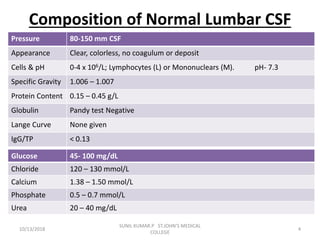
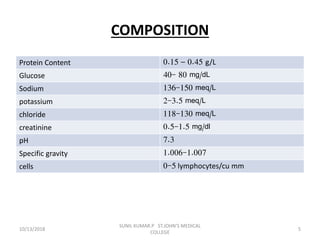
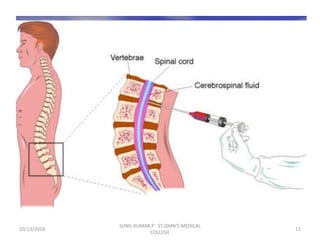
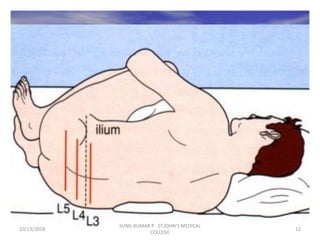
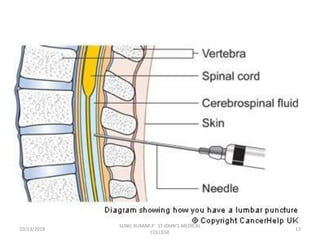
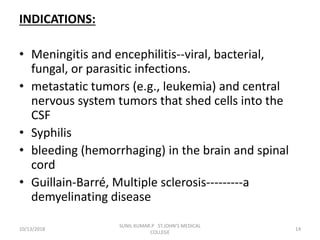
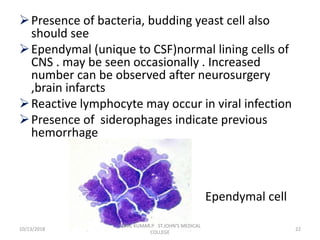
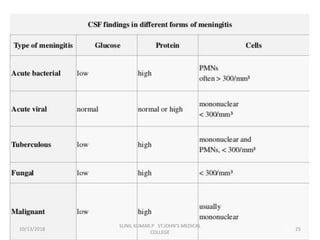
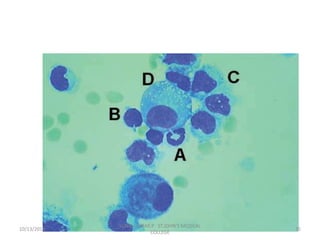
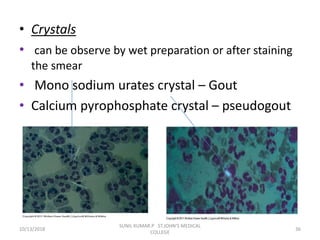
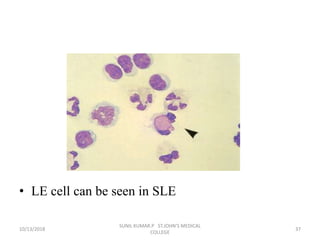
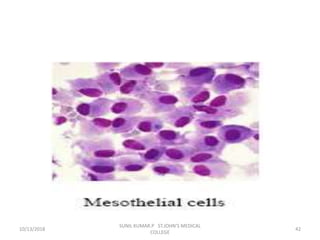
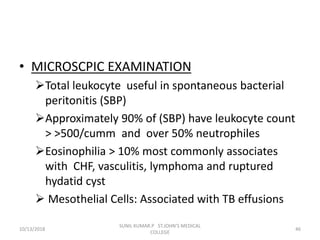
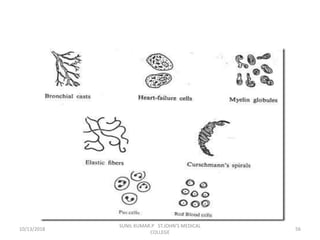
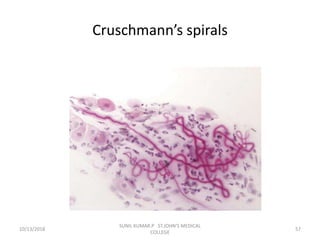
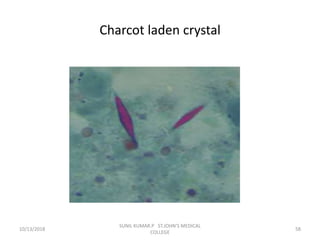
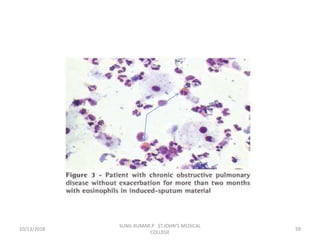
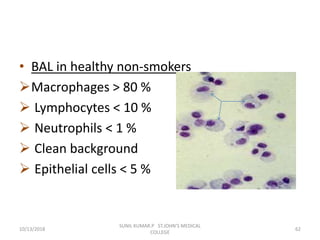
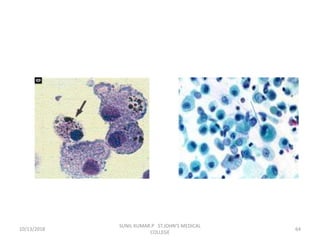
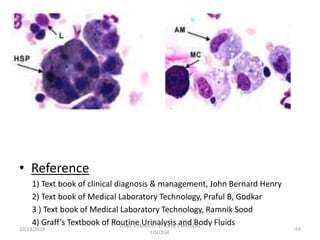
This document discusses various body fluids that can be analyzed, including cerebrospinal fluid, synovial fluid, and pleural fluid. It provides details on the composition of normal cerebrospinal fluid and synovial fluid. The document describes how to collect cerebrospinal fluid via lumbar puncture and synovial fluid via arthrocentesis. It also outlines the physical, microscopic, and chemical examinations that can be performed on these fluids to analyze cells, proteins, glucose, and other components.