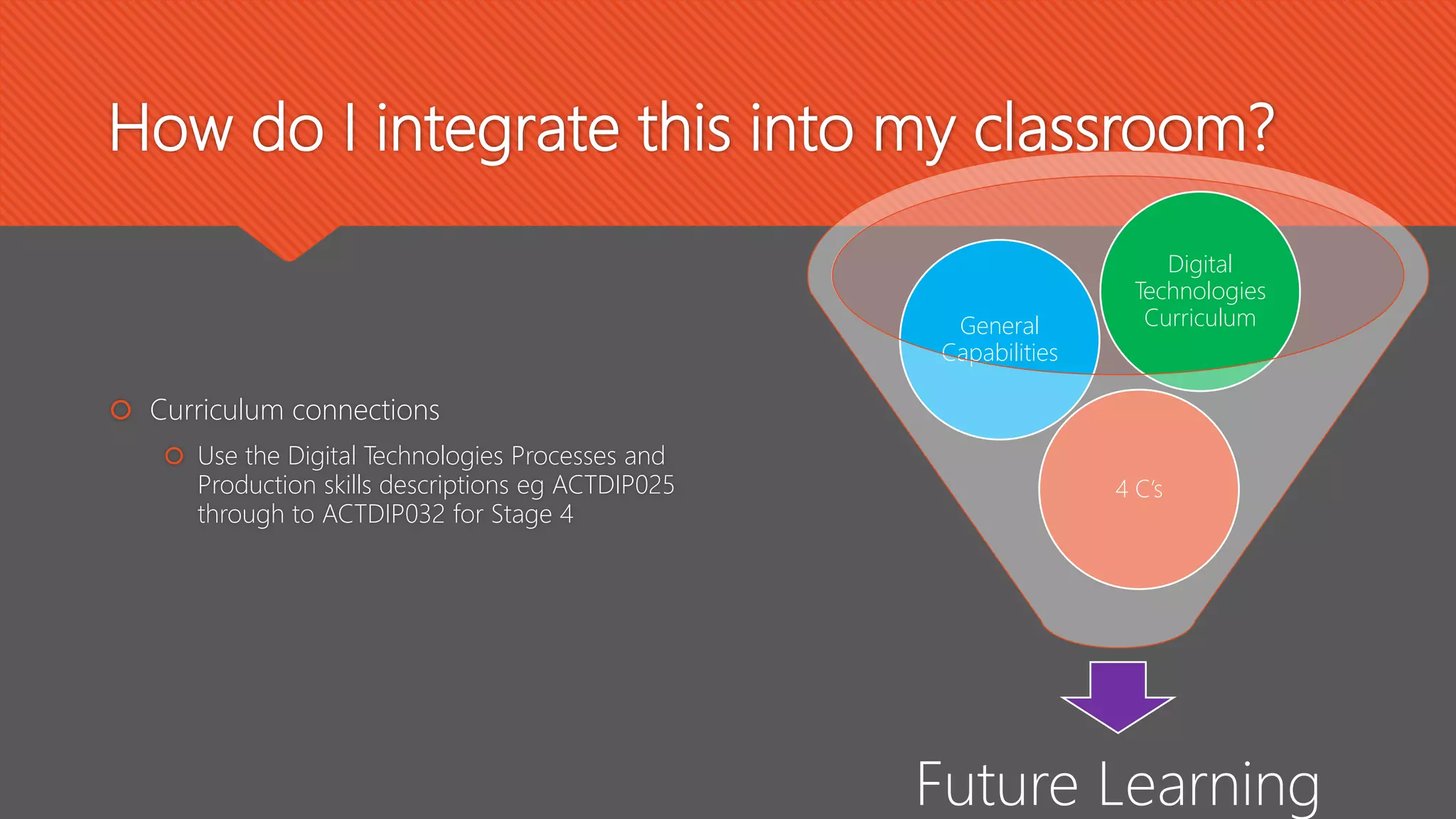
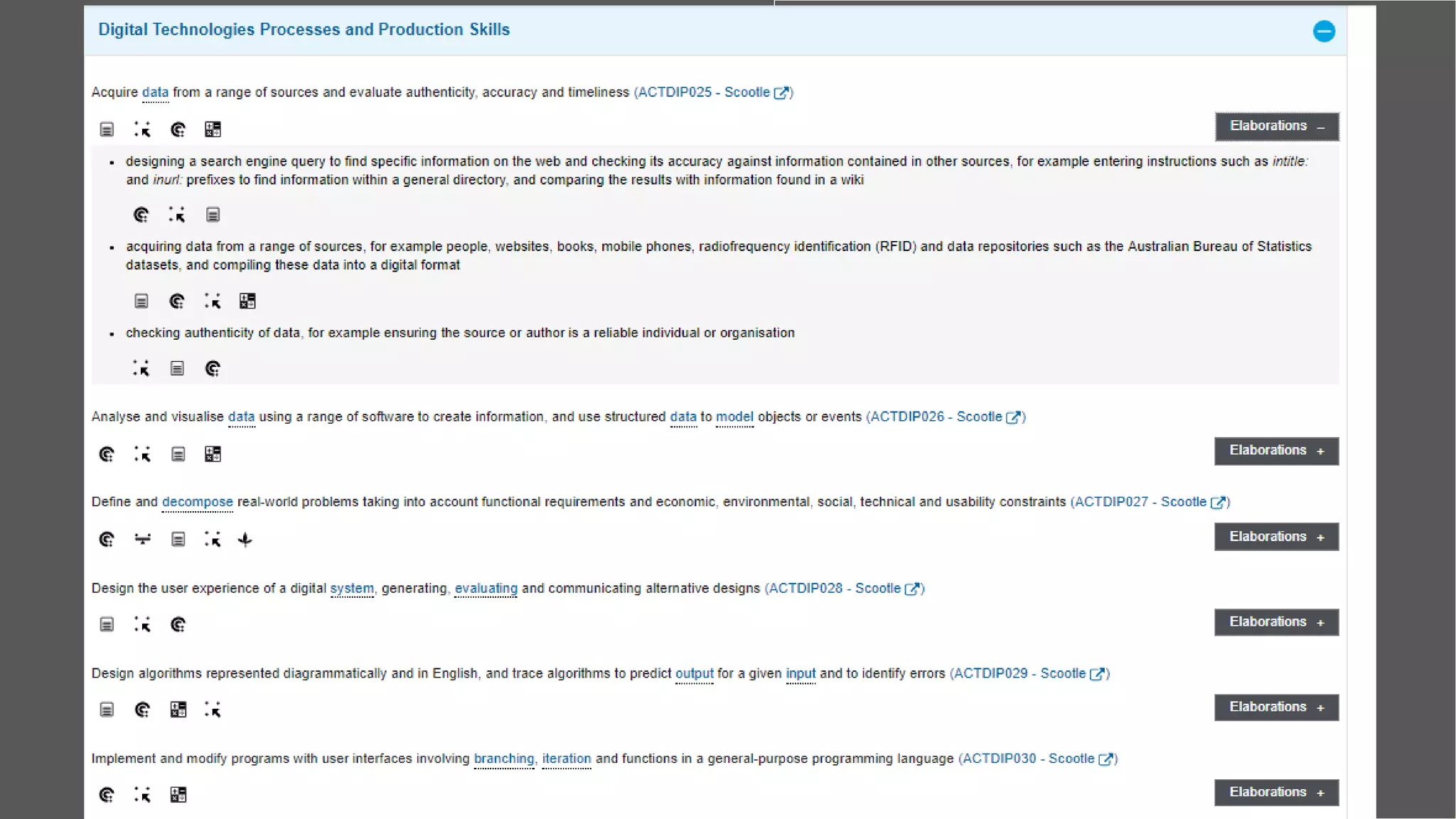
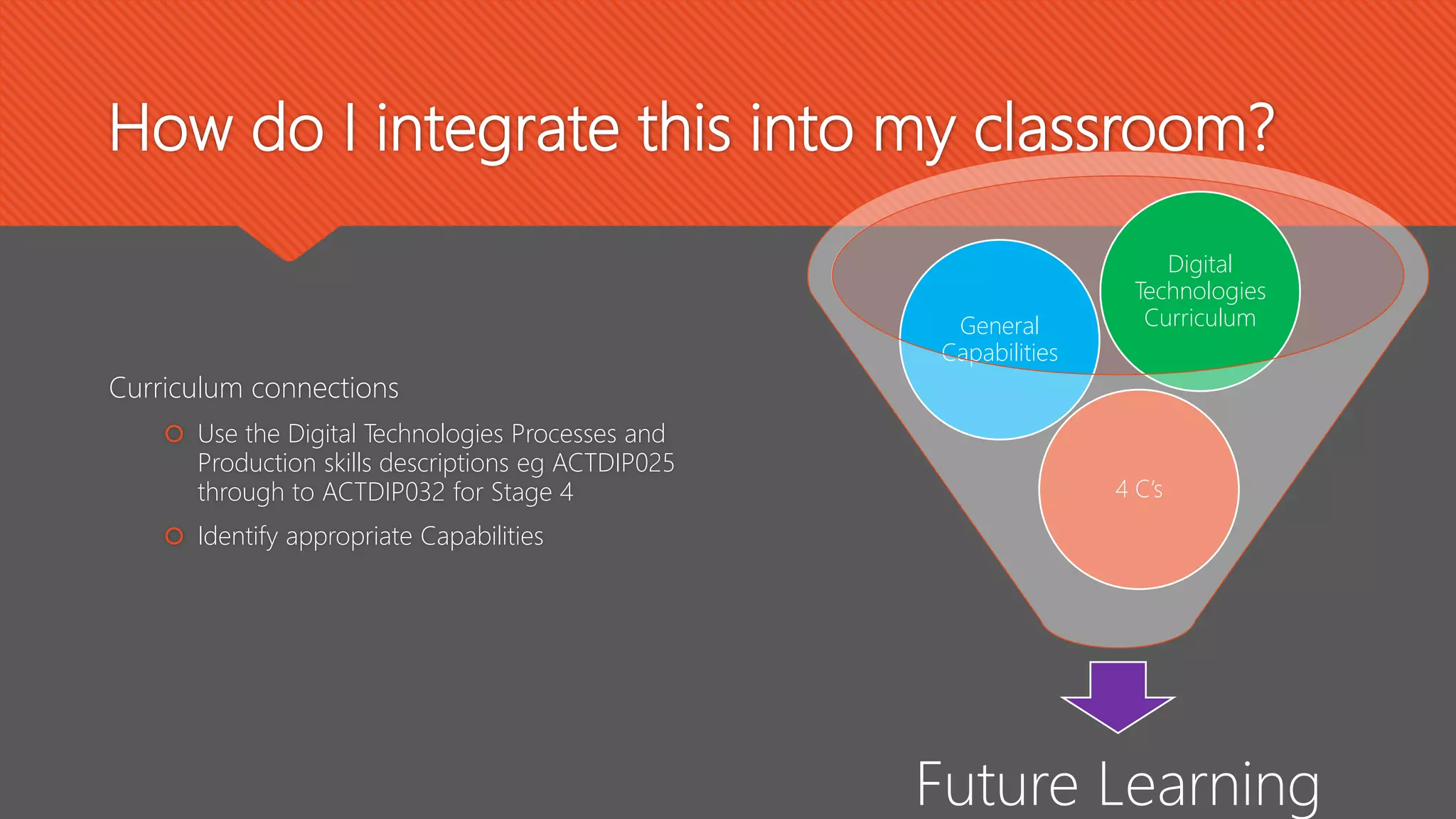
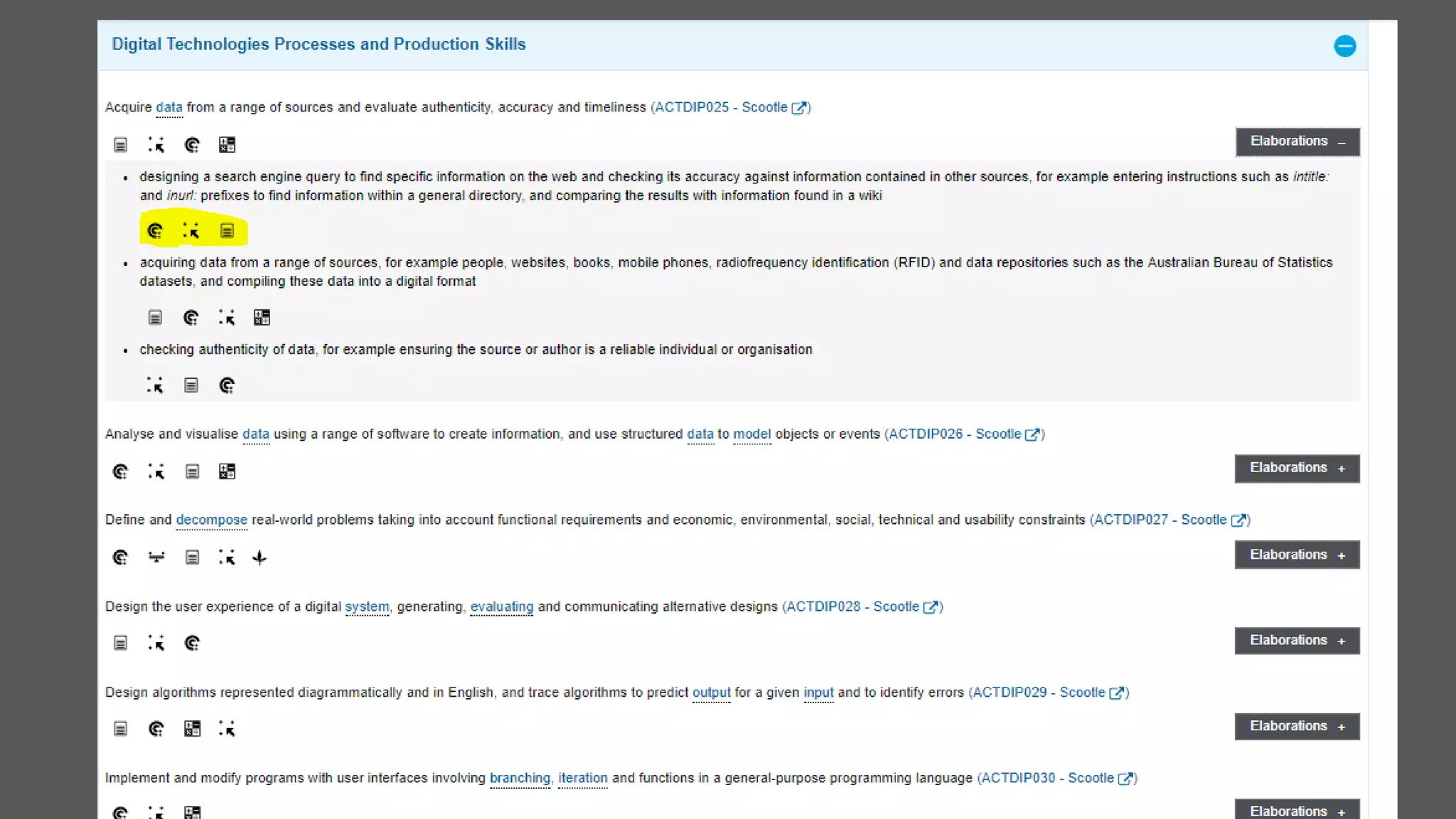
