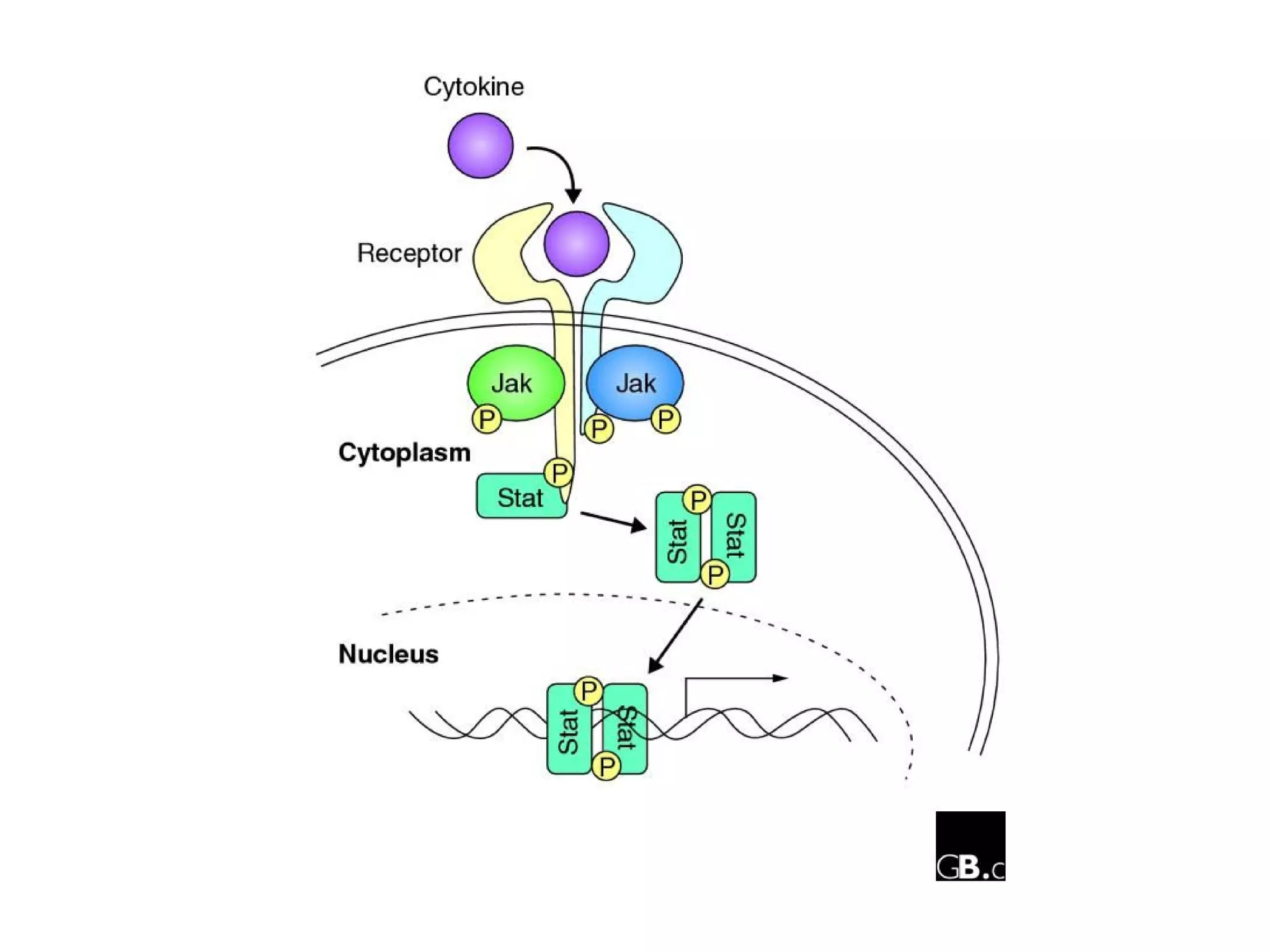
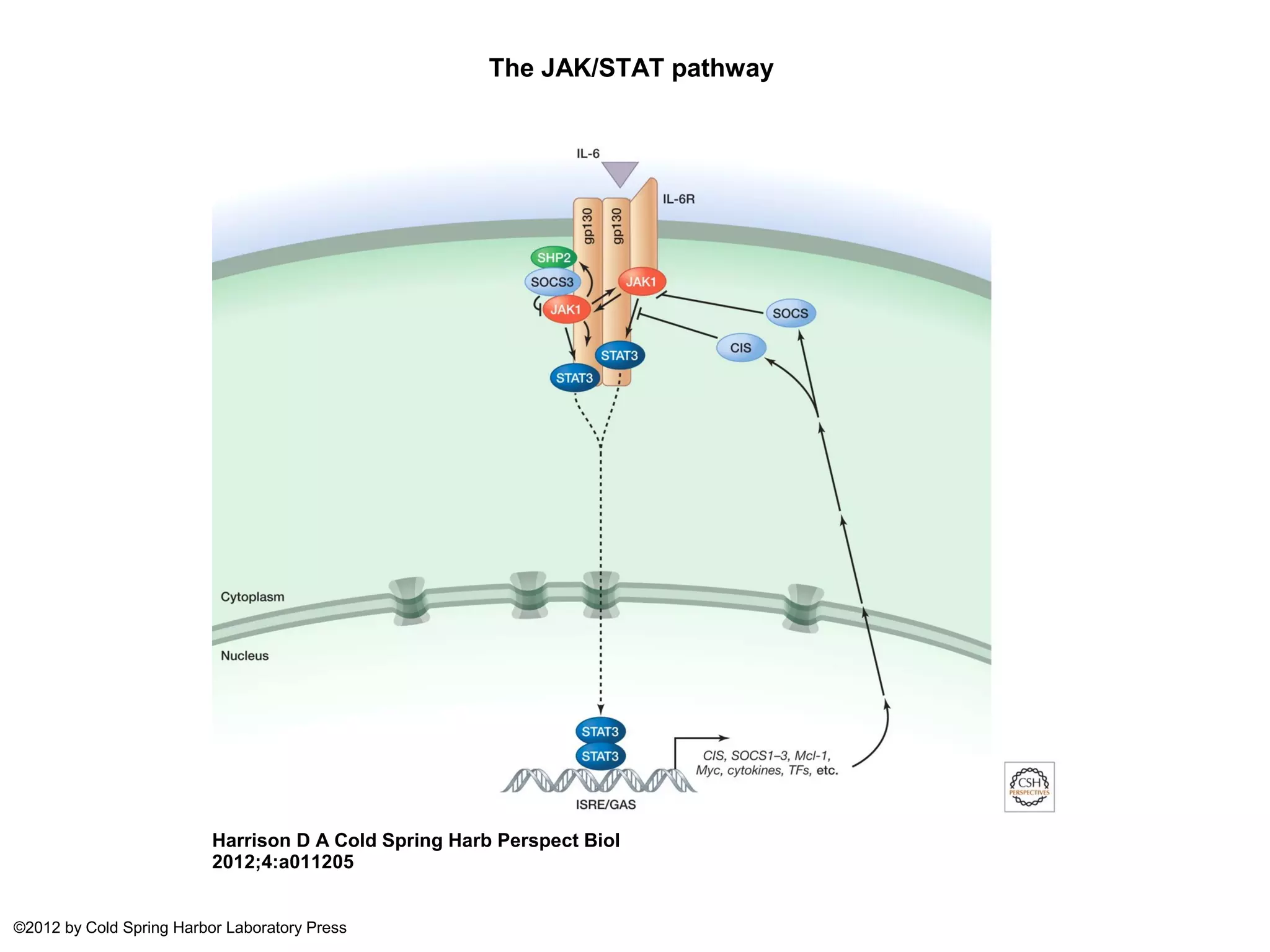
The JAK/STAT pathway involves cytokines binding to cell surface receptors which activates JAK kinases, leading to phosphorylation of STAT transcription factors. STAT dimers then enter the nucleus and regulate transcription of genes involved in processes like proliferation, differentiation, and survival. Disregulation of the JAK/STAT pathway contributes to diseases like leukemia, and JAK inhibitors have been developed for leukemia therapy.