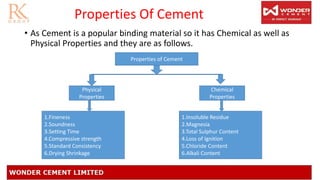
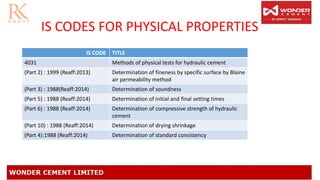
This document summarizes the test certificate of Wonder Cement PPC. It discusses the batch number coding system used on cement bags and provides details on the physical and chemical properties tested, including fineness, setting time, soundness, and compressive strength. The presentation was given by Pawan Dhillon and Krishna Soni from the concrete testing department. Test results for the specific batch of Wonder Cement PPC met all Indian standards requirements for properties such as insoluble residue, magnesia content, and chloride content.