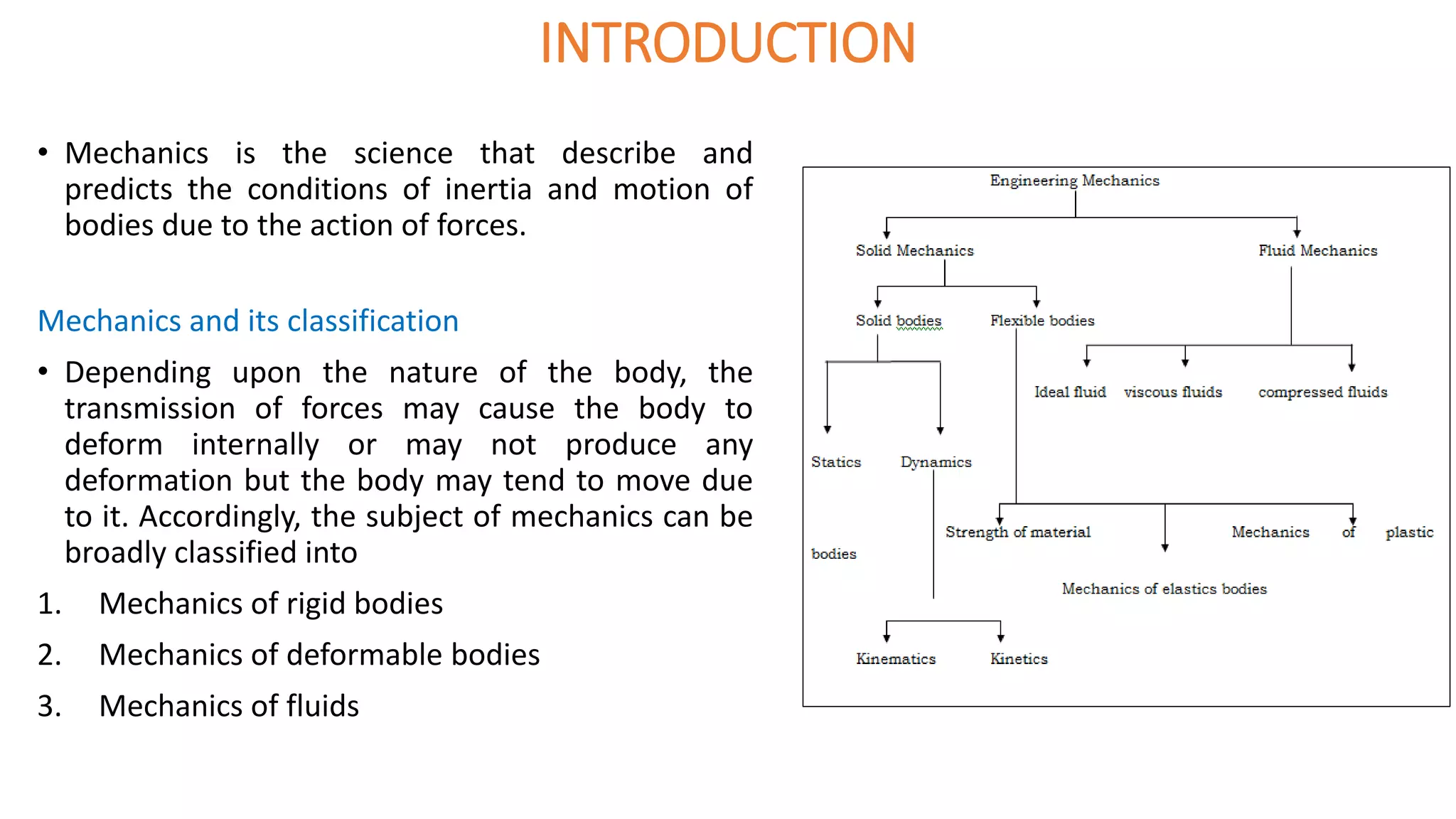
