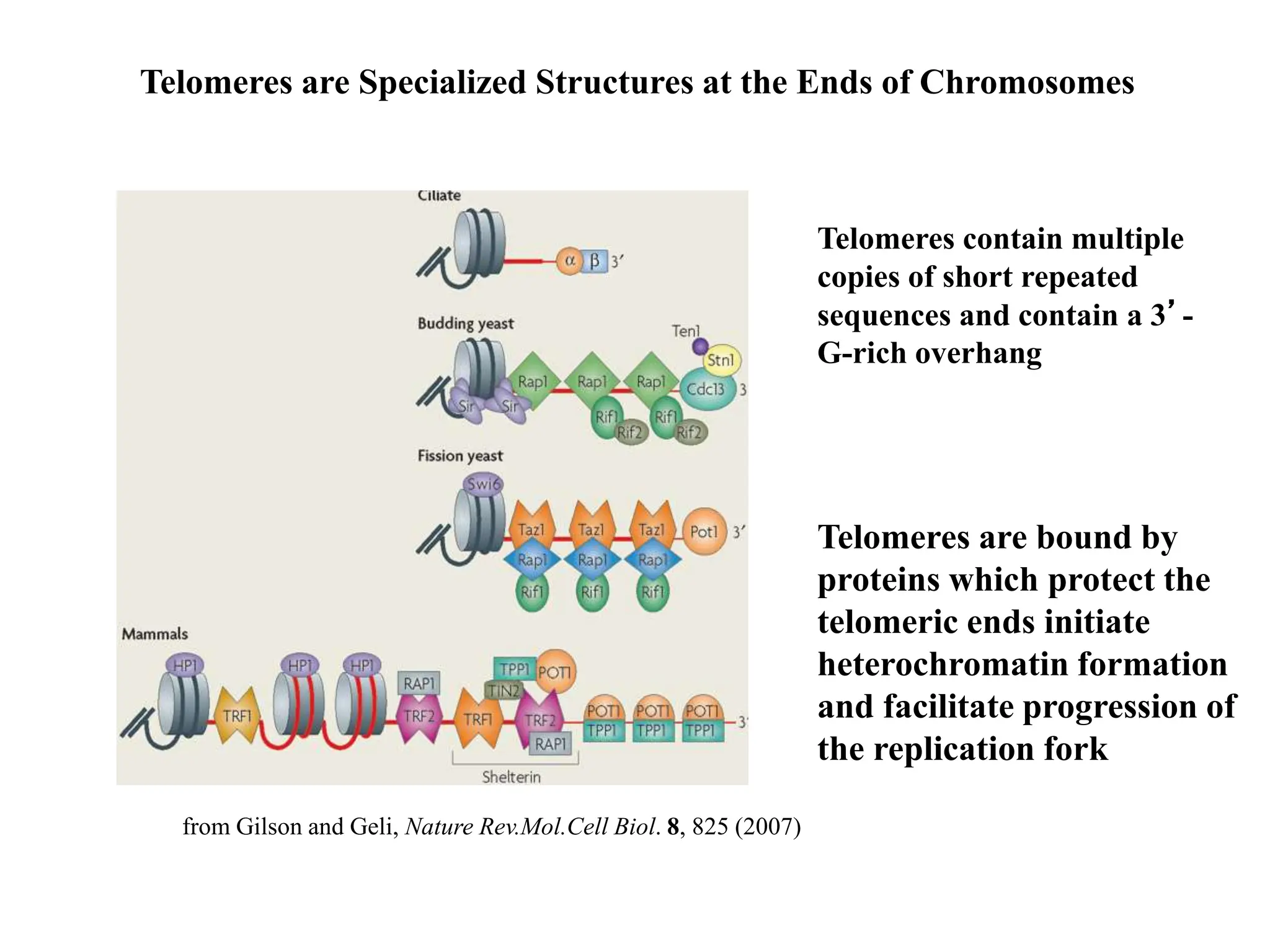
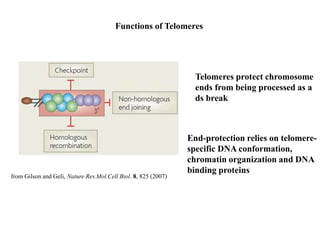
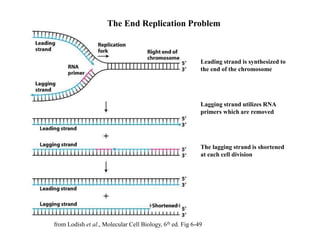
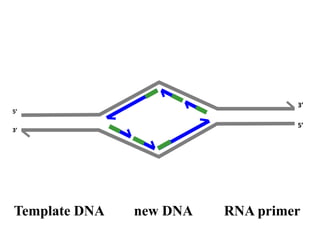
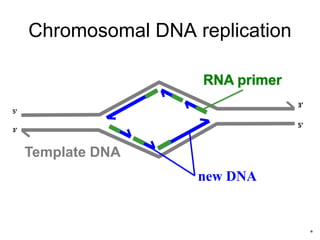
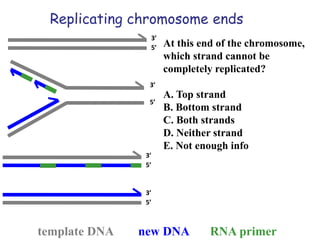
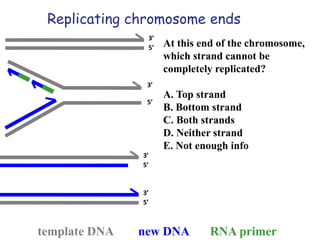
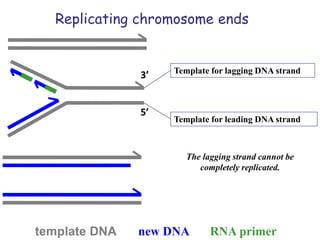
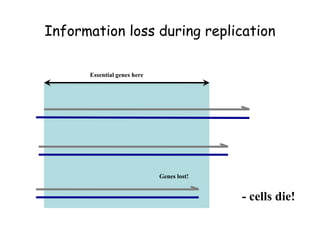
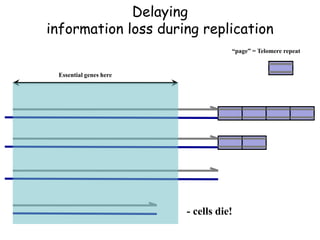
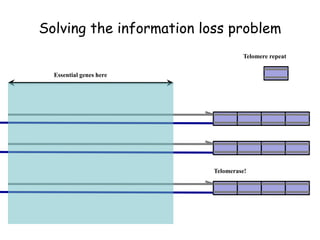
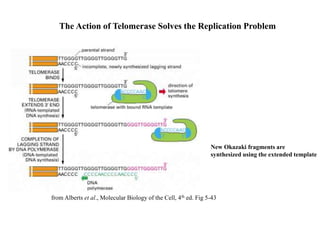
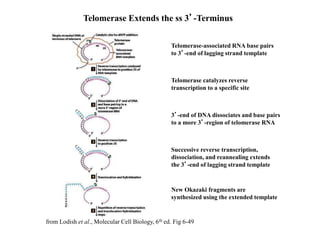
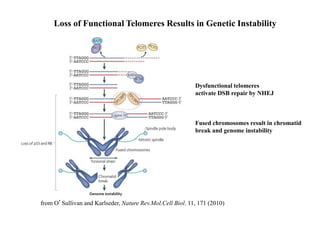
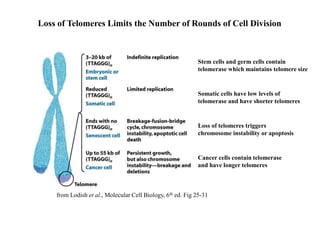
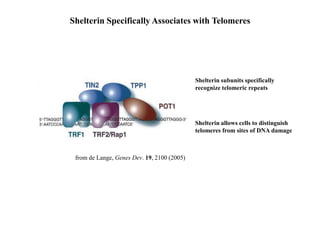
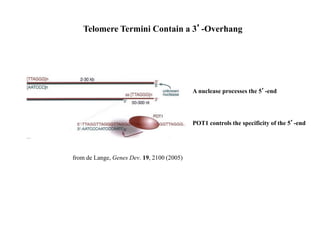
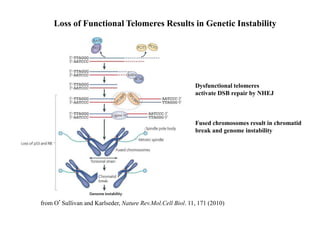
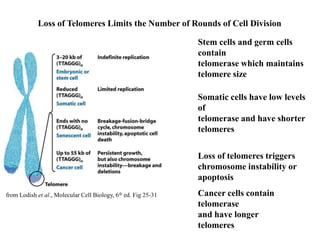
Telomeres are specialized structures at the ends of chromosomes that contain repeated DNA sequences and proteins. They protect chromosome ends from being recognized as DNA damage. During cell division, the lagging strand of DNA cannot be fully replicated, resulting in telomere shortening over time. This eventually leads to chromosome instability and cell death. Telomerase is an enzyme that maintains telomere length by adding DNA repeats to chromosome ends and counteracts replication-induced shortening. Its expression allows stem cells and cancer cells to divide indefinitely.