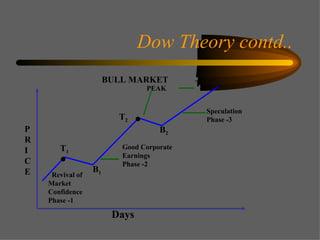
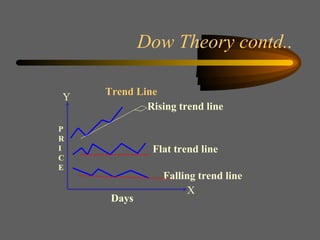
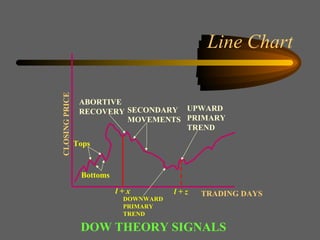
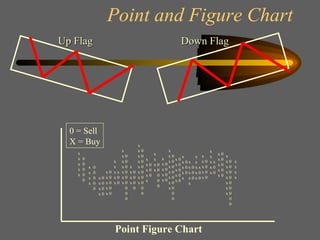
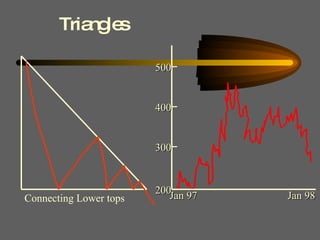
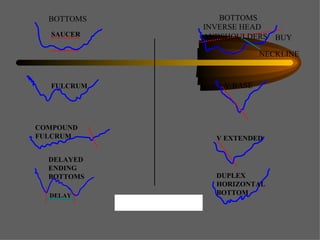
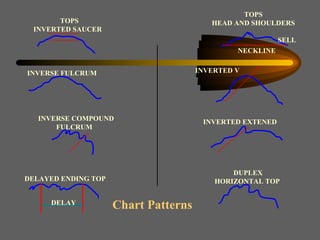
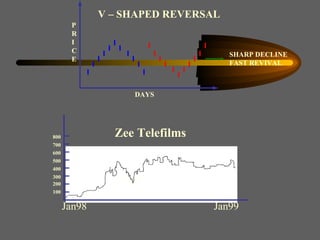
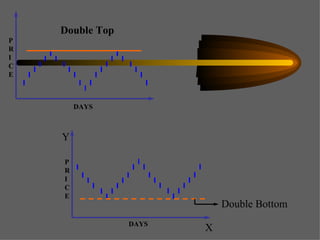
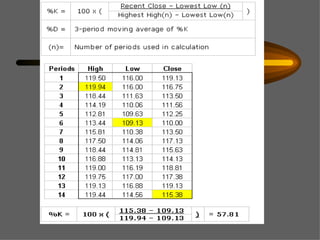
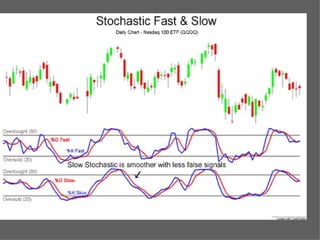
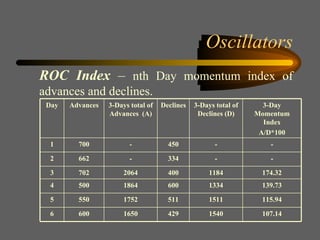
Technical analysis uses charts of market action to detect trends and predict future prices based on the idea that history repeats itself. Various technical indicators are used to analyze price, time, volume, and market breadth to identify trend changes. Dow theory analyzes market averages to identify primary bull and bear markets through confirmation between averages. Charts like line charts, bar charts, and point and figure charts along with common patterns like triangles, head and shoulders, and rectangles are used to identify trends and signals.