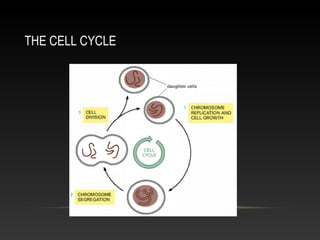
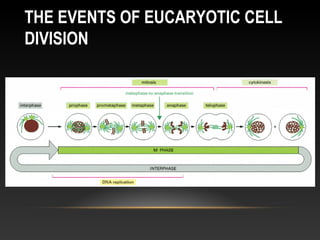
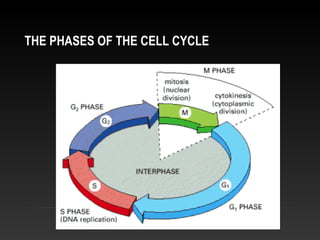
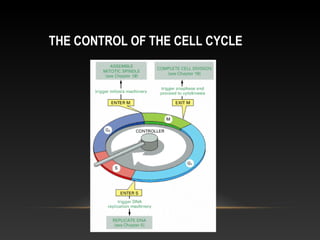
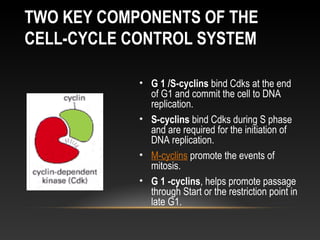
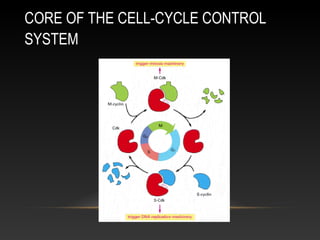
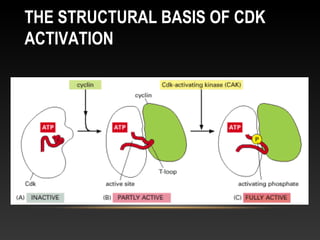
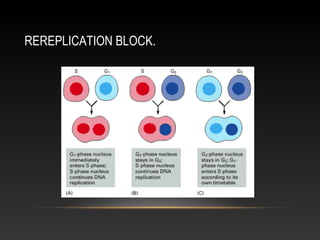
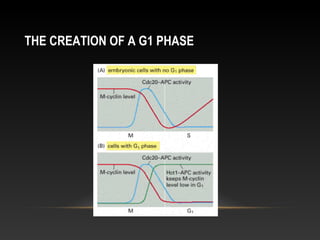
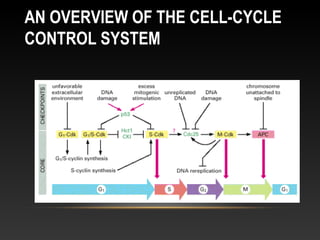
The document summarizes key aspects of the cell cycle and its control mechanisms. It describes the main phases of the eukaryotic cell cycle - G1, S, G2, and M phase. It explains that cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) control progression between phases by promoting specific events like DNA replication and mitosis. CDK activity is regulated by binding with cyclins and proteolytic degradation of cyclins by the anaphase promoting complex. Checkpoints in the cell cycle arrest progression under negative intracellular signals to ensure DNA replication and chromosome separation are properly completed.