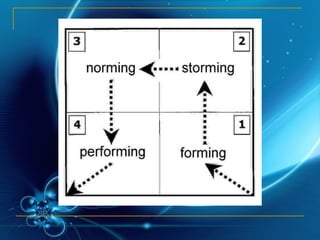
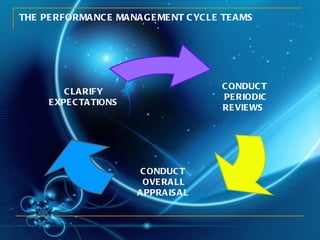
The document discusses different aspects of team knowledge and management. It defines teams and different types of teams. It discusses how job characteristics like skill variety and autonomy can impact employee satisfaction and productivity. It also outlines the developmental stages teams go through. It provides guidance on managing team meetings, problem solving, performance reviews, and leadership. The document suggests applying this knowledge at Nestle's Kejayan factory through interviews, observation, assessment, documentation, learning, and doing.