Embed presentation
Download to read offline






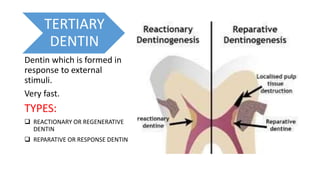

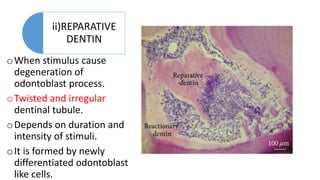





This document summarizes different types of dentin found in teeth. It discusses primary, secondary, tertiary, reactionary, reparative, and sclerotic dentin. Tertiary dentin is formed in response to external stimuli and can be reactionary or reparative dentin. Reactionary dentin is formed by original odontoblast cells when the stimulus does not cause cell death. Reparative dentin has irregular tubules and is formed by new odontoblast-like cells when the stimulus causes cell death. Sclerotic dentin has blocked tubules that decreases permeability and protects the pulp.












