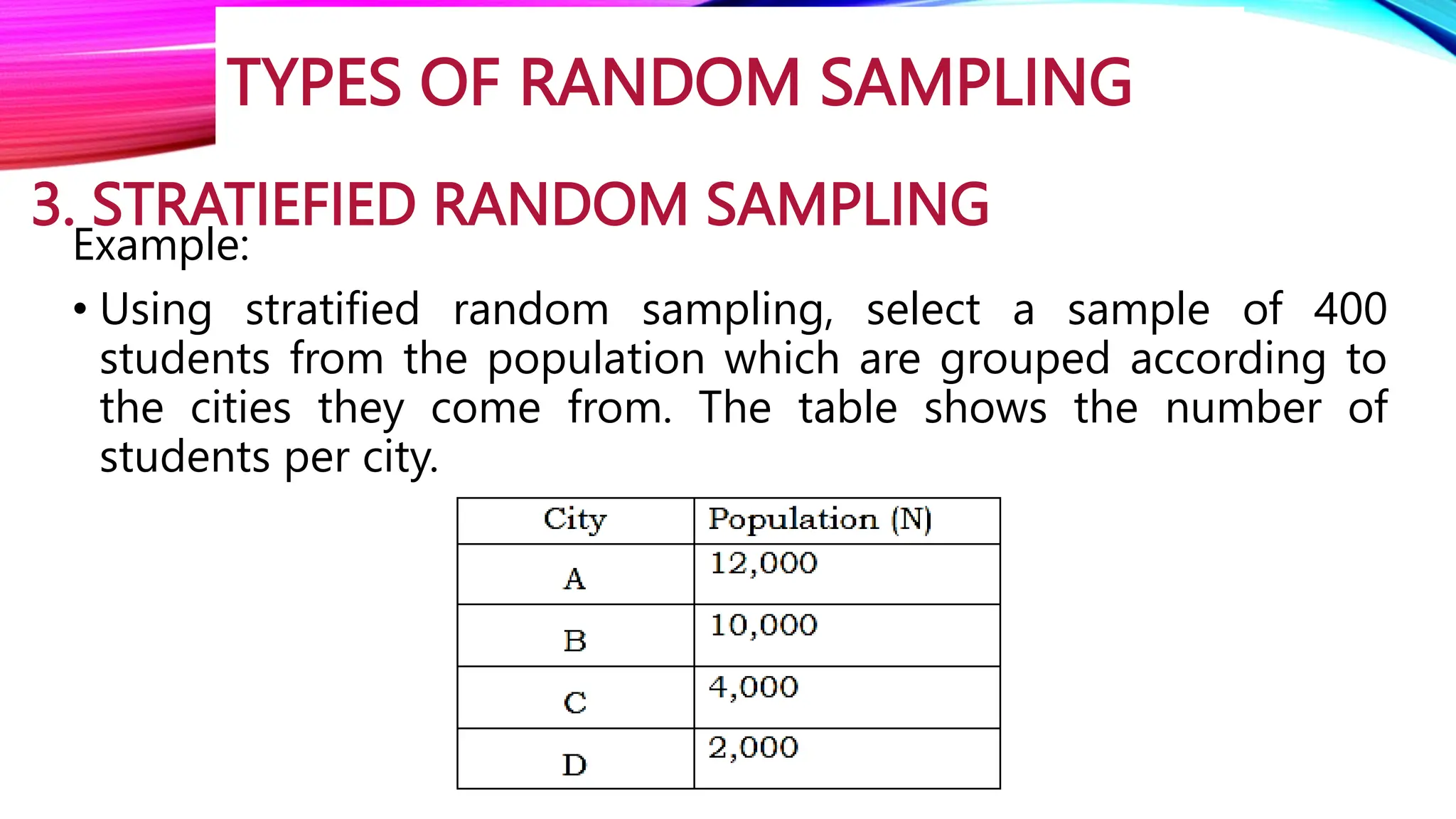
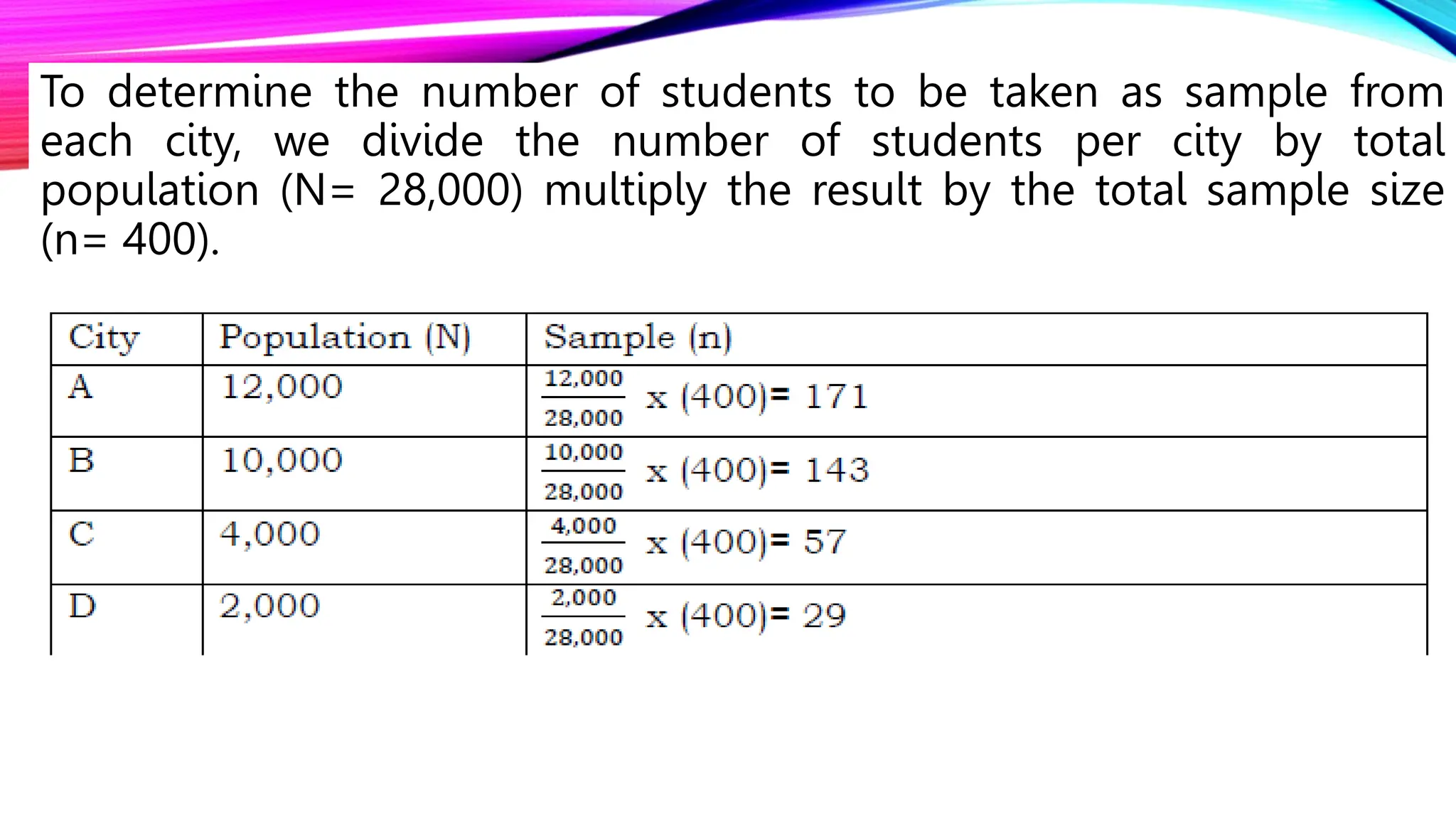
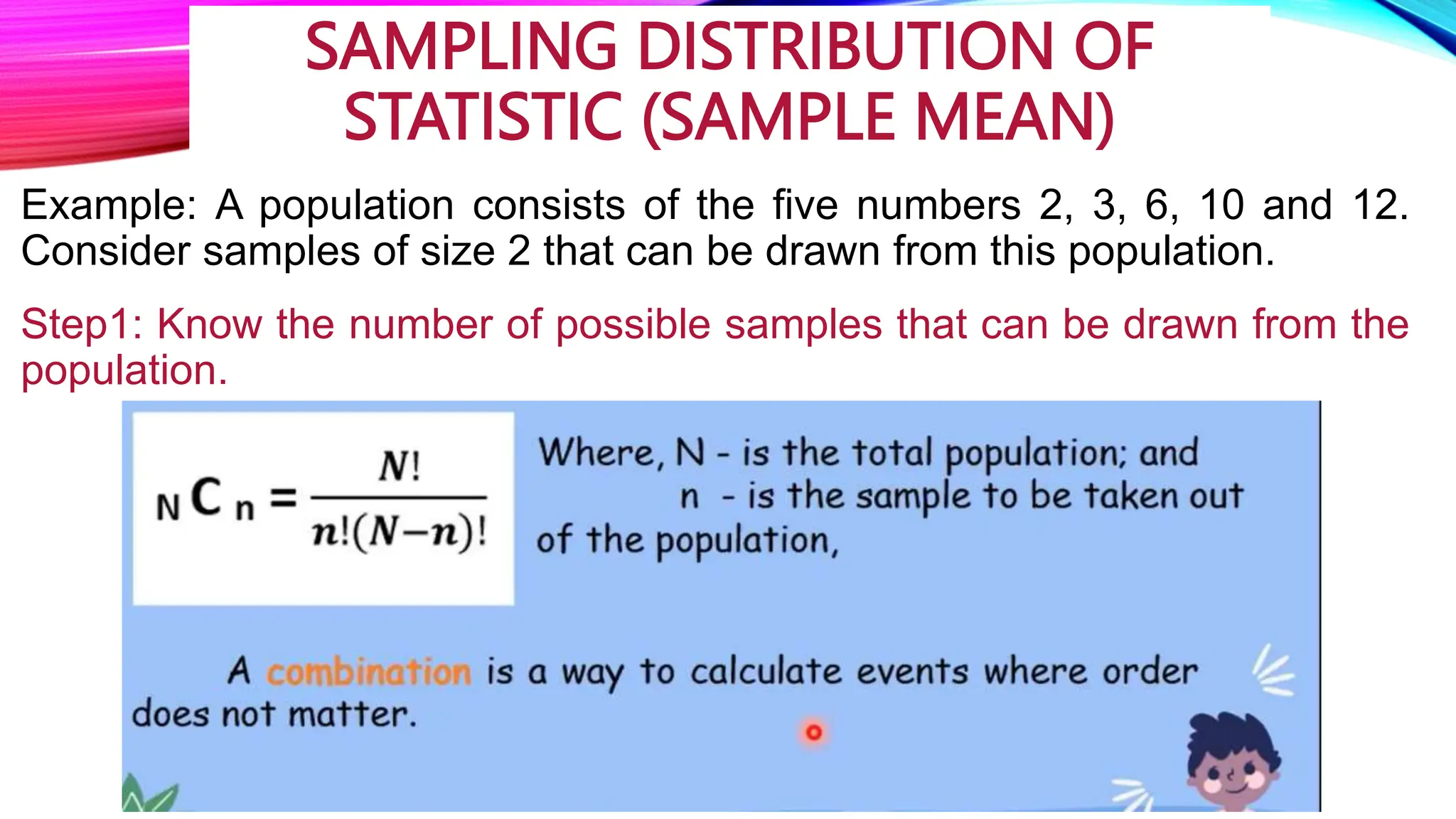
