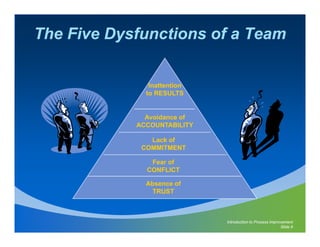
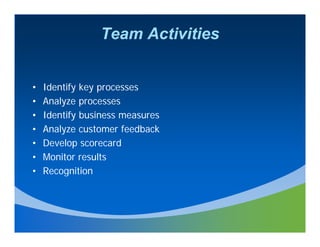
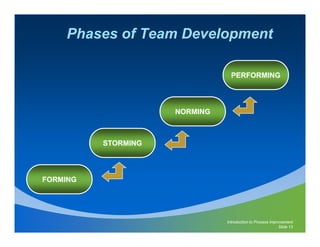
This document discusses team dynamics and process improvement. It provides information on forming effective teams, including defining roles and responsibilities, developing a balanced scorecard, and giving regular feedback and recognition. The document outlines different types of team lifecycles and functions. It also discusses factors for team success, such as being results-oriented and customer-focused. Common questions that arise during team formation are presented. Guidance is provided on facilitation skills to effectively lead team meetings and discussions.