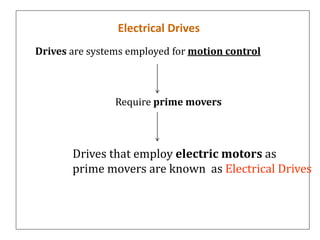
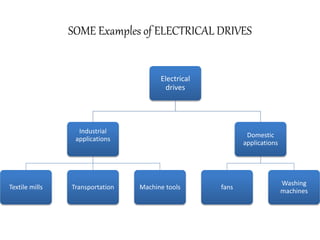
1. Electrical drives are systems used for motion control that employ electric motors as prime movers.
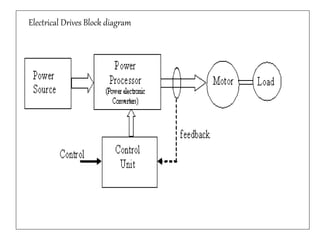
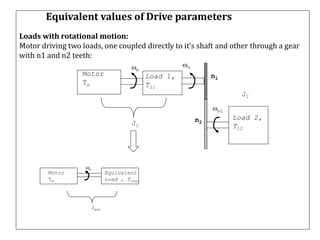
2. The key components of an electrical drive system are the power source, power processor/modulator, motor, load, control unit, and sensing unit. The power modulator converts and regulates power from the source for use by the motor according to the demands of the load.
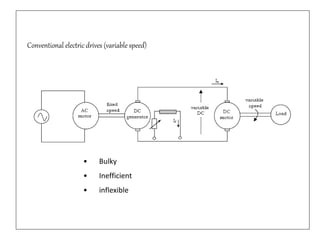
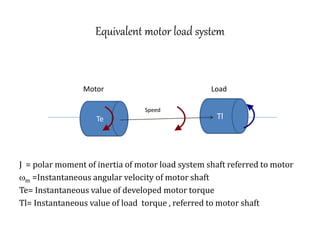
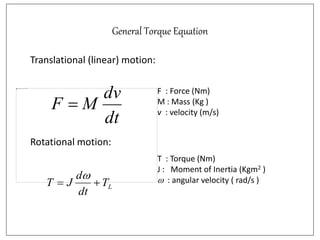
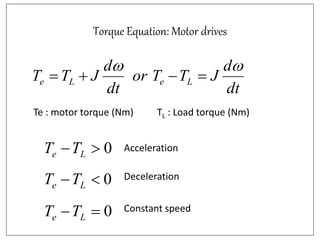
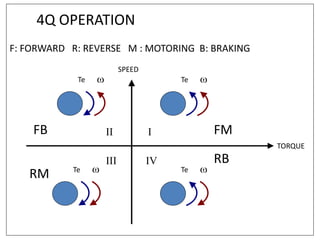
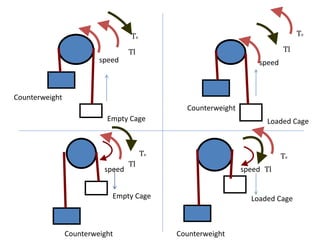
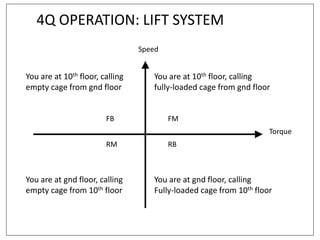
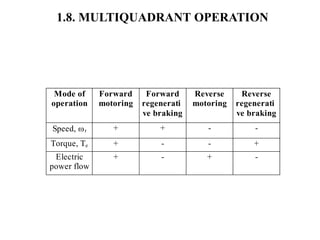
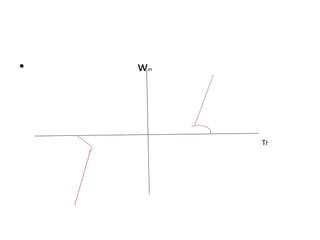
3. Electrical drives can operate in any of the four quadrants defined by positive or negative speed and torque. The motor provides positive or negative torque to accelerate, decelerate, or maintain the speed of the load as needed.