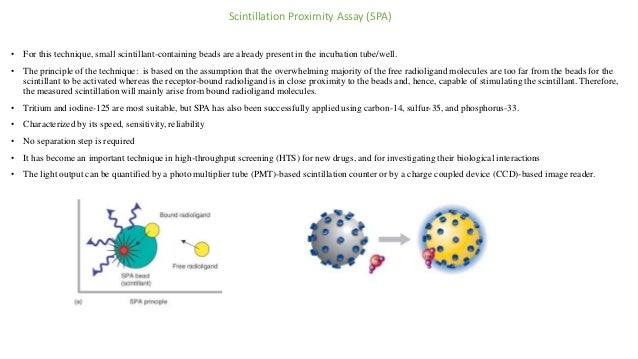
Receptor binding assays are essential for new drug development. Radioligand binding assays using radioactive isotopes like tritium and iodine were traditionally used but have drawbacks. Homogenous scintillation proximity assays avoid separation steps but are expensive. Fluorescent ligand binding assays provide safer alternatives with techniques like direct fluorescence measurement and fluorescence polarization. Label-free methods like surface plasmon resonance allow real-time kinetic analysis. NMR and X-ray crystallography provide high resolution structural data of receptor-ligand complexes.

![Radioligand binding assay:
• Radioligand binding is initiated by the incubation of cells, cell homogenates or purified plasma membrane preparations with an
adequate radioactively labelled drug – “The radioligand”
• Tritium [3H] and iodine [125I] are the most frequently used isotopes
• Separation of free and receptor-bound drug represents the most delicate step.
Filtration: the free radioligand passes through the filter whereas the receptor-bound radioligand remains on the filter.
• Counting the radioactivity on the filter allows the amount of receptor-bound radioligand to be quantified.
• Able to handle a large number of samples with relative ease as well as the commercial availability of a variety of filtration devices.
• The filters are usually of glass fibre, but sometimes it is also necessary to coat them with
polyethyleneimine or to siliconize them to prevent radioligand absorption to the filter.
• For 'high throughput screening', the radioligand binding may be performed in
microtiter plates with 96 or 384 or even more wells.
• After the incubation, the contents of the wells are filtered simultaneously with a cell harvester.
• For modern high-throughput screening, robots are used to handle screen compounds and buffers
as well as to perform the filtration step.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/techniquesformeasuringreceptorbindingitsuses-220318161044/95/Techniques-for-measuring-receptor-binding-Its-uses-pptx-3-638.jpg)