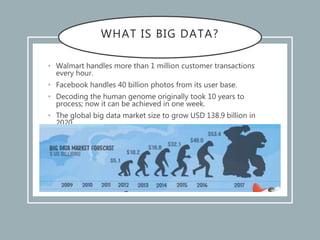
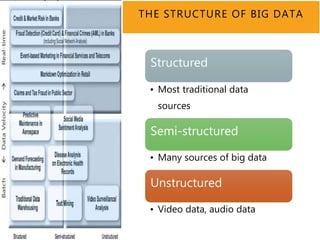
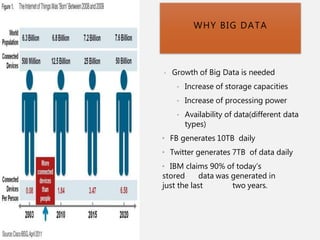
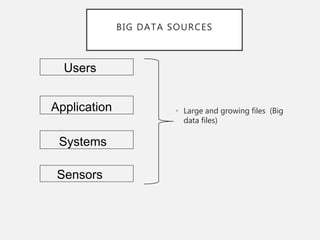
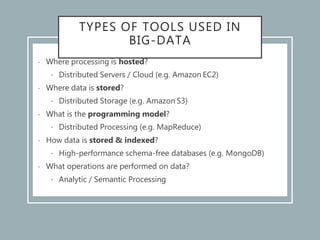
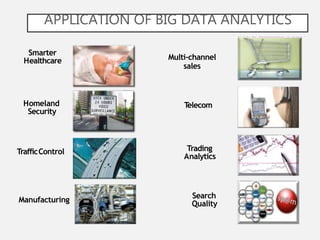
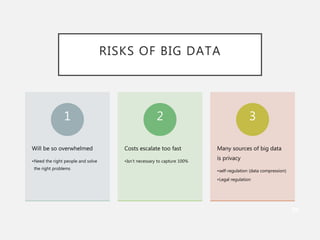
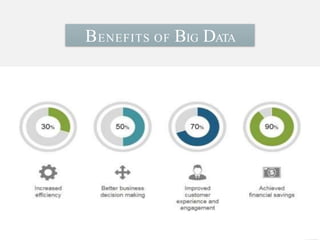
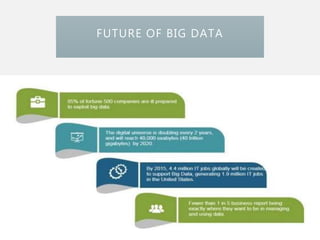
The document discusses the concept of big data, its characteristics, sources, and implications for various fields including IT and analytics. It highlights the growth and vastness of big data, the need for specialized tools and techniques to manage it, and the potential benefits and risks associated with its application. Furthermore, it emphasizes the necessity for organizations to adapt to the challenges and opportunities presented by big data to remain competitive.