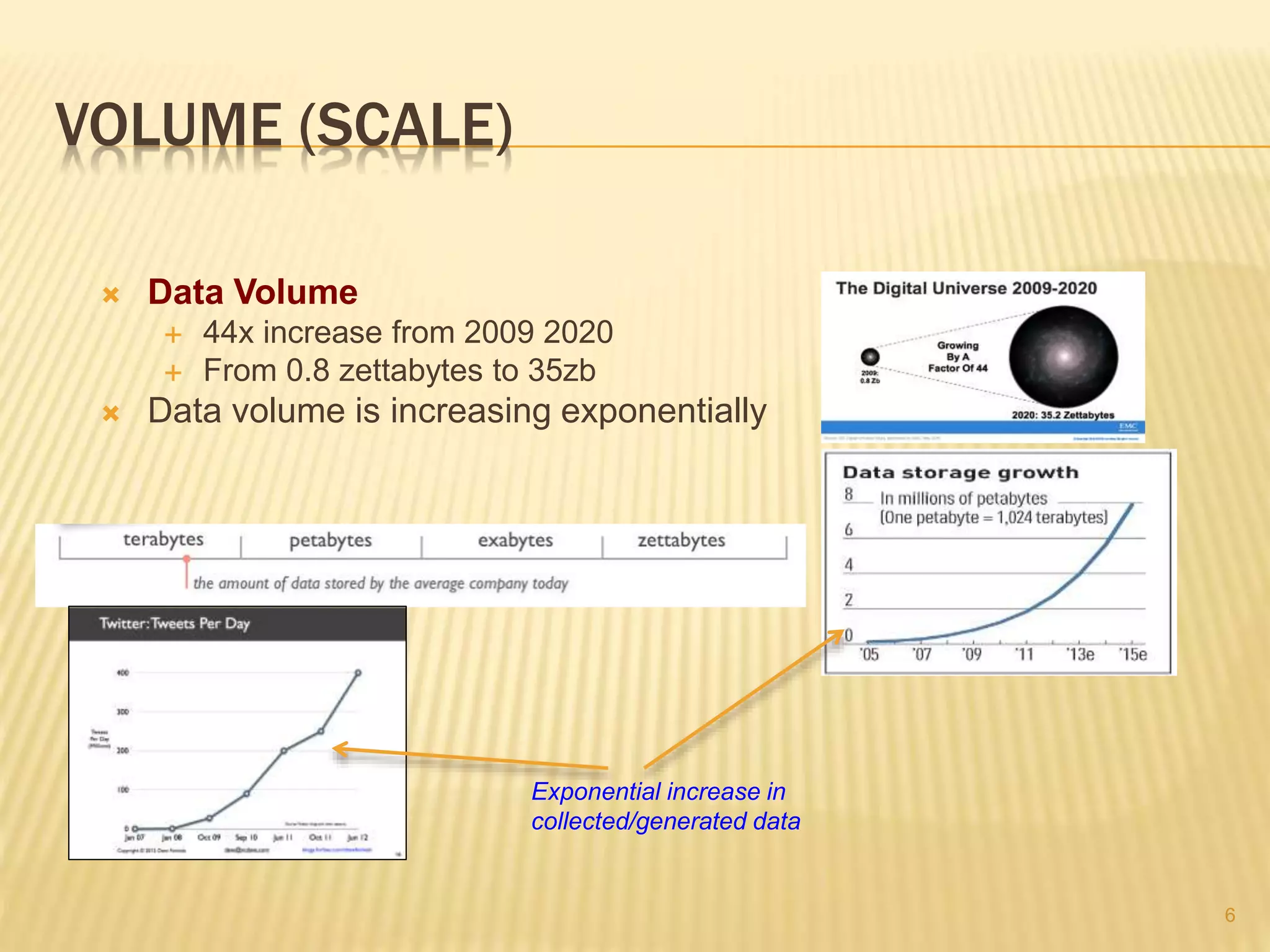
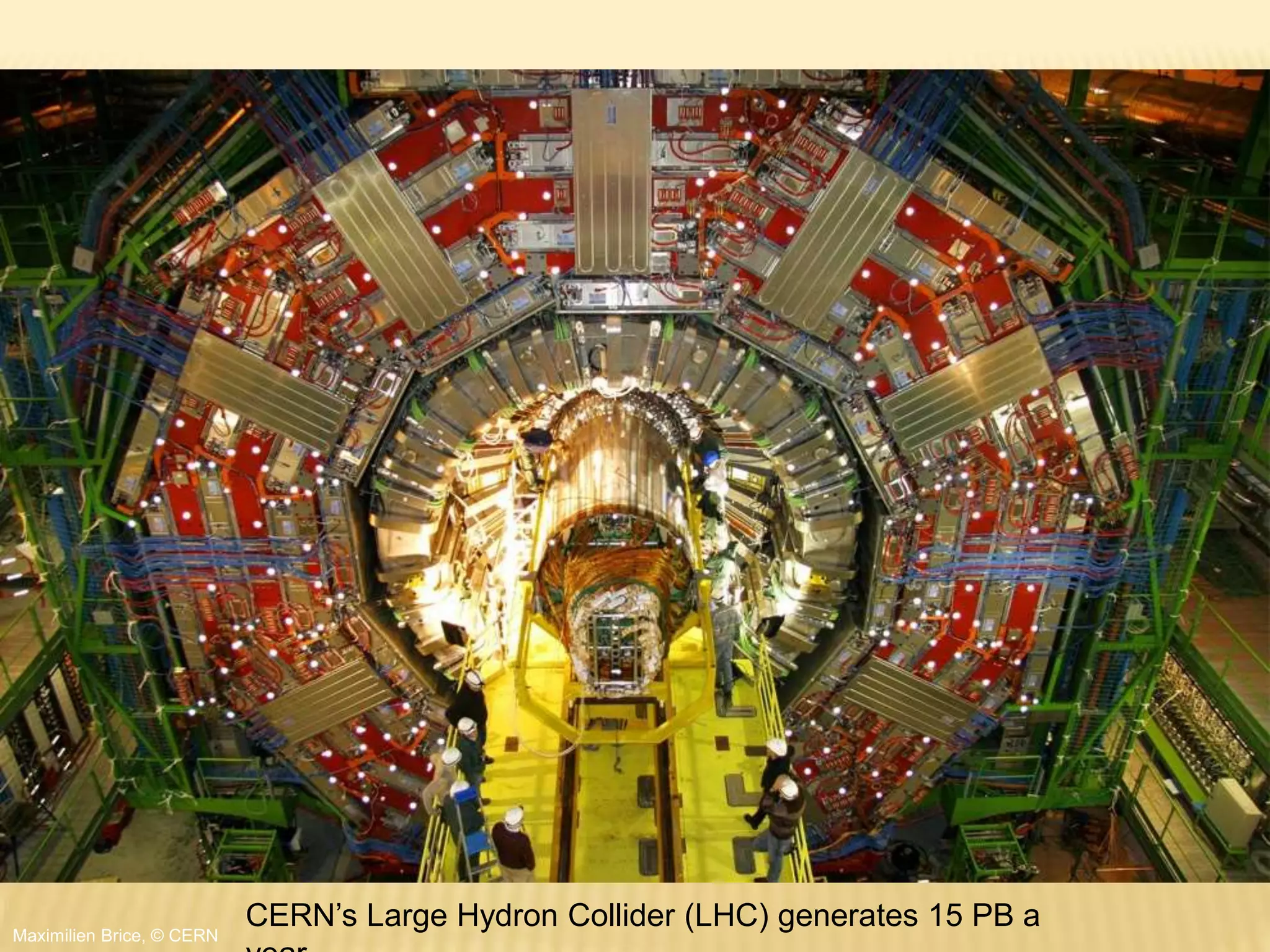
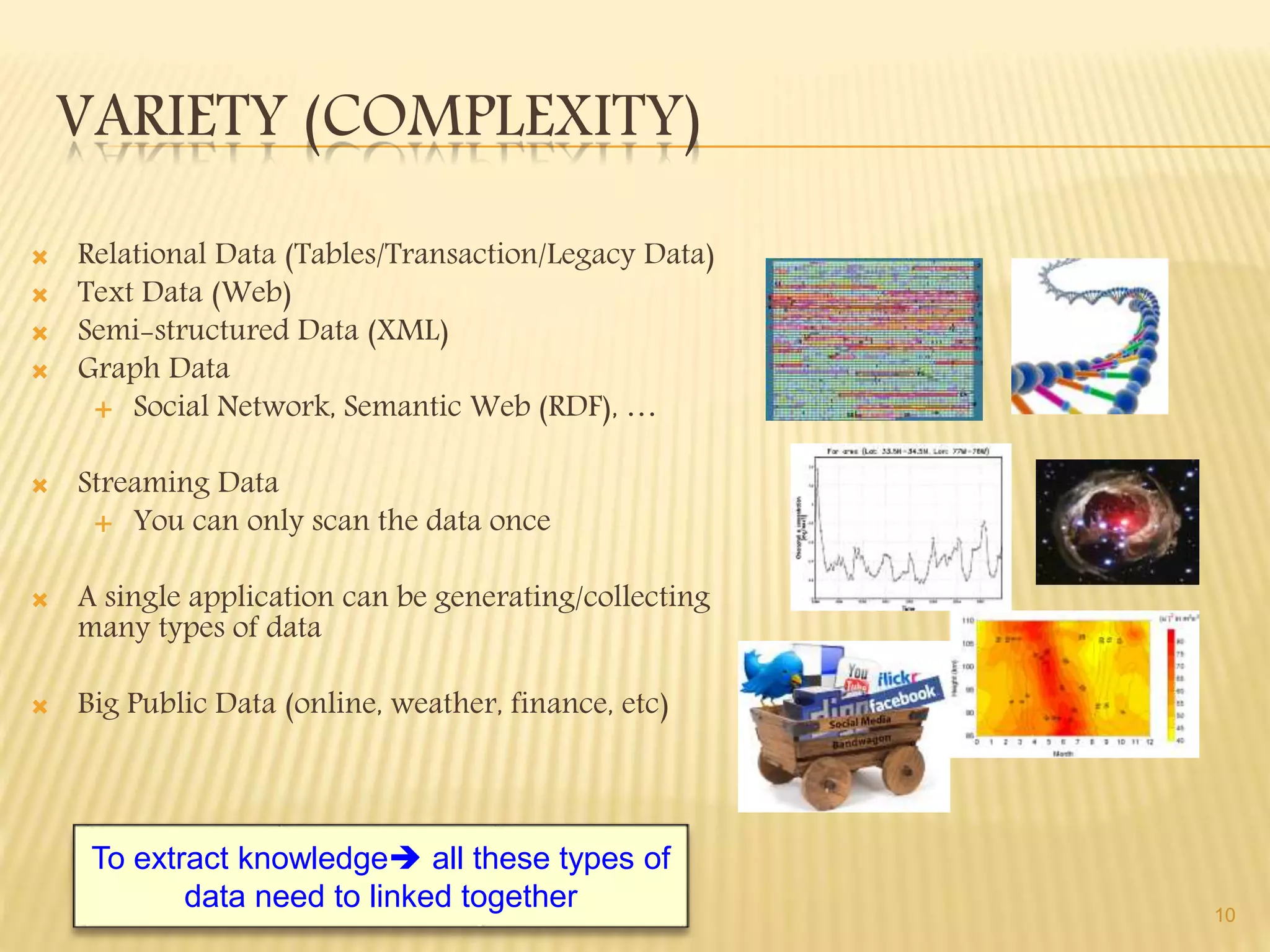
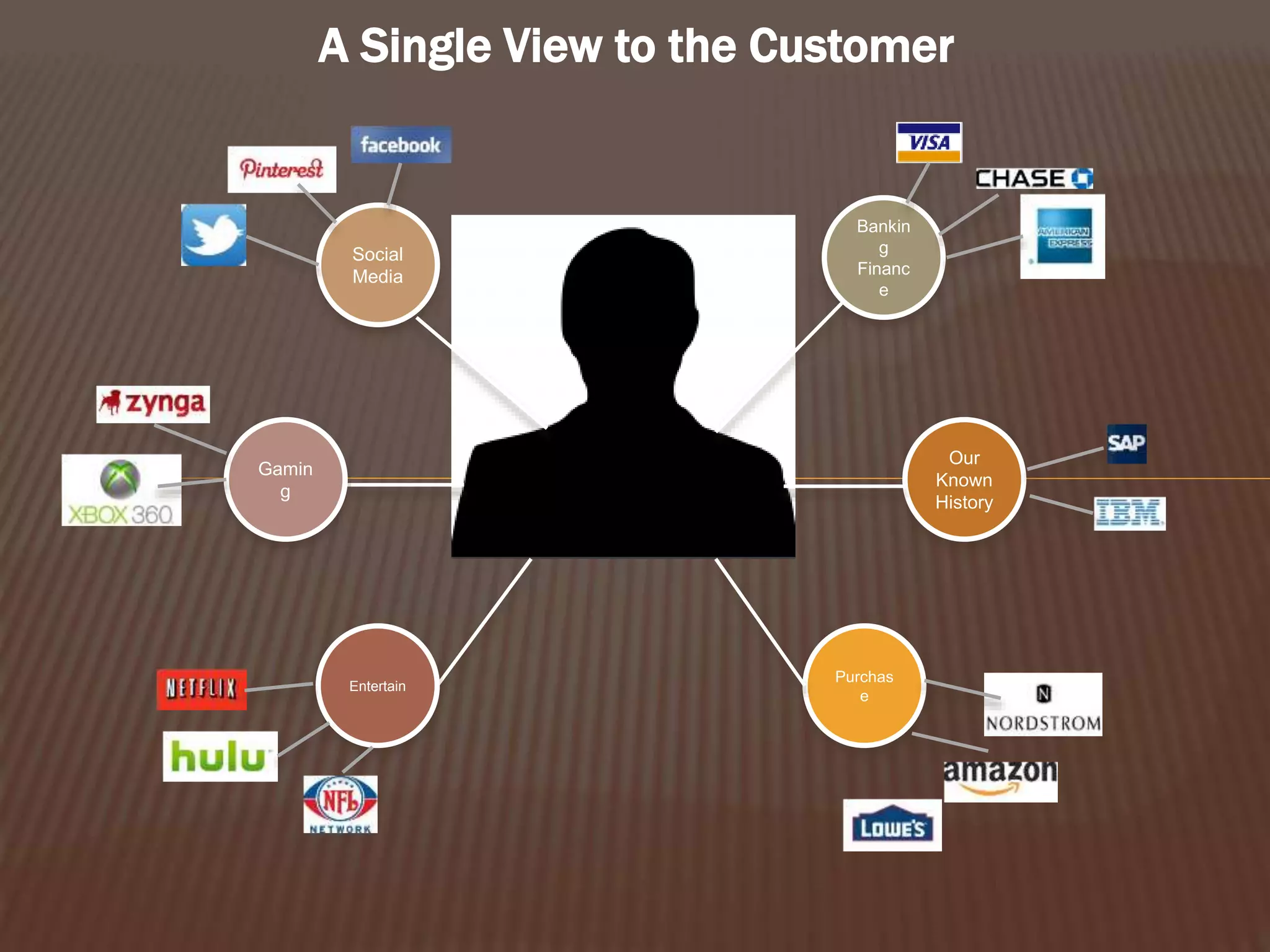
