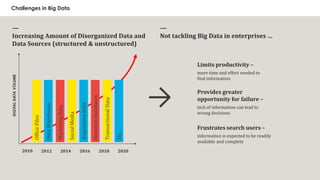
- Big data refers to large volumes of data from various sources that is analyzed to reveal patterns, trends, and associations.
- The evolution of big data has seen it grow from just volume, velocity, and variety to also include veracity, variability, visualization, and value.
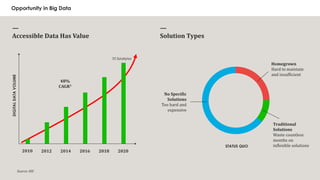
- Analyzing big data can provide hidden insights and competitive advantages for businesses by finding trends and patterns in large amounts of structured and unstructured data from multiple sources.