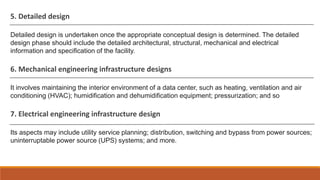
A data center is a facility that centralizes IT operations and equipment, manages data, and ensures security and redundancy in power and data communication. Concerns include operational continuity, information security, and the need for high standards in infrastructure, which involve design considerations such as facility topology, engineering infrastructure, and technology infrastructure. Additionally, data center infrastructure management integrates IT and facility management for effective monitoring and management of critical systems within the data center.