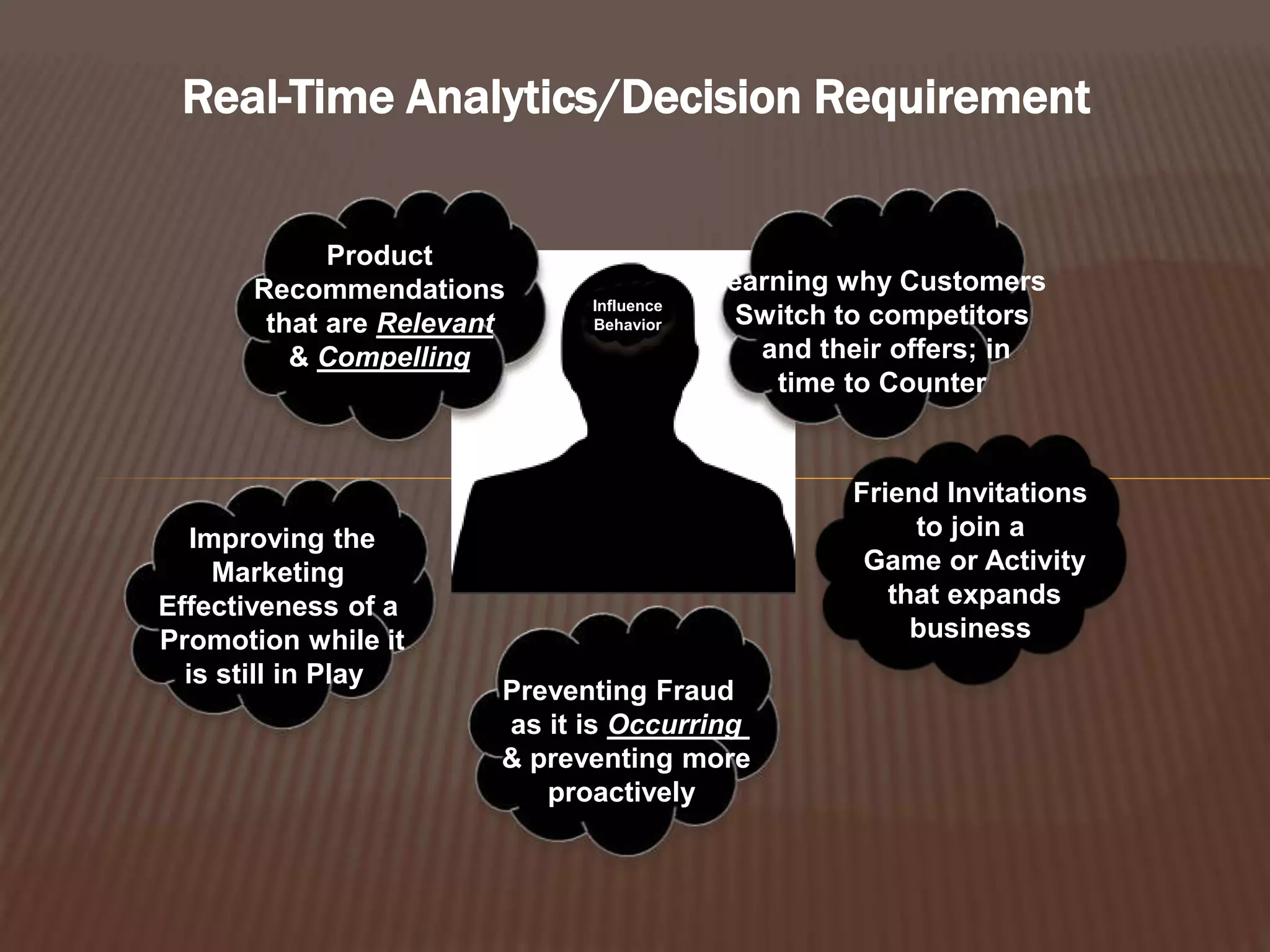
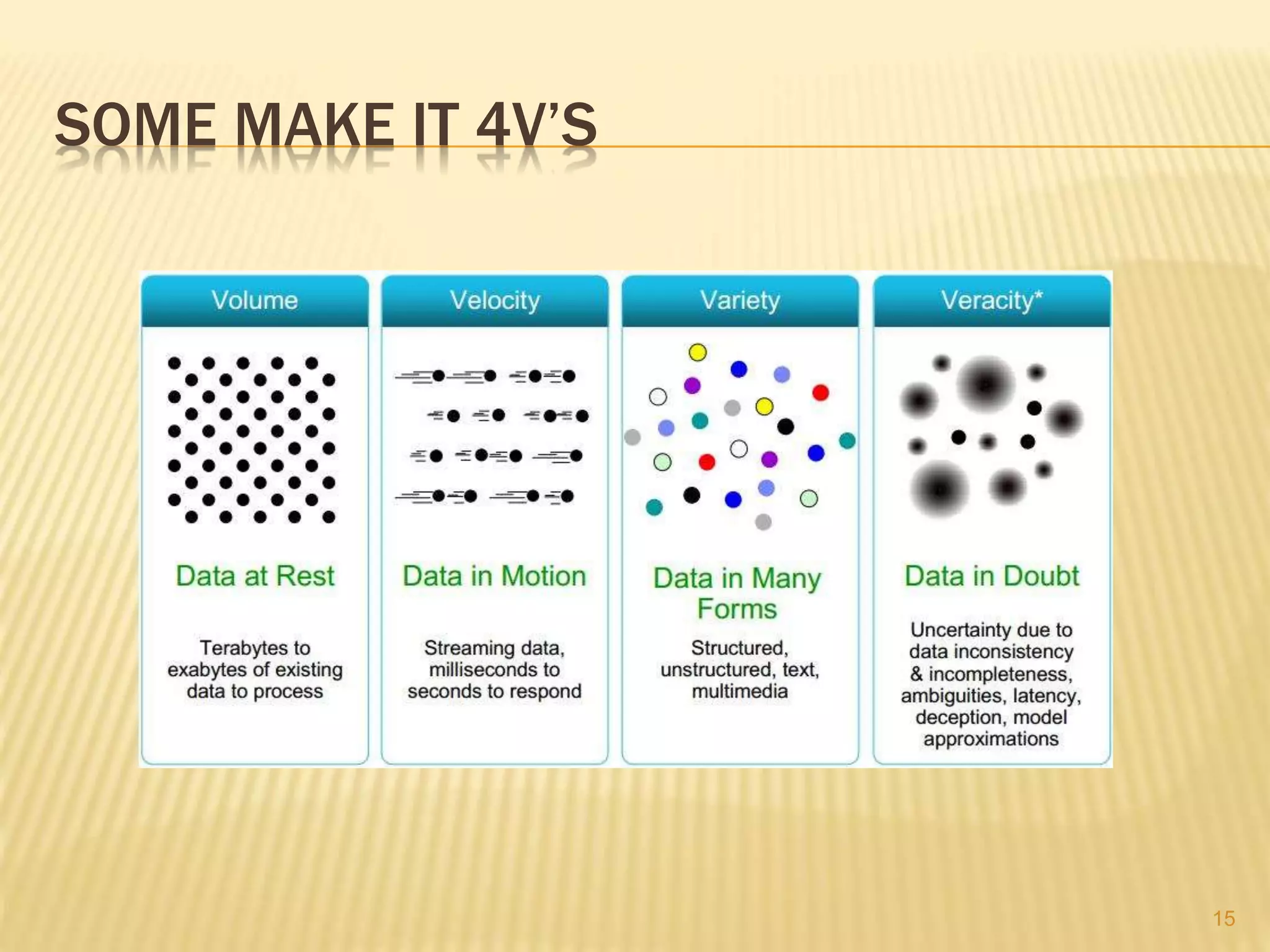
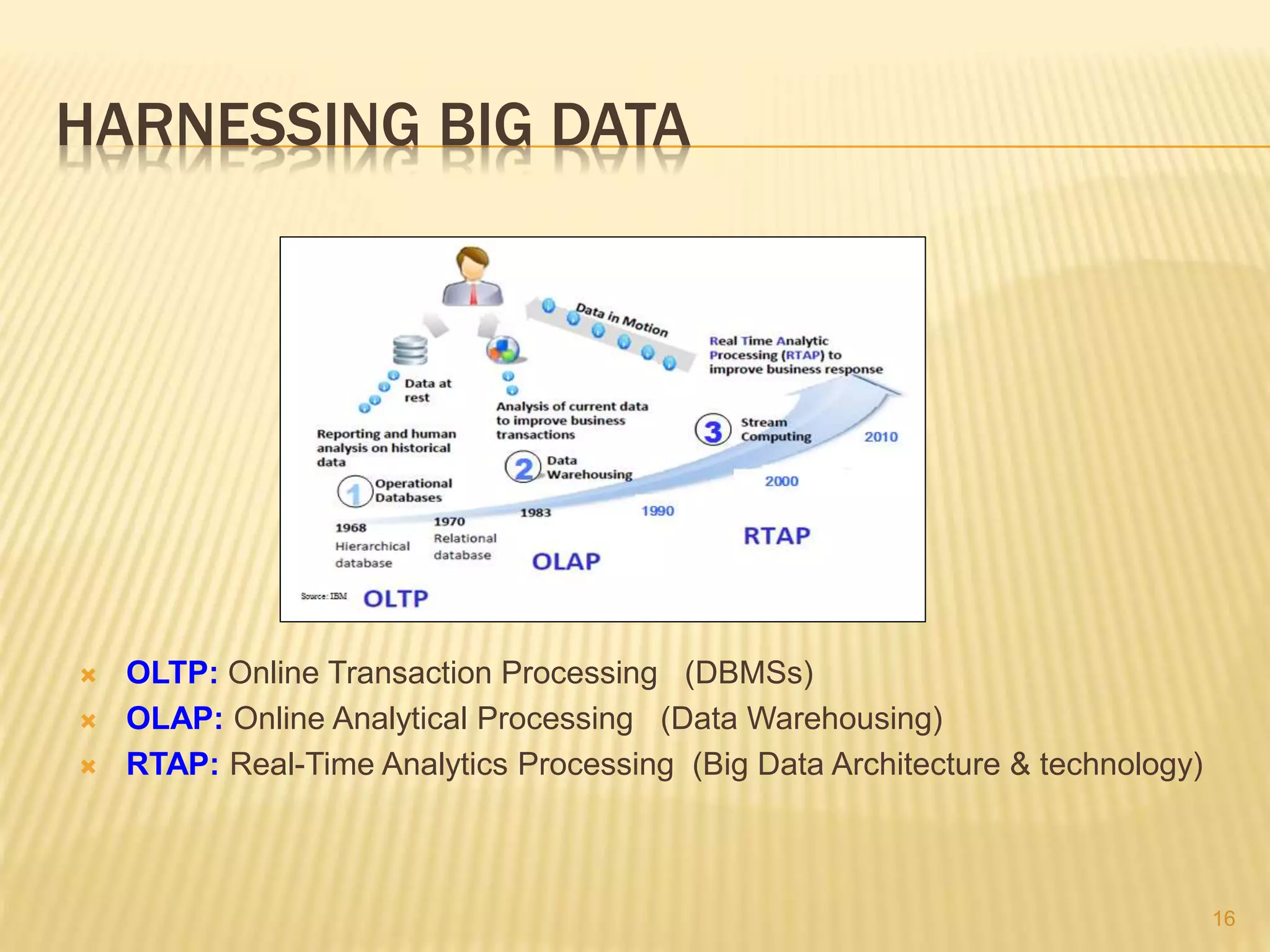
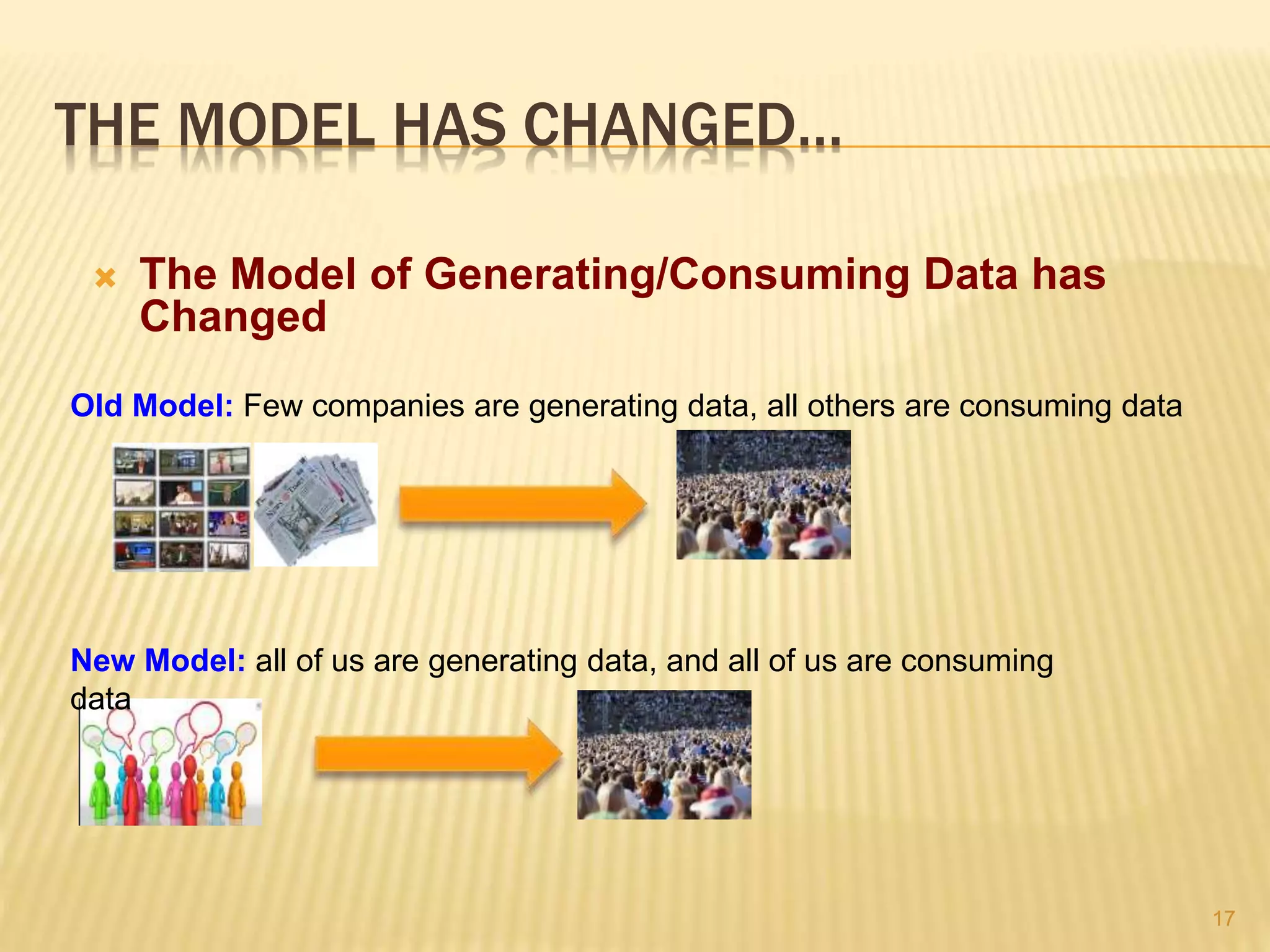
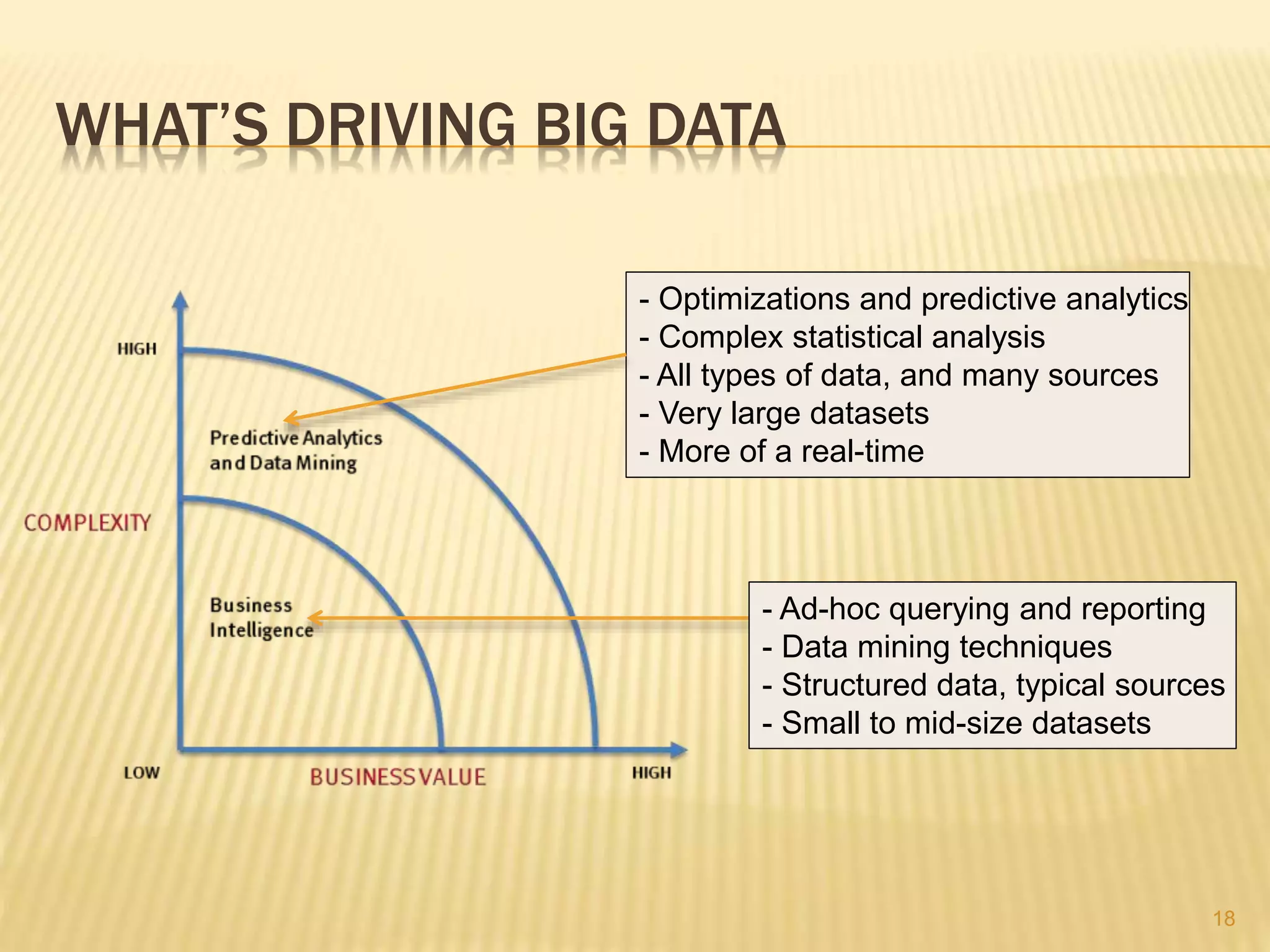
