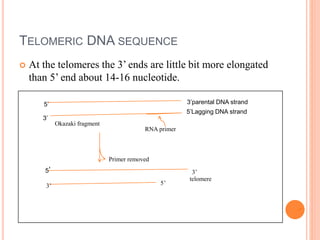
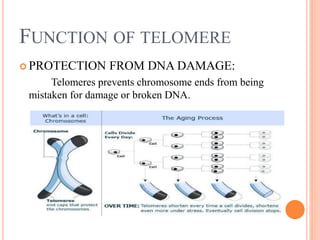
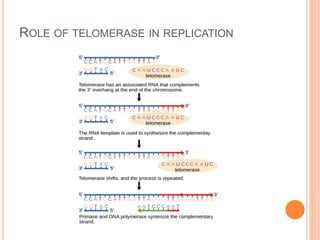
Telomeres are repetitive DNA sequences that cap the ends of chromosomes. They contain the sequence TTAGGG and associated proteins that help protect chromosome ends from damage or fusion. As cells divide, telomeres slowly shorten due to the end replication problem. Once telomeres reach a critical short length, cells enter a permanent state of growth arrest called senescence. The enzyme telomerase helps maintain telomere length by adding back TTAGGG repeats and allowing cells to avoid senescence and continue dividing. Telomeres and telomerase play important roles in aging, cellular replication limits, and preventing chromosome fusion.