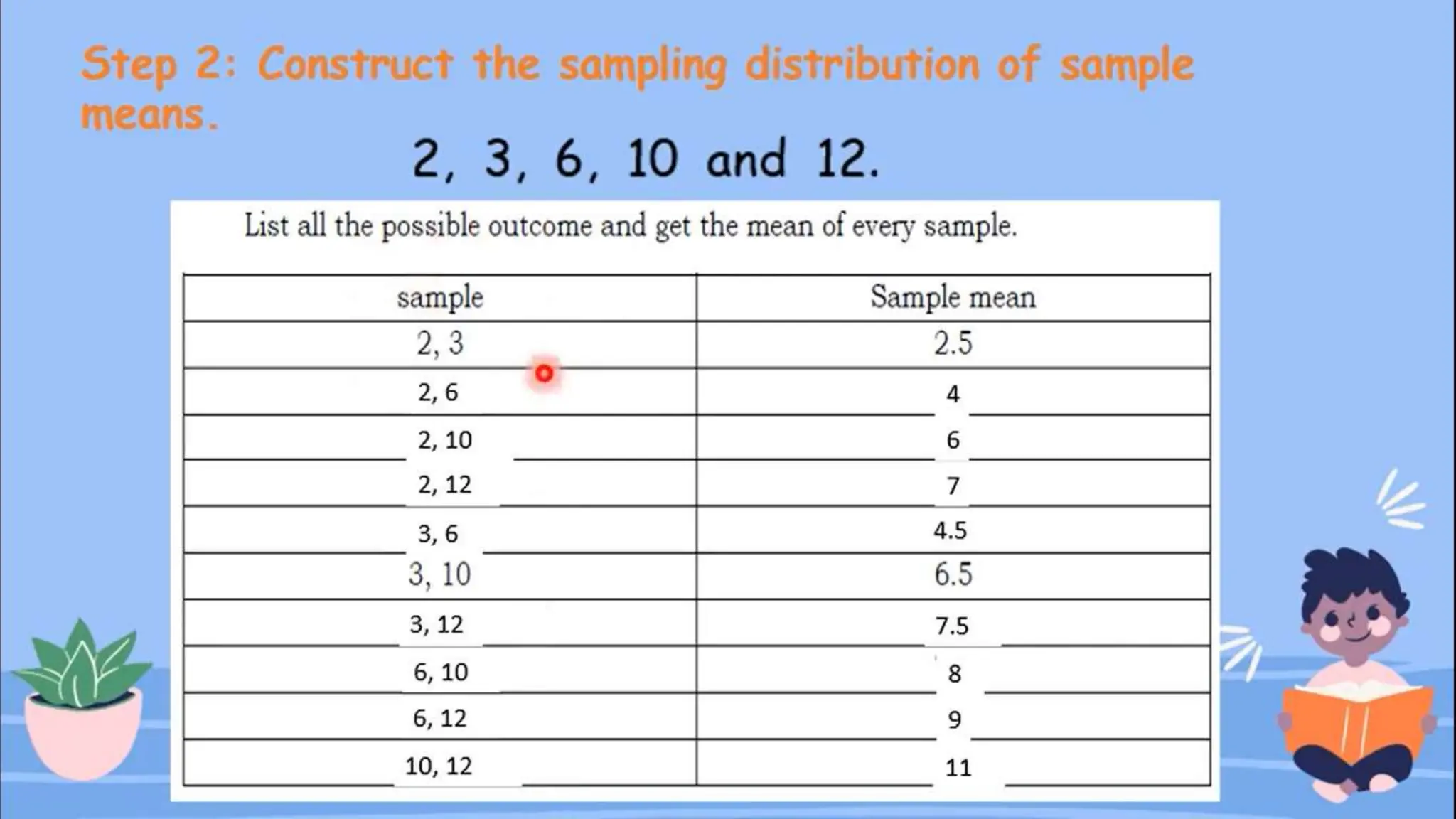
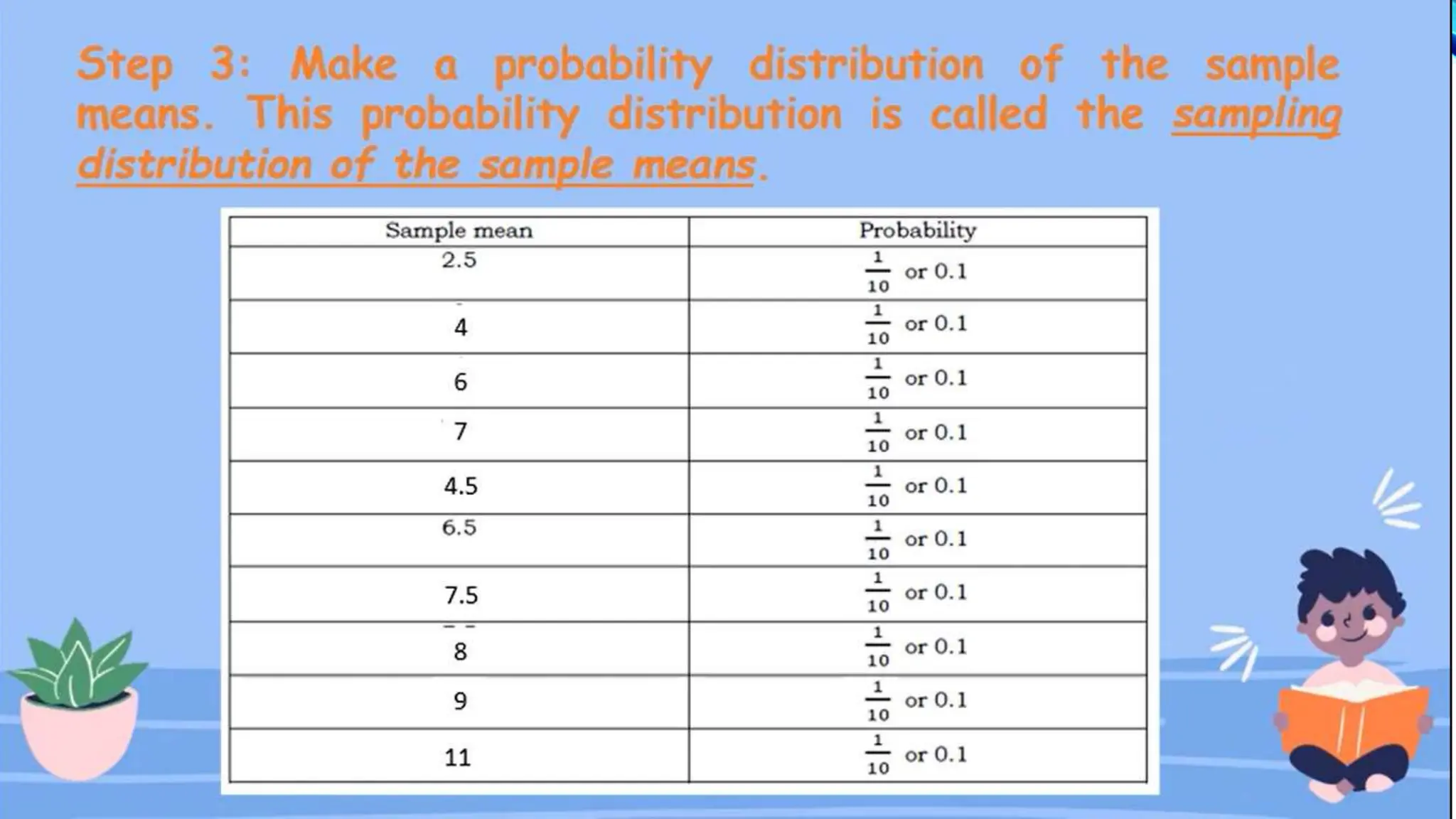
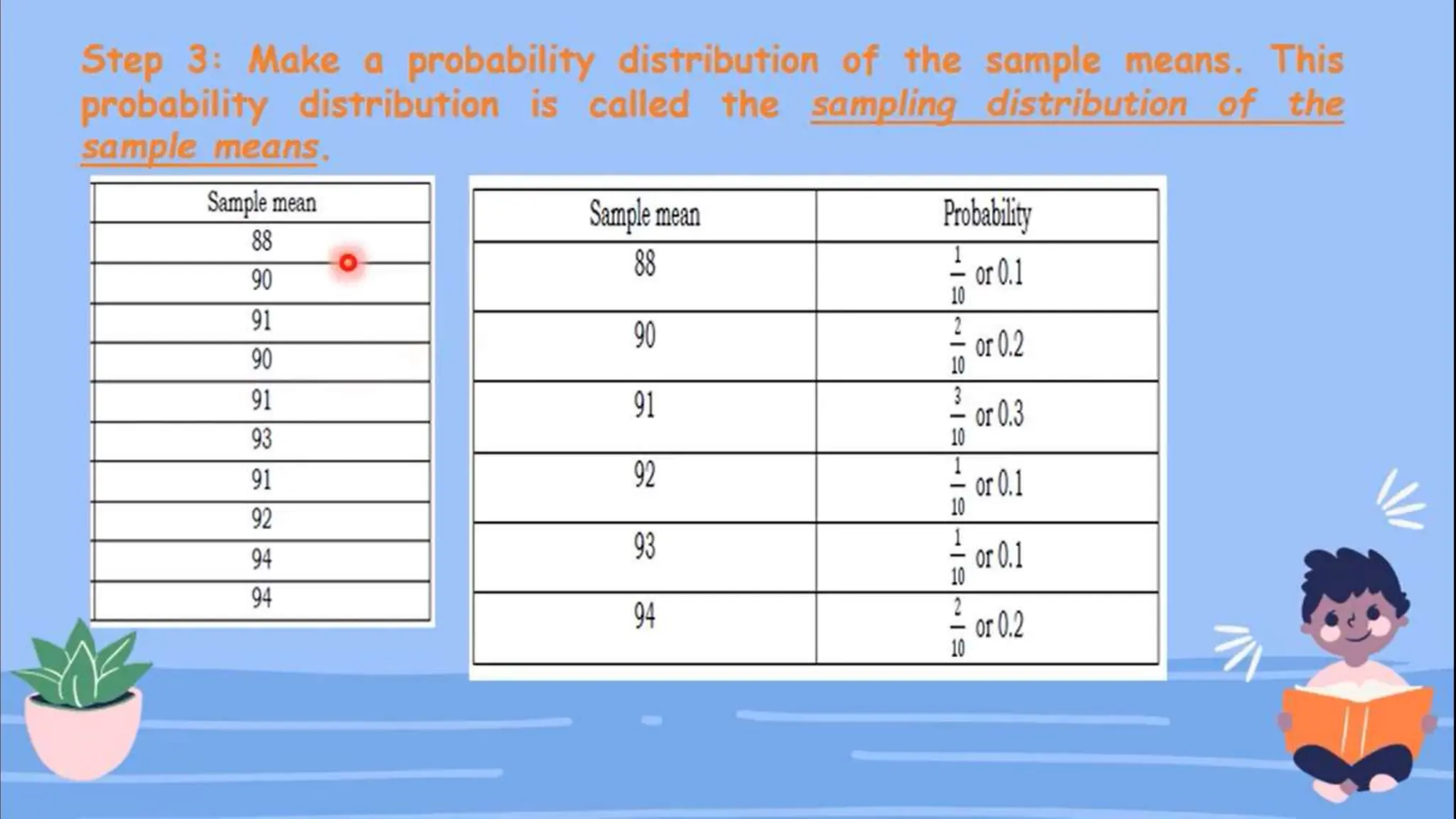
