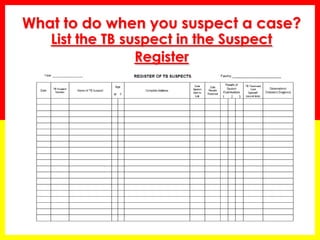
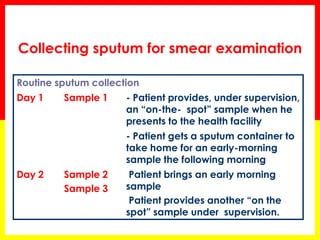
1. The document provides guidance on identifying and managing tuberculosis (TB) suspects, including symptoms that should raise suspicion of TB and procedures for collecting and examining sputum samples.
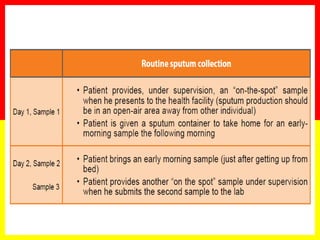
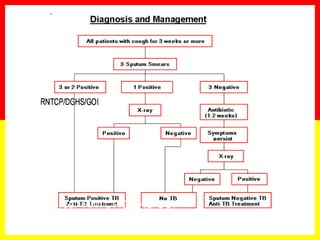
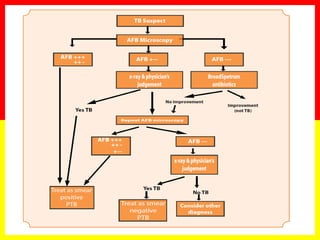
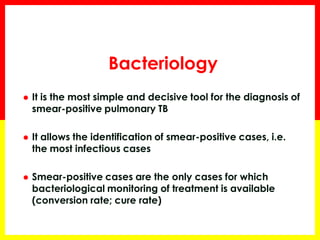
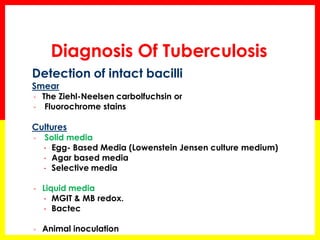
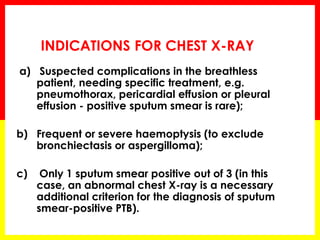
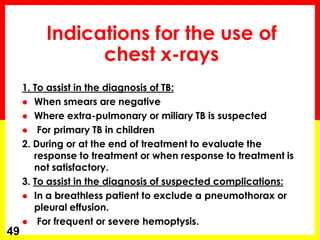
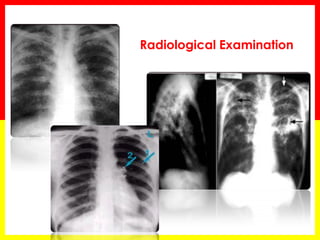
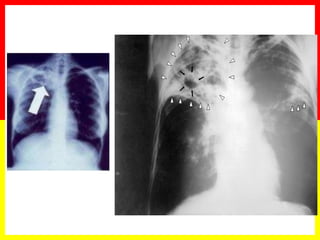
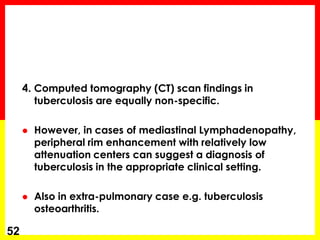
2. Sputum smear microscopy is the primary tool for diagnosing pulmonary TB, allowing identification of infectious cases. Sputum culture and chest x-rays can also assist with diagnosis when smears are negative or extrapulmonary TB is suspected.
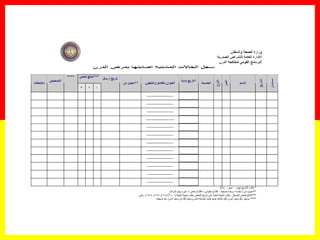
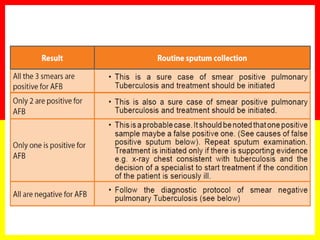
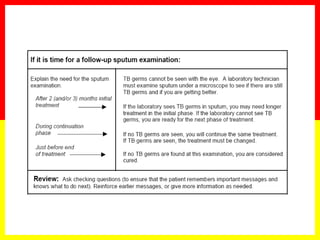
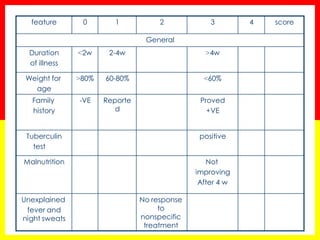
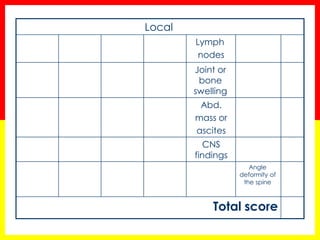
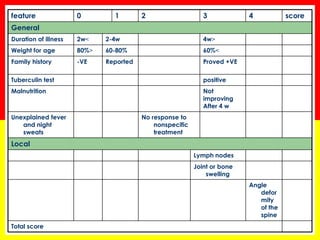
3. Positive TB diagnosis requires identification of acid-fast bacilli in sputum samples through microscopy or culture. Sputum results should be recorded and suspects followed up accordingly.