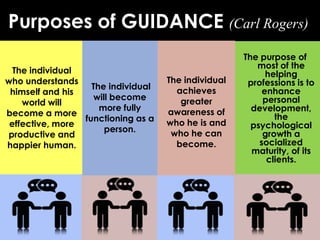
This document discusses temper tantrums and emotional outbursts in adults. It identifies common causes as emotional immaturity, insecurity, unforgiveness, stress, selfishness, and certain personality traits. Guidance and counseling can help address the underlying issues. The document also discusses techniques for emotional control, including identifying automatic thoughts, detaching from emotions, and therapies like thought field therapy and idenics.