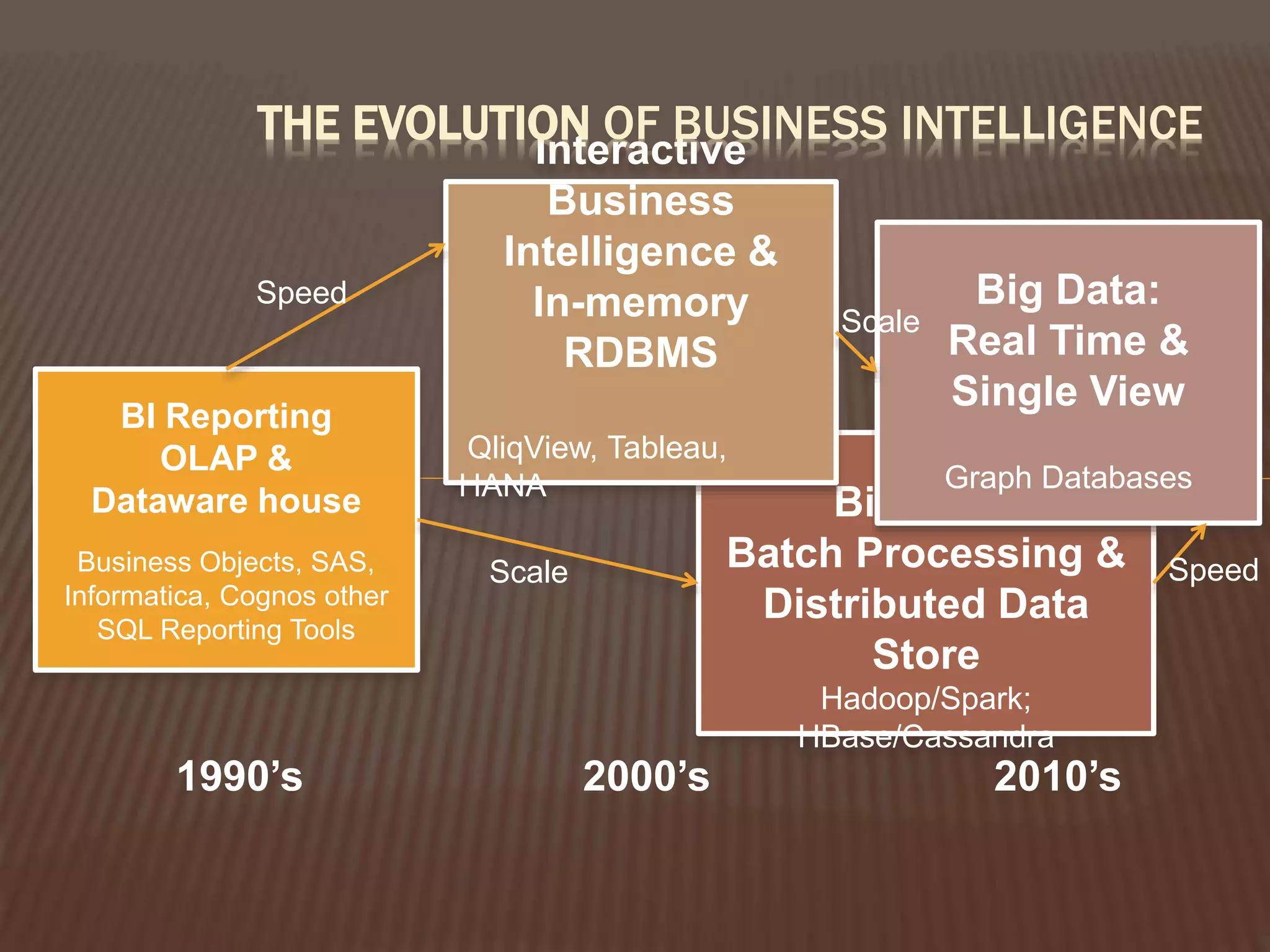
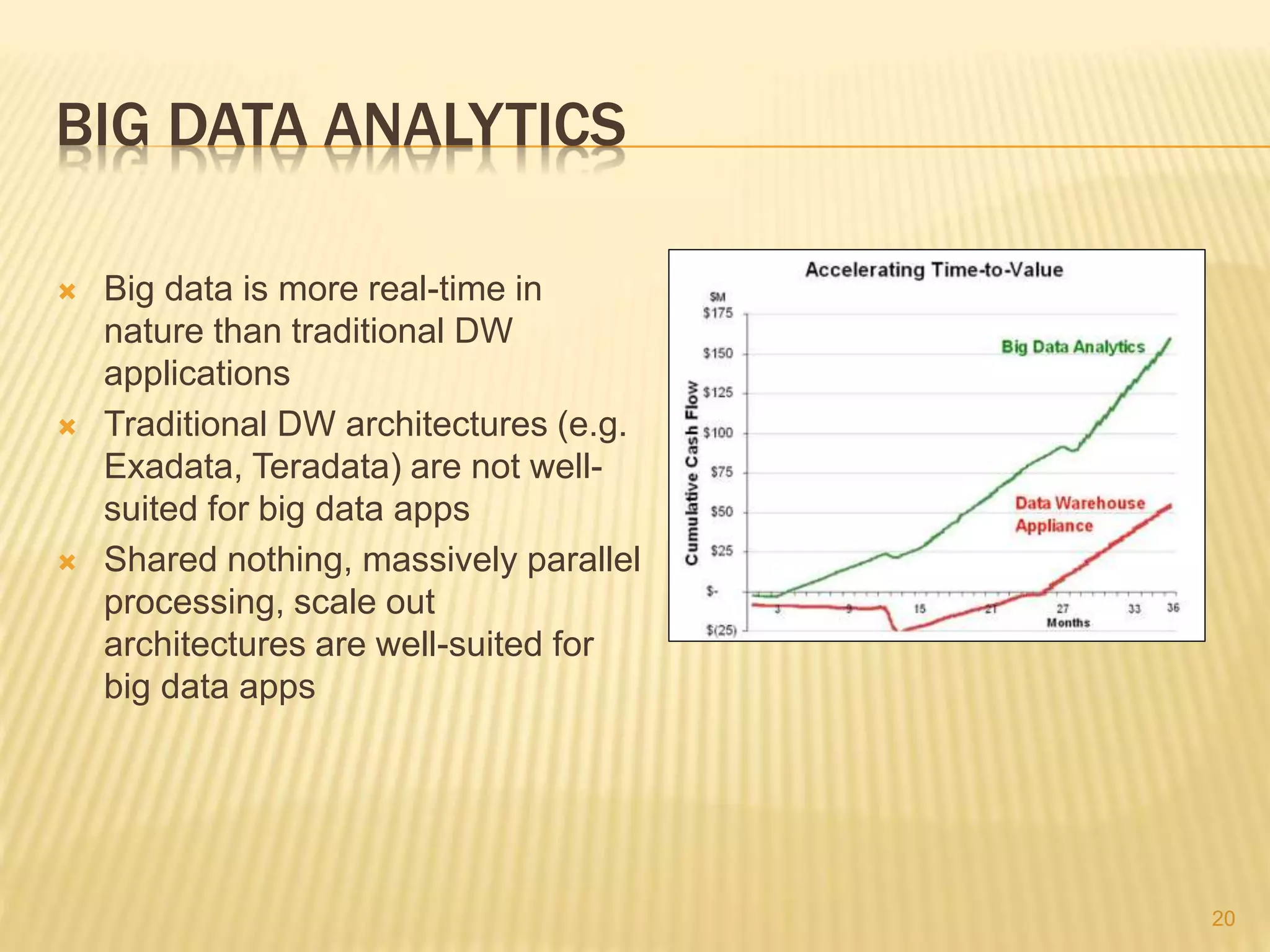
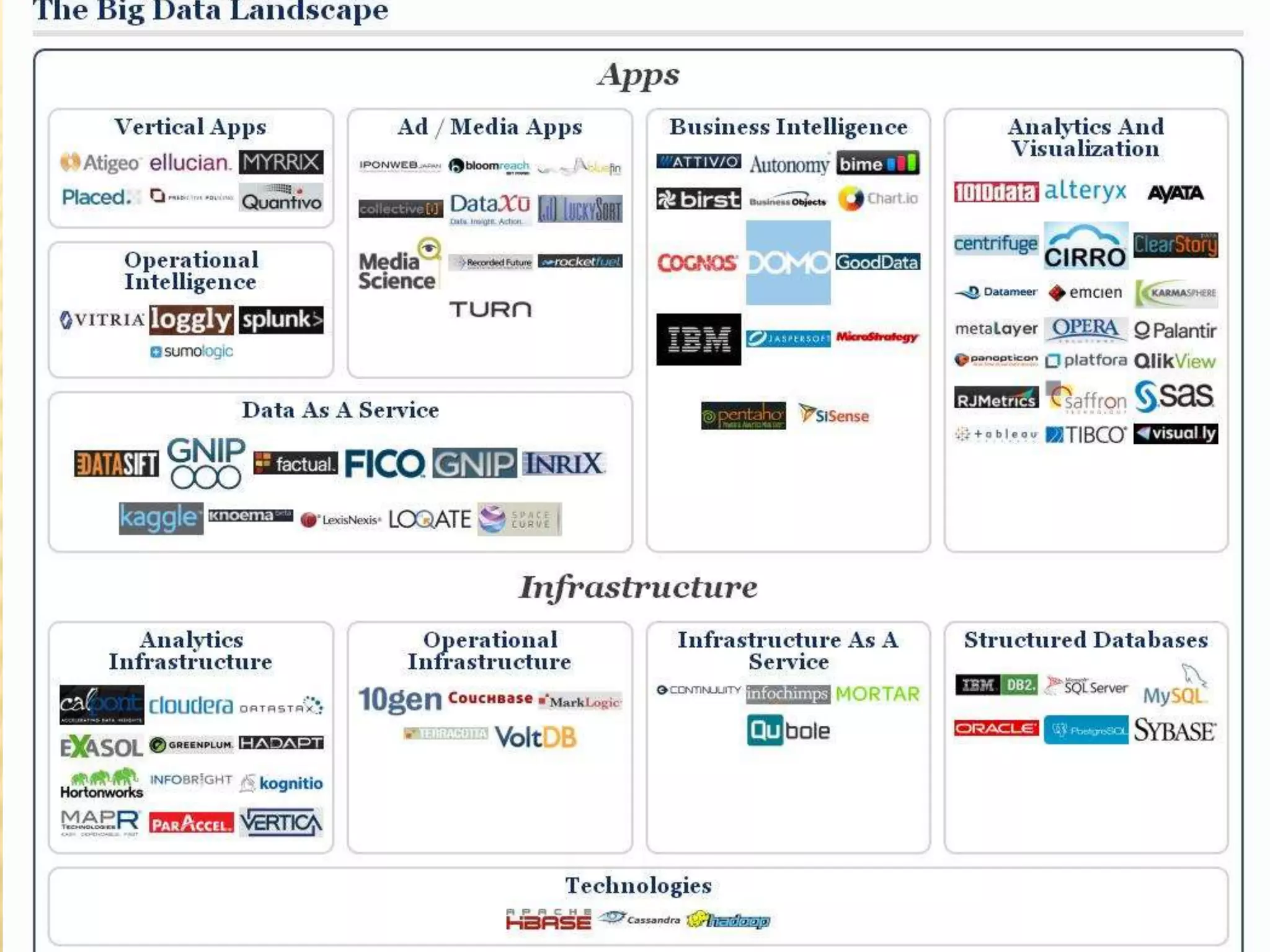
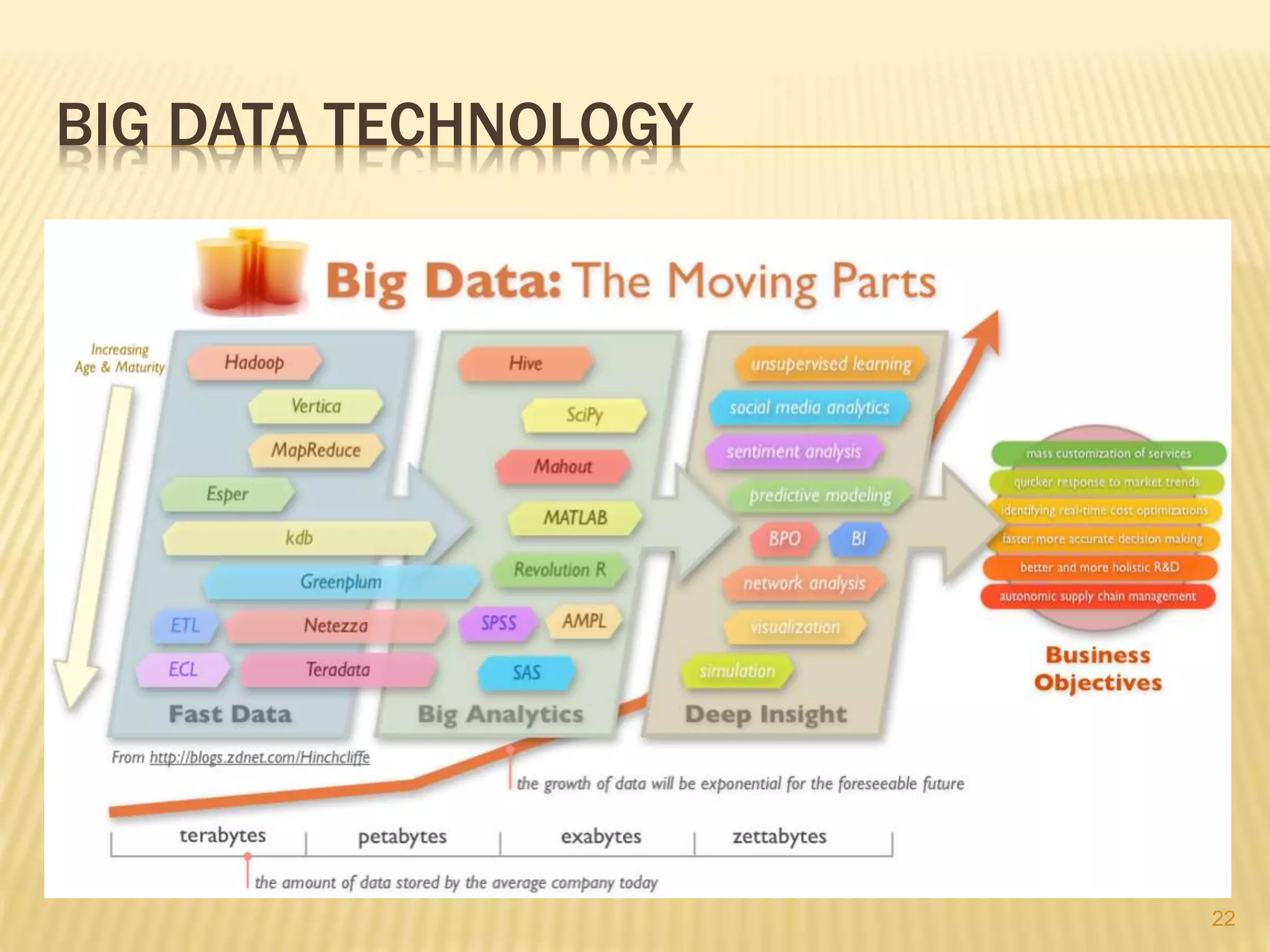