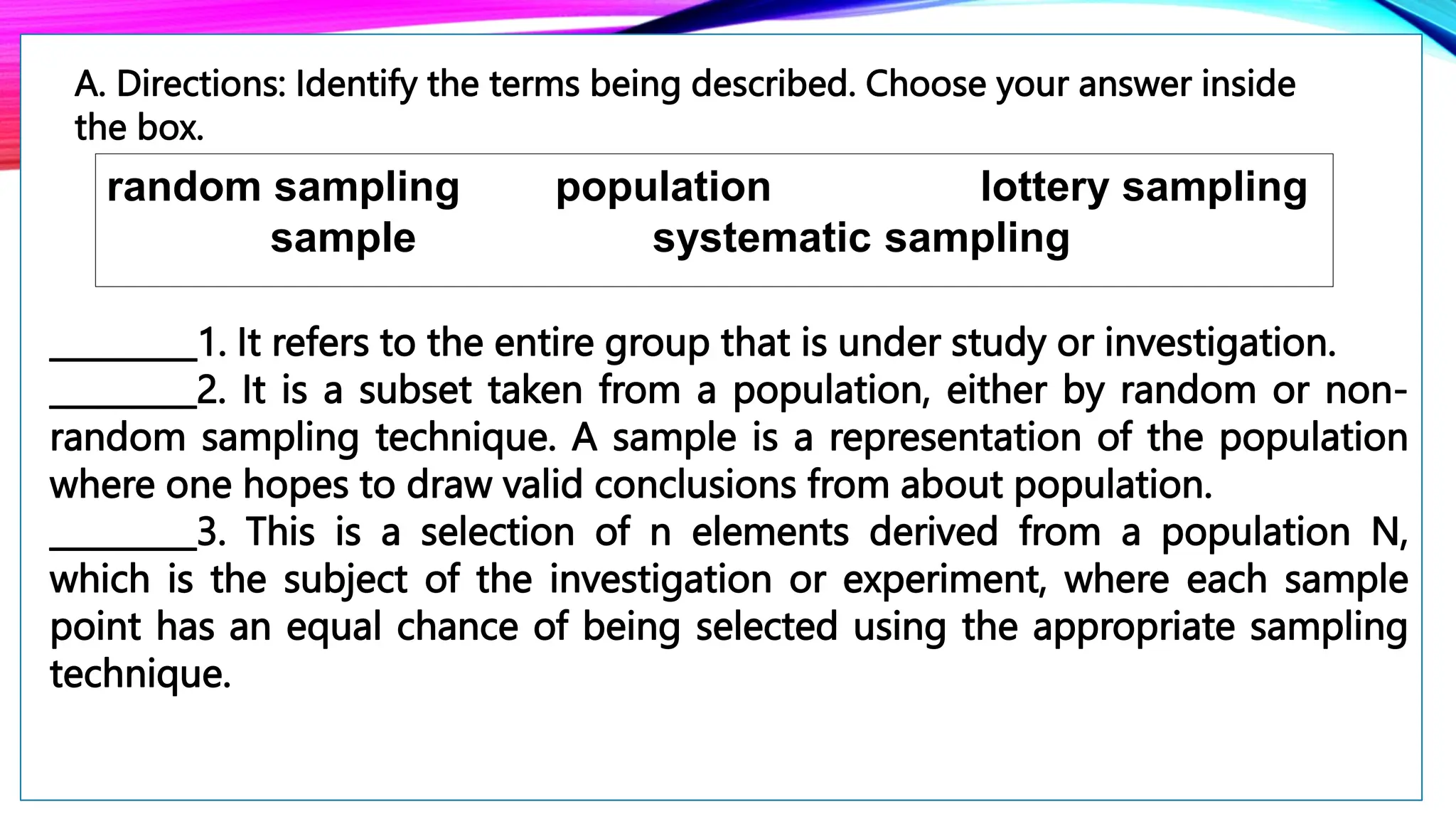
The document discusses the concept of sampling in research, distinguishing between population and sample, and outlining various random sampling techniques such as lottery, systematic, stratified, cluster, and multi-stage sampling. It explains the importance of parameters and statistics, emphasizing their roles in representing population characteristics and drawing conclusions from sample data. Additionally, it provides examples of how to implement these sampling methods and the significance of understanding sampling distributions.