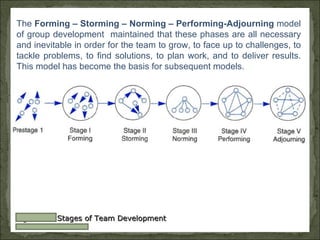
The document discusses techniques for effective team management, including understanding team dynamics, building trust and collaboration among team members, and establishing clear goals and roles. It emphasizes the importance of communication, problem solving, and adapting to change as a team. Barriers to effective team building like unclear objectives or lack of role definition are also outlined.