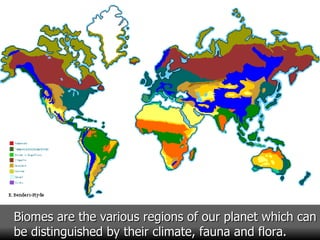
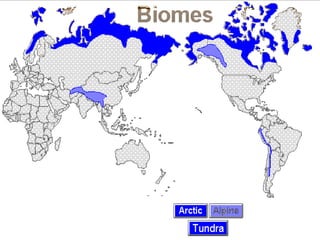
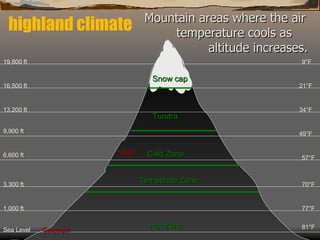
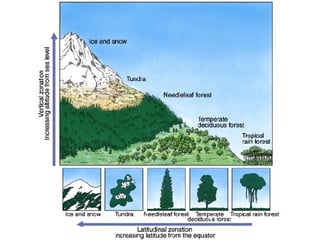
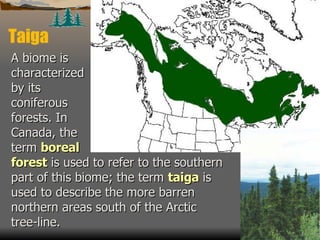
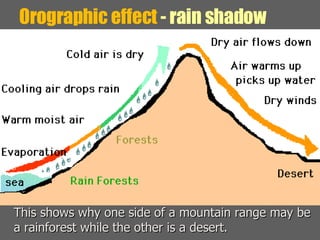
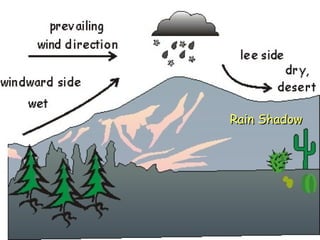
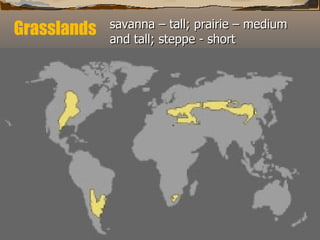
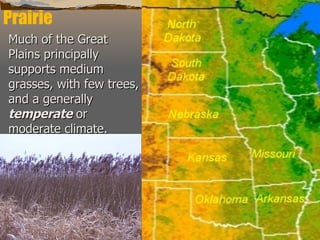
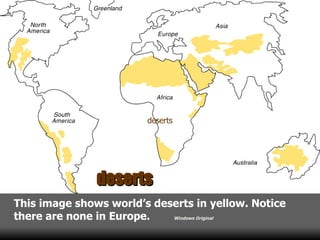
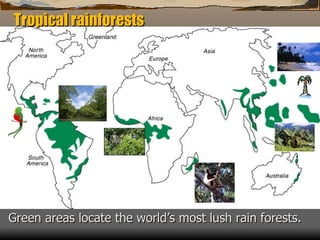
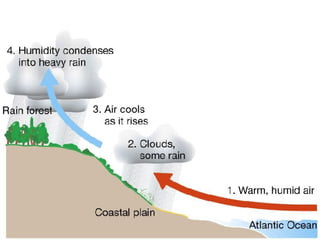
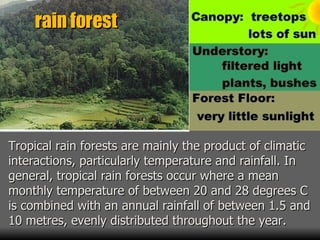
This document summarizes the main biomes (regions) of the world, which include polar ice caps, tundra, forests, grasslands, deserts, and aquatic biomes. It provides details on the defining characteristics, climates, vegetation, and animals found in each biome type. Some of the specific biomes mentioned include boreal forests, taiga, temperate deciduous forests, prairies, steppes, savannas, rainforests, wetlands, estuaries, and oceans.