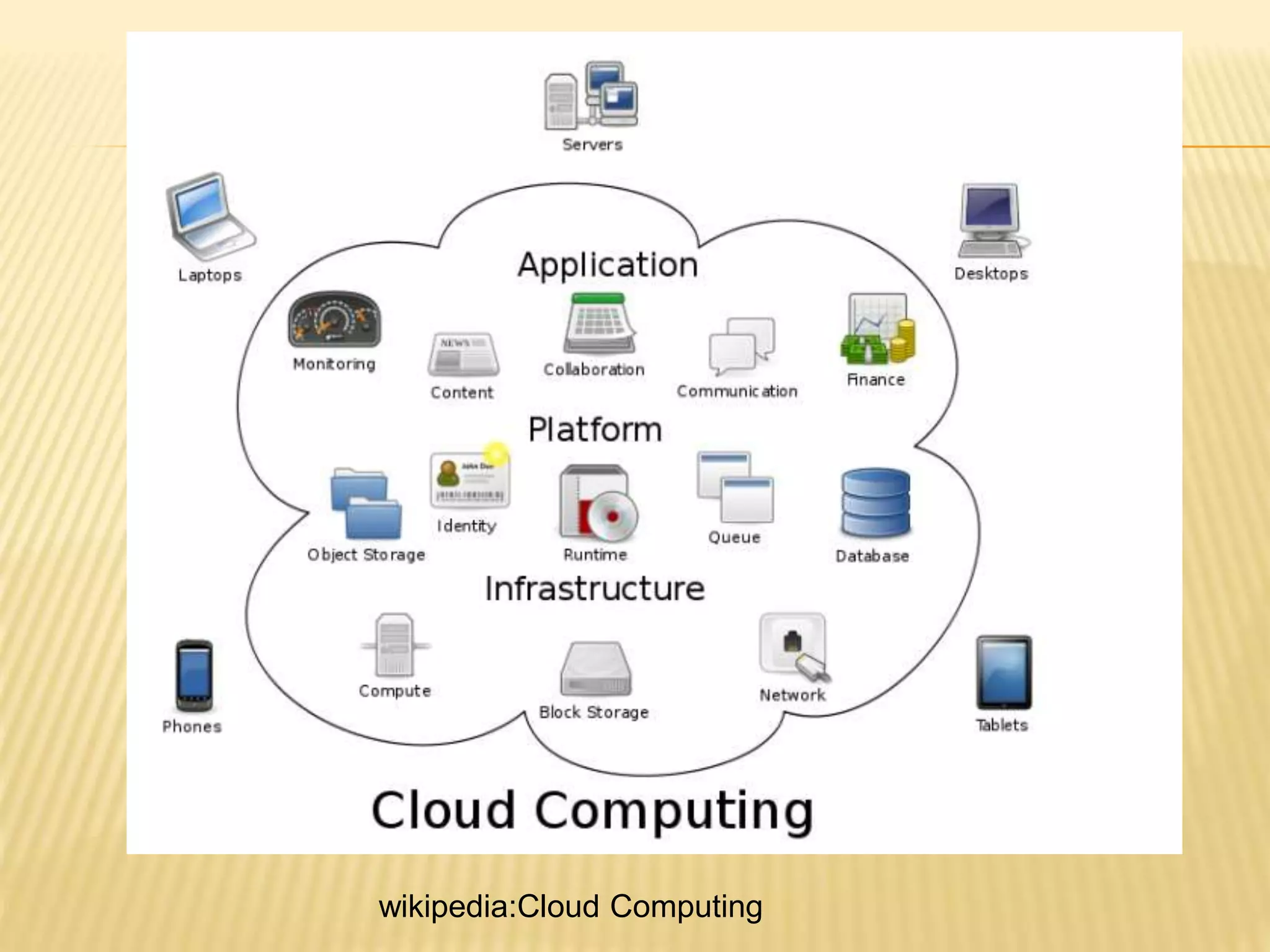
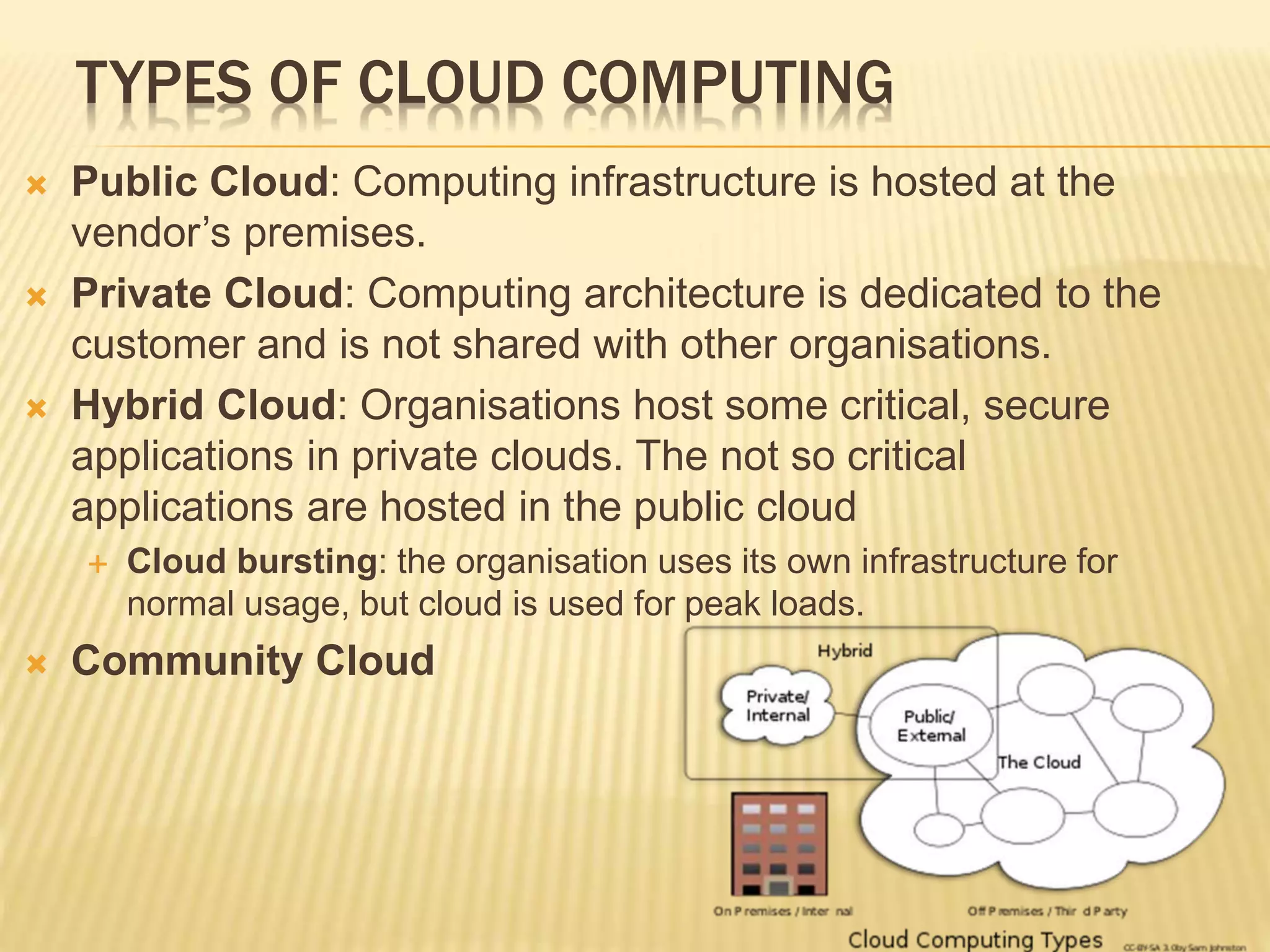
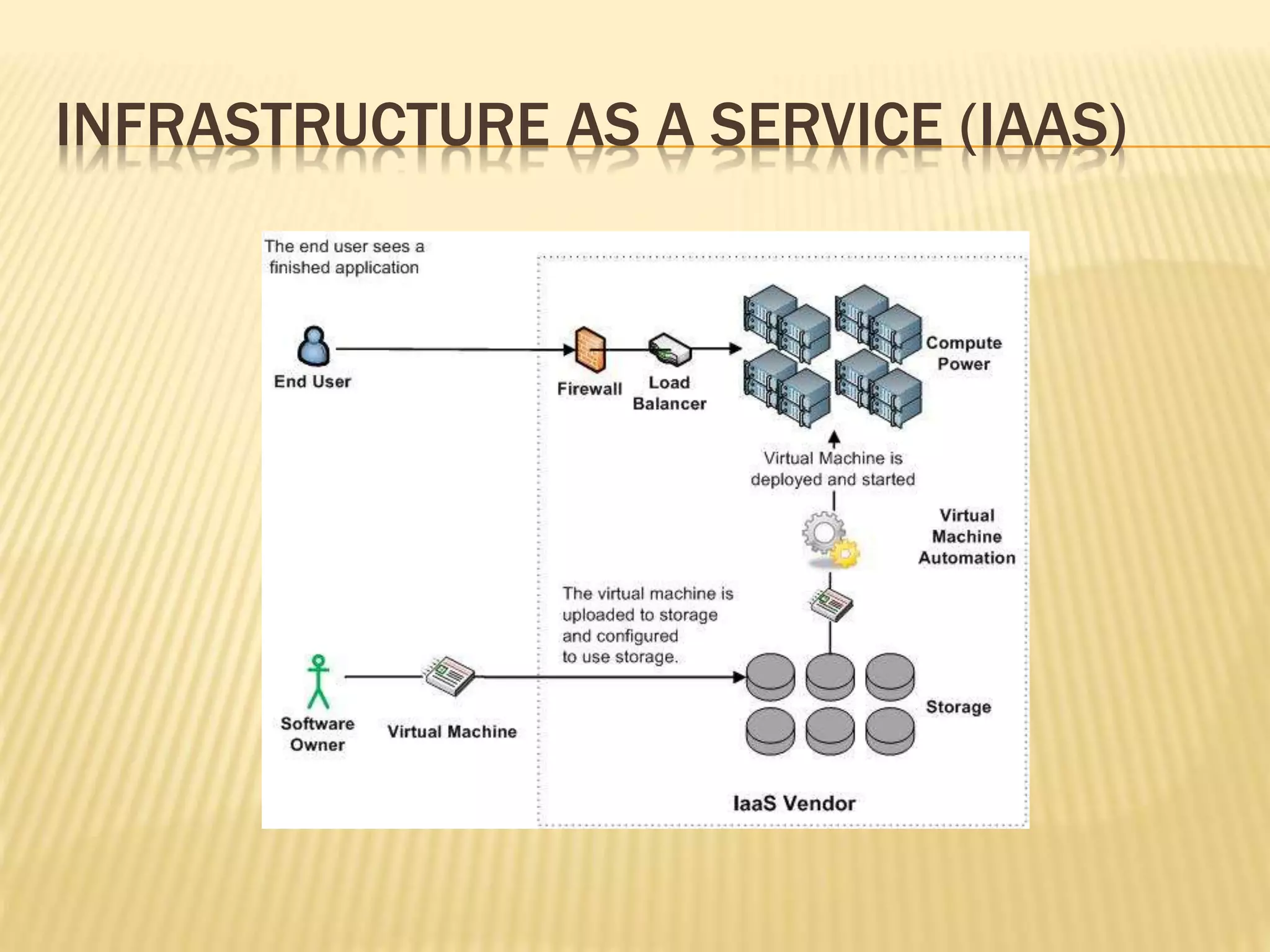
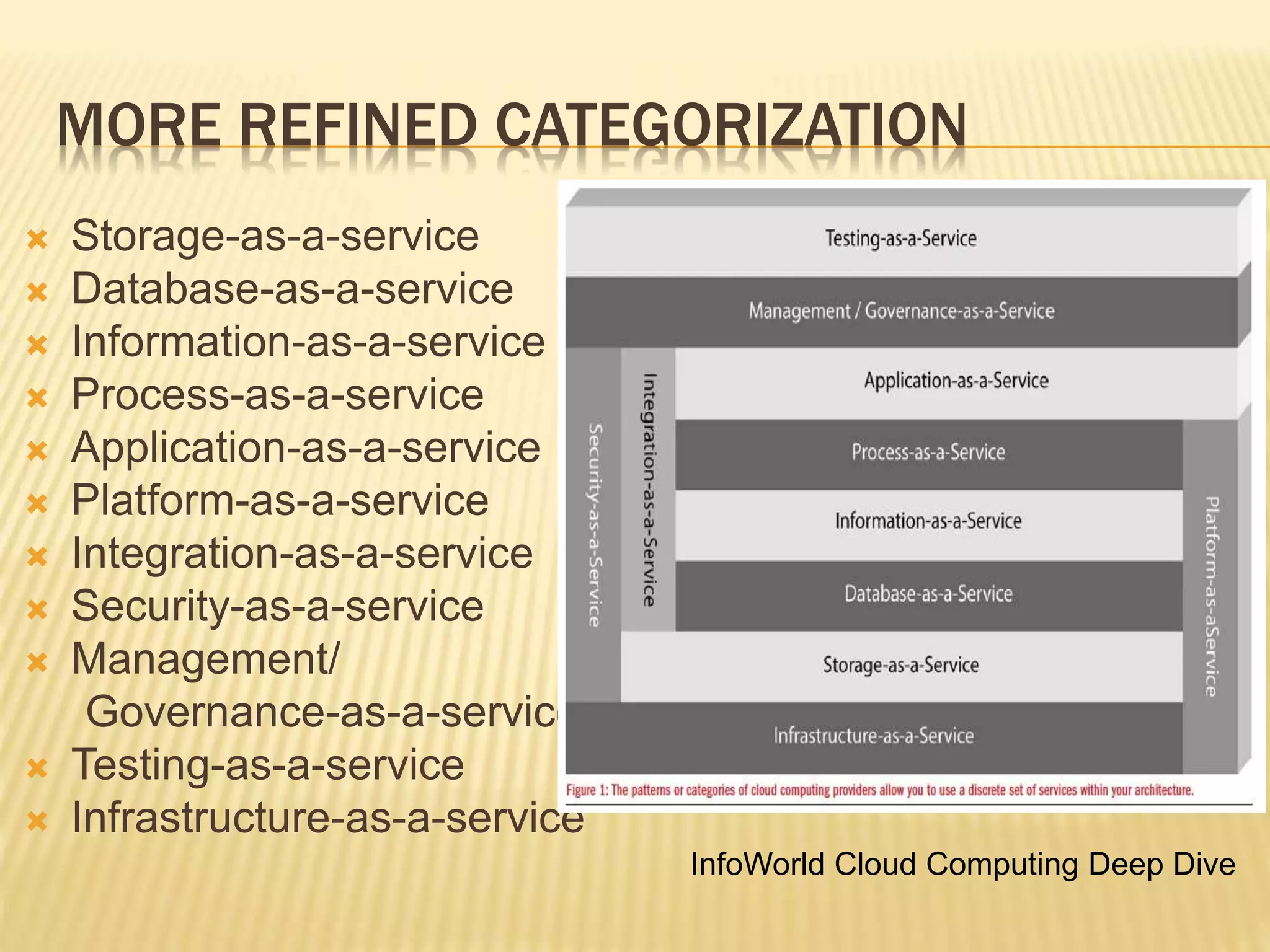
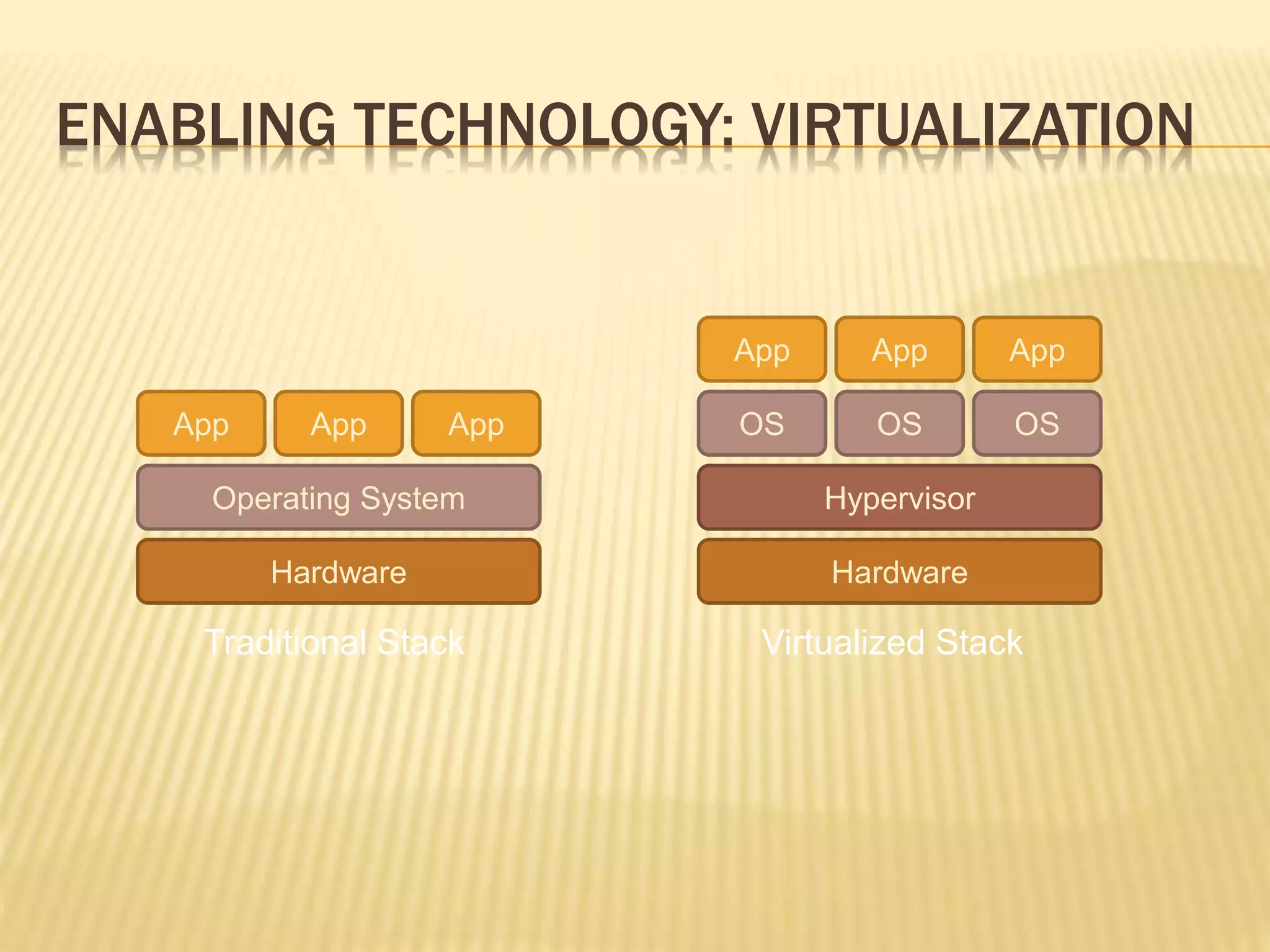
