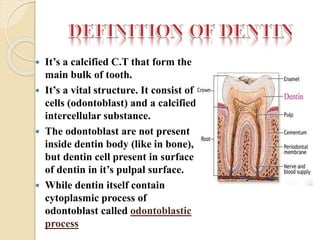
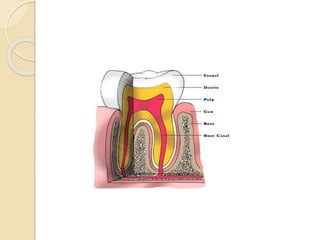
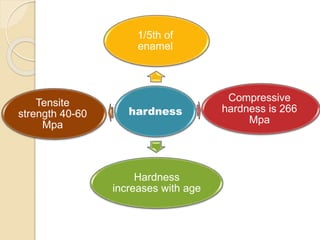
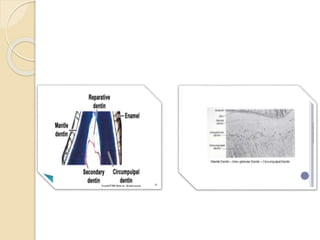
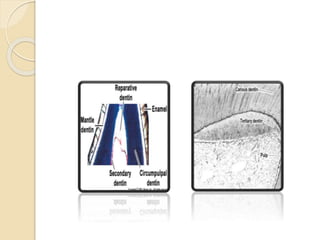
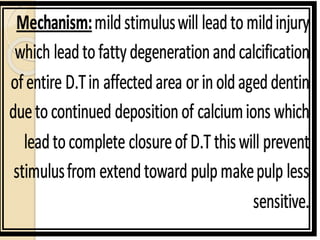
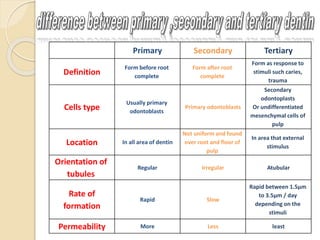
This document discusses the structure and properties of dentin. It is composed of 70% hydroxyapatite crystals, 20% collagen, and 10% water. Dentin is lighter yellow in young individuals and darker with age. It is approximately 3-3.5mm thick on coronal surfaces and increases with secondary and tertiary dentin formation. Dentin is one-fifth the hardness of enamel and its hardness increases with age. It contains dentinal tubules that originate from odontoblasts and provide pathways for stimulation of the dental pulp. There are three types of dentin - primary, secondary, and tertiary - which differ in their location, rate of formation, orientation of tubules, and permeability.