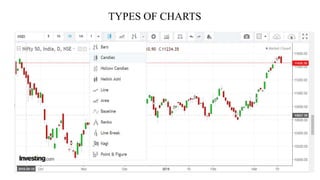
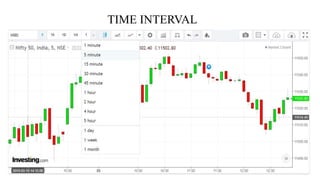
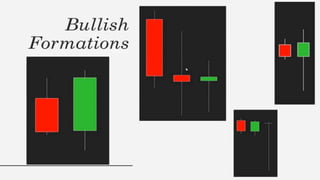
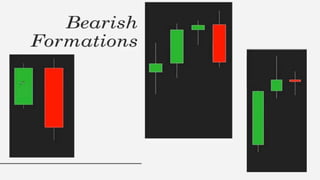
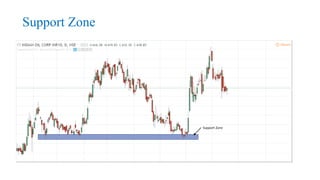
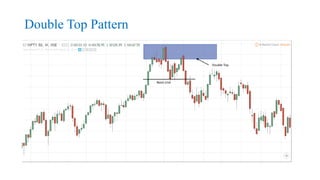
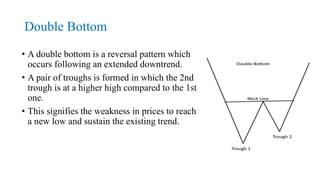
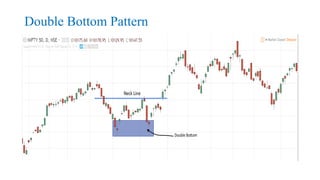
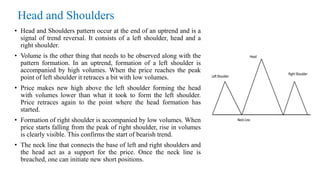
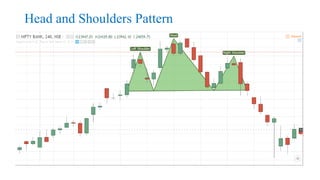
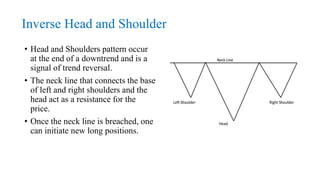
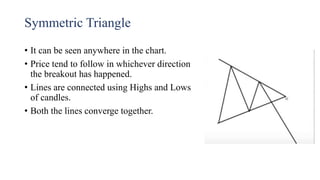
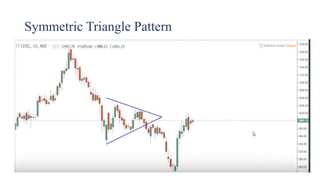
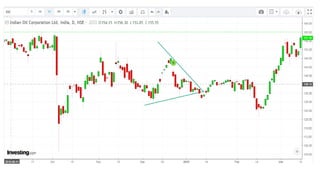
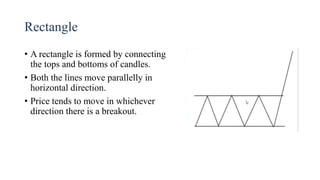
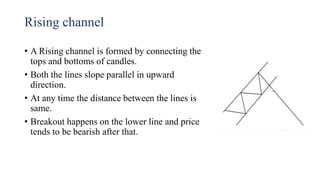
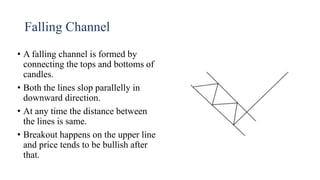
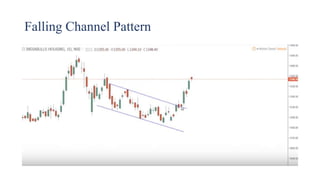
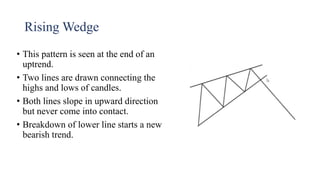
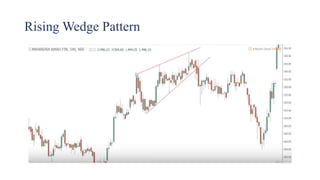
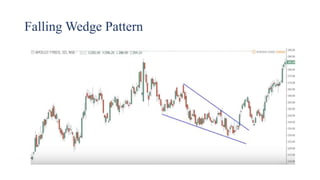
This document discusses stock charts and chart patterns. It begins by defining different types of stock charts, including line charts, bar charts, and candlestick charts. It then explains common chart patterns such as double tops and bottoms, head and shoulders, triangles, channels, and wedges. Key aspects of these patterns like support and resistance zones are described. The document provides examples of each pattern and discusses how technical analysts use patterns to potentially predict future price movements and identify reversal signals.