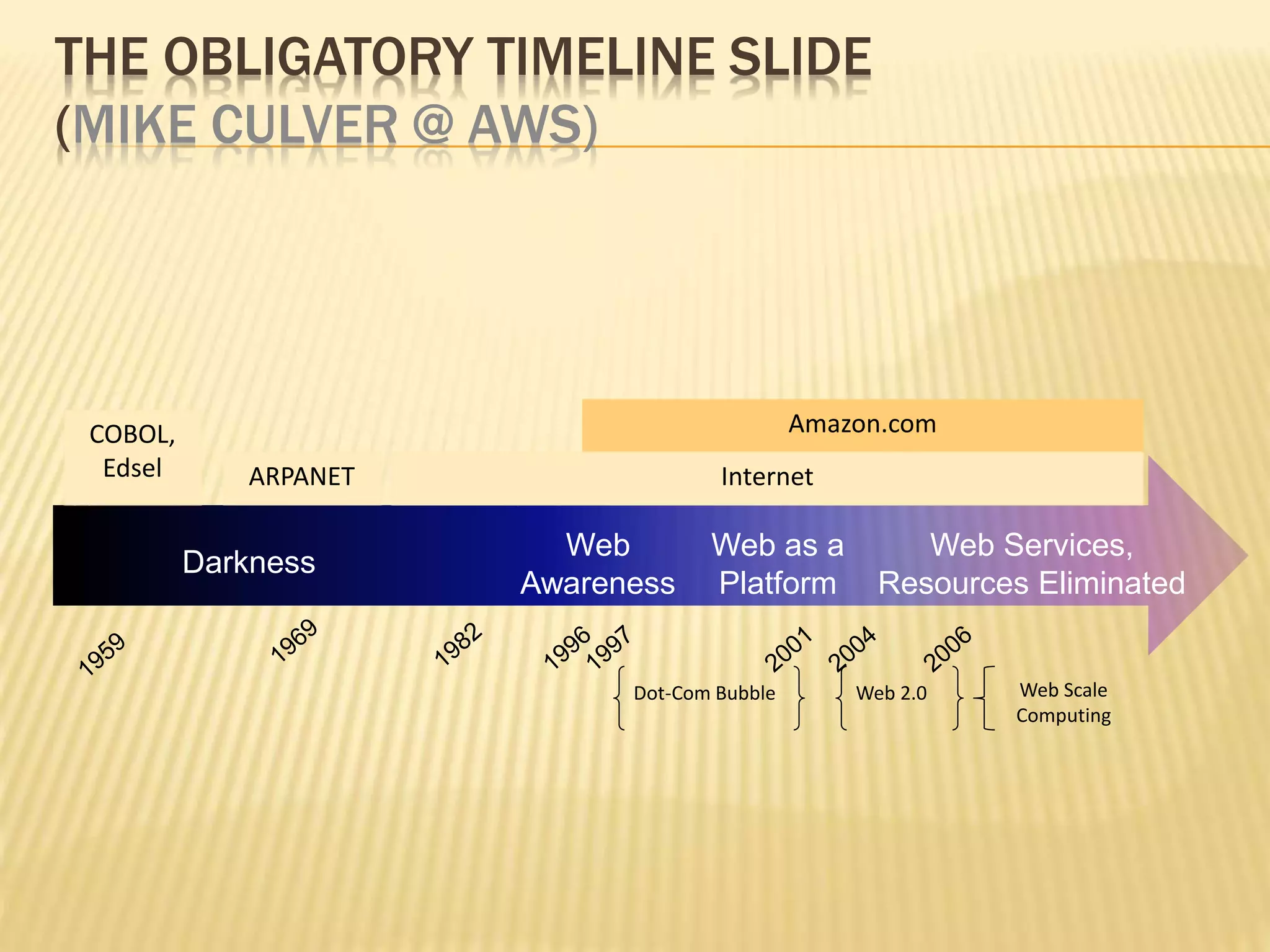
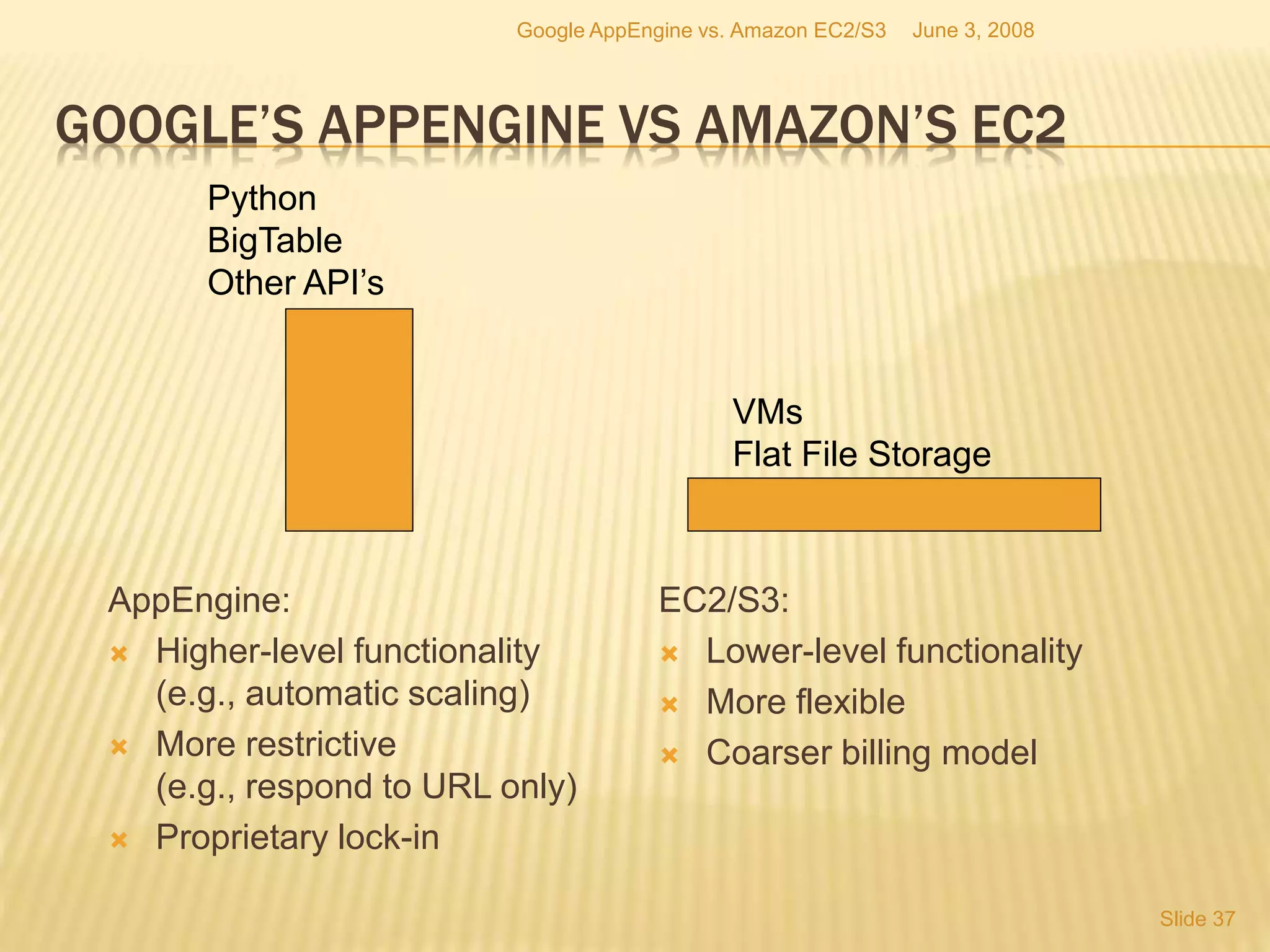
This document provides an introduction to big data. It defines big data as large and complex data sets that are difficult to process using traditional data management tools. It discusses the three V's of big data - volume, variety and velocity. Volume refers to the large scale of data. Variety means different data types. Velocity means the speed at which data is generated and processed. The document outlines topics that will be covered, including Hadoop, MapReduce, data mining techniques and graph databases. It provides examples of big data sources and challenges in capturing, analyzing and visualizing large and diverse data sets.