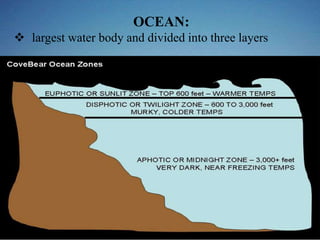
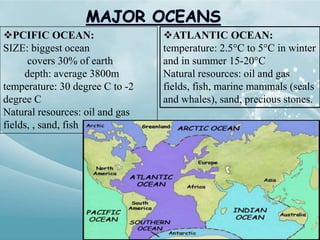
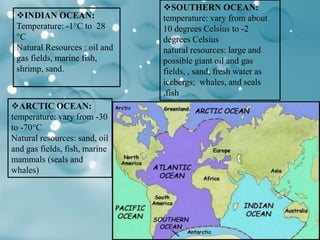
Aquatic biomes occupy most of the biosphere and are divided into marine and freshwater biomes. The marine biome contains the world's oceans, which cover 70% of the Earth and are divided into layers. They provide many natural resources and support ecosystems like coral reefs and estuaries. Freshwater biomes include ponds, lakes, rivers, and wetlands and have a lower salt concentration than marine biomes. They are important sources of water, food, transportation, recreation and more.