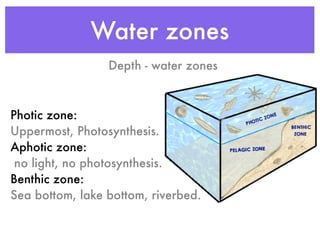
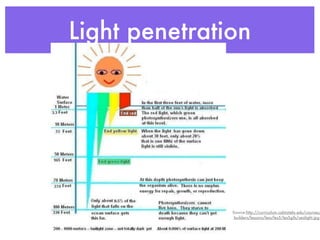
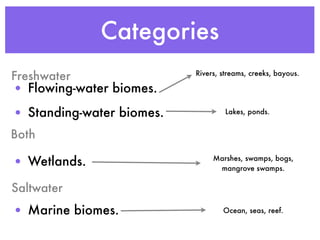
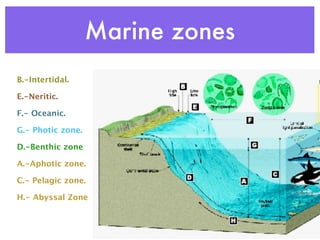
This document summarizes the major water biomes on Earth. It notes that 75% of the Earth's surface is covered by water and that most of the biosphere consists of aquatic ecosystems. It then describes the main zones of both freshwater and saltwater environments, including photic and aphotic zones, benthic zones, categories of freshwater (rivers, lakes, wetlands), coastal wetlands, estuaries, and marine zones. It provides examples of characteristic organisms found in each biome.