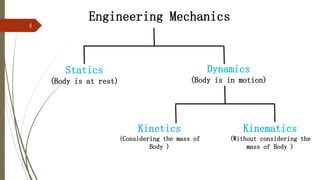
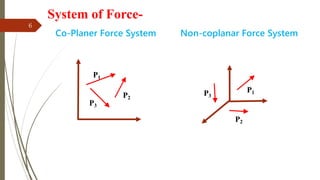
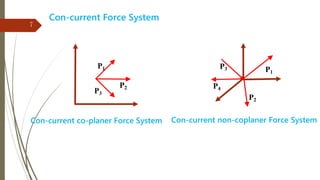
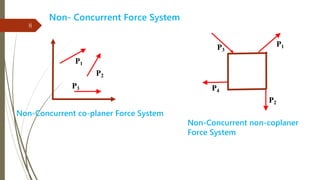
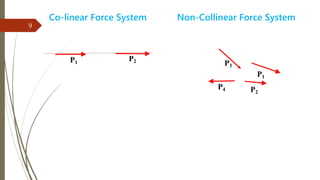
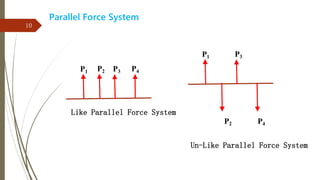
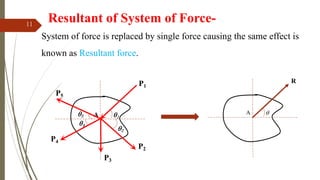
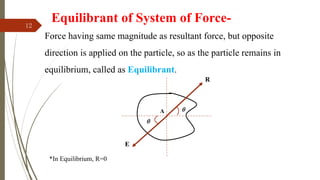
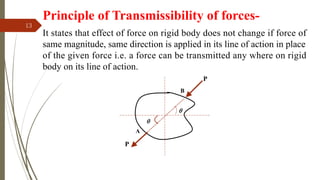
The document outlines a presentation on engineering mechanics by Miss Shinde Bharti M., detailing core concepts such as systems of forces, moments, and resultant forces. Key terms such as particle, rigid body, scalar, and vector quantities are defined, along with distinctions between dynamics, statics, kinetics, and kinematics. It also explains the principle of transmissibility of forces and various methods to find the resultant of force systems.