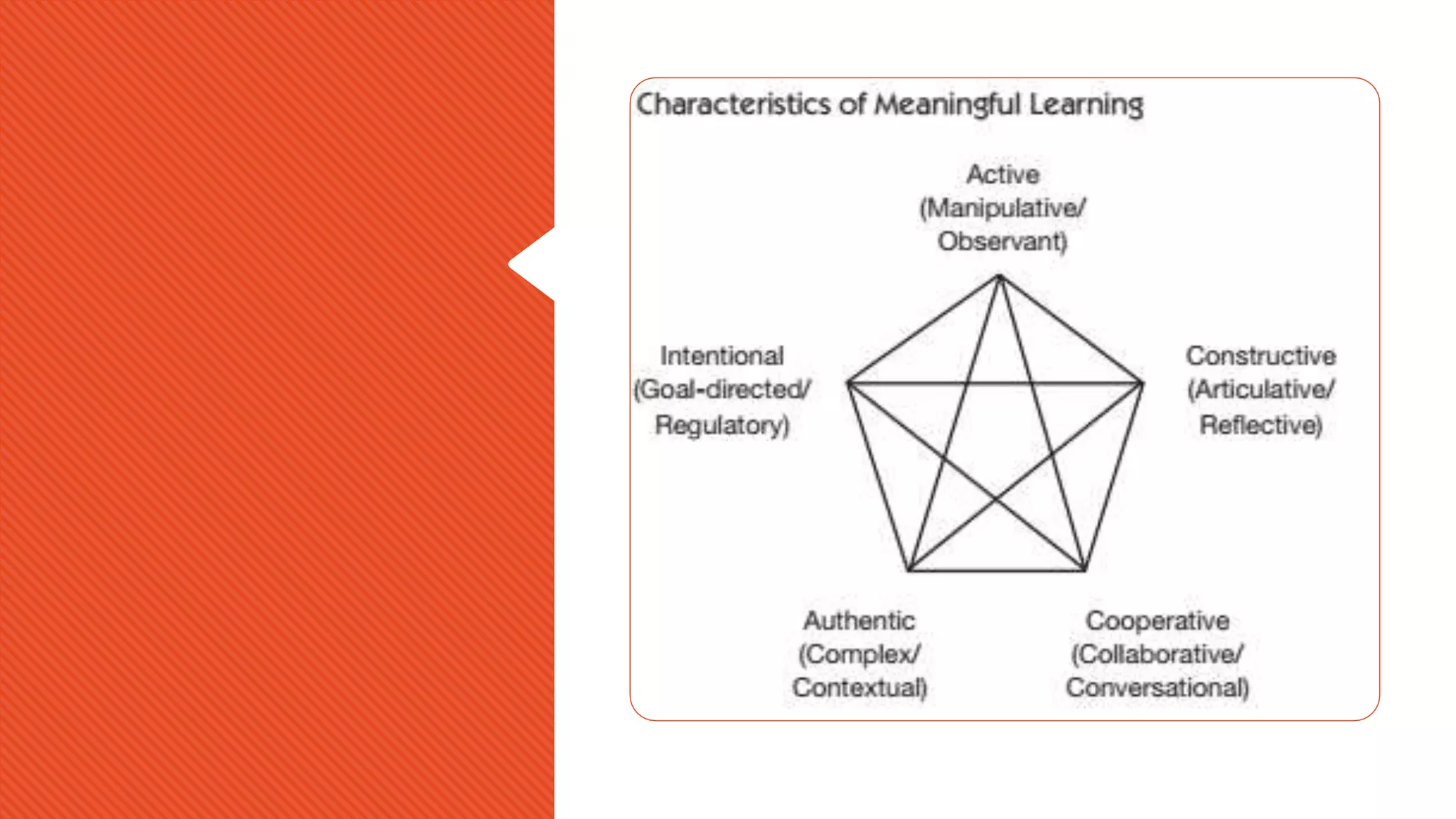
The document outlines effective teaching strategies for enhancing digital literacy in students, emphasizing the importance of core digital skills such as managing information, communication, research, problem-solving, and creation. It provides a structured approach to integrating digital technologies into the classroom, suggesting various activities and assessments tailored to both primary and secondary students. Additionally, it highlights the significance of using appropriate digital tools and fostering an inquiry-based learning environment.