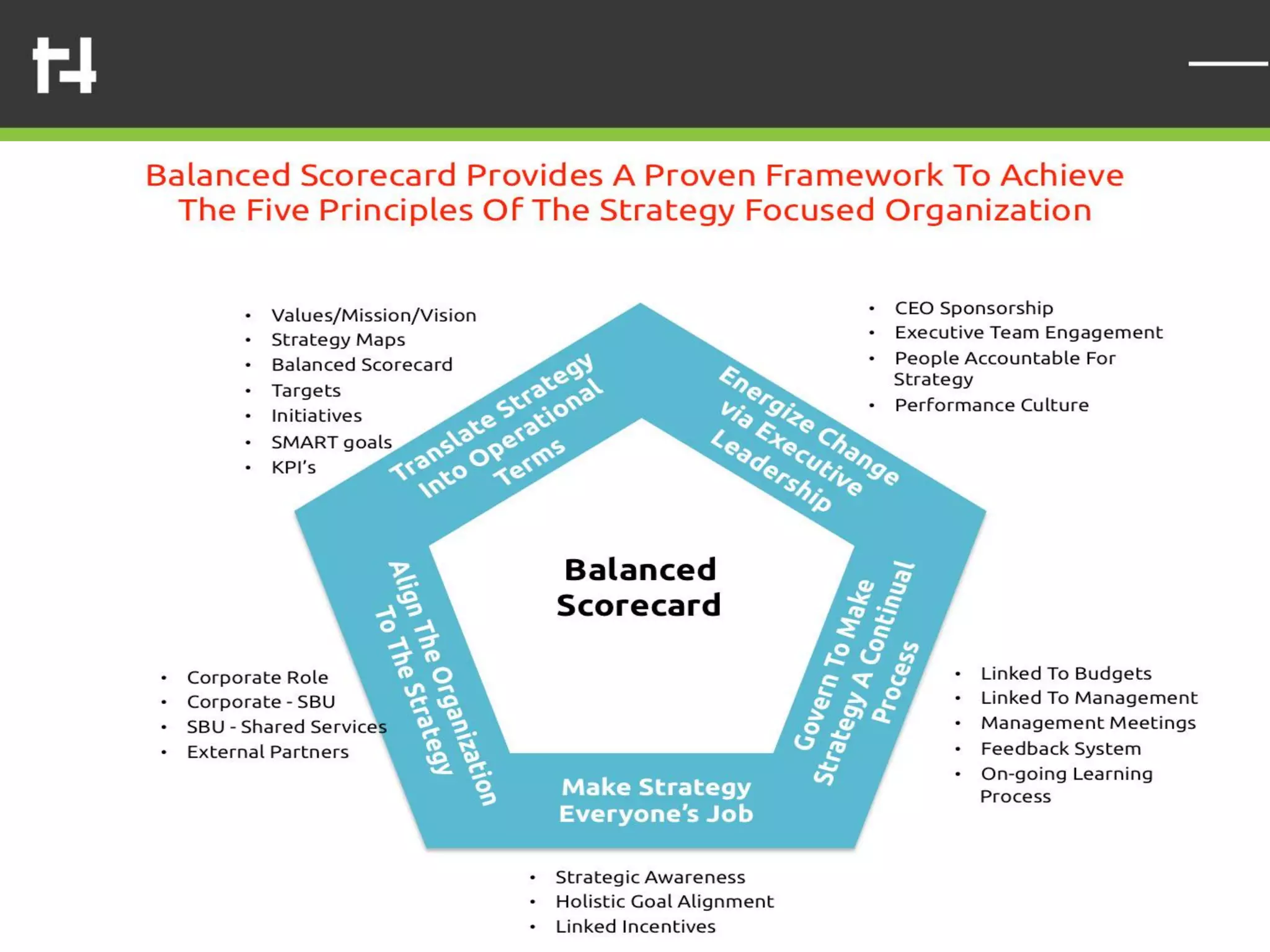
The document discusses the balanced scorecard framework. It explains that the balanced scorecard translates an organization's vision and strategy into objectives and measures across four perspectives: financial, customer, internal business processes, and learning and growth. Each perspective contains objectives, measures, targets, and initiatives. The balanced scorecard helps organizations execute their strategies, align measures to strategy, and facilitate communication of goals throughout the organization.