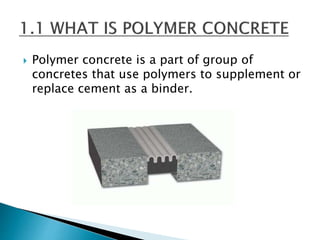
The document discusses the properties and applications of polymer concrete, a composite material that utilizes polymers to enhance the strength, durability, and resistance to environmental factors compared to traditional cement concrete. It outlines various types of polymer concrete, including polymer concrete, polymer modified concrete, and polymer impregnated concrete, each with unique benefits such as low permeability and accelerated curing times. Additionally, the document highlights the disadvantages, such as brittleness and cost, while emphasizing the superior mechanical and chemical resistance of polymer impregnated concrete.