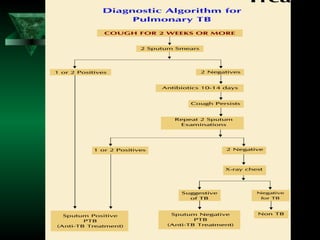
This document outlines guidelines for identifying and diagnosing tuberculosis patients. It describes that undiagnosed pulmonary tuberculosis cases are the main source of infection in communities. The key diagnostic tools discussed are sputum microscopy, x-rays, tuberculin tests, and mycobacterium tuberculosis culture. It provides details on the process of diagnosing tuberculosis using sputum examination at designated microscopy centers, including collecting two sputum samples from patients over two days.

![TOOLS FOR DIAGNOSIS
Sputum microscopy [key diagnostic tool of RNTCP]
– Simple, not expensive, requires minimum training.
– Specific with minimum inter-reader variation.
– Used for diagnosis, monitoring & defining cure.
– Can be done at the Peripheral Health Institutions.
– Correlates with infectivity in undiagnosed Pulmonary TB cases.
X-Ray
– Supportive to microscopy.
– High inter-reader variation.
– No shadow is typical for TB.
– 10-15 % of culture positive cases remain undiagnosed.
Tuberculin test
– May be useful as additional tool for diagnosing Pediatric TB.
Culture of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
– Very sensitive and specific.
– Expensive, requires a specialized laboratory.
– Results are available after a several weeks.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ensuringidentificationoftuberculosissuspects-160923165928/85/Ensuring-identification-of-tuberculosis-suspects-3-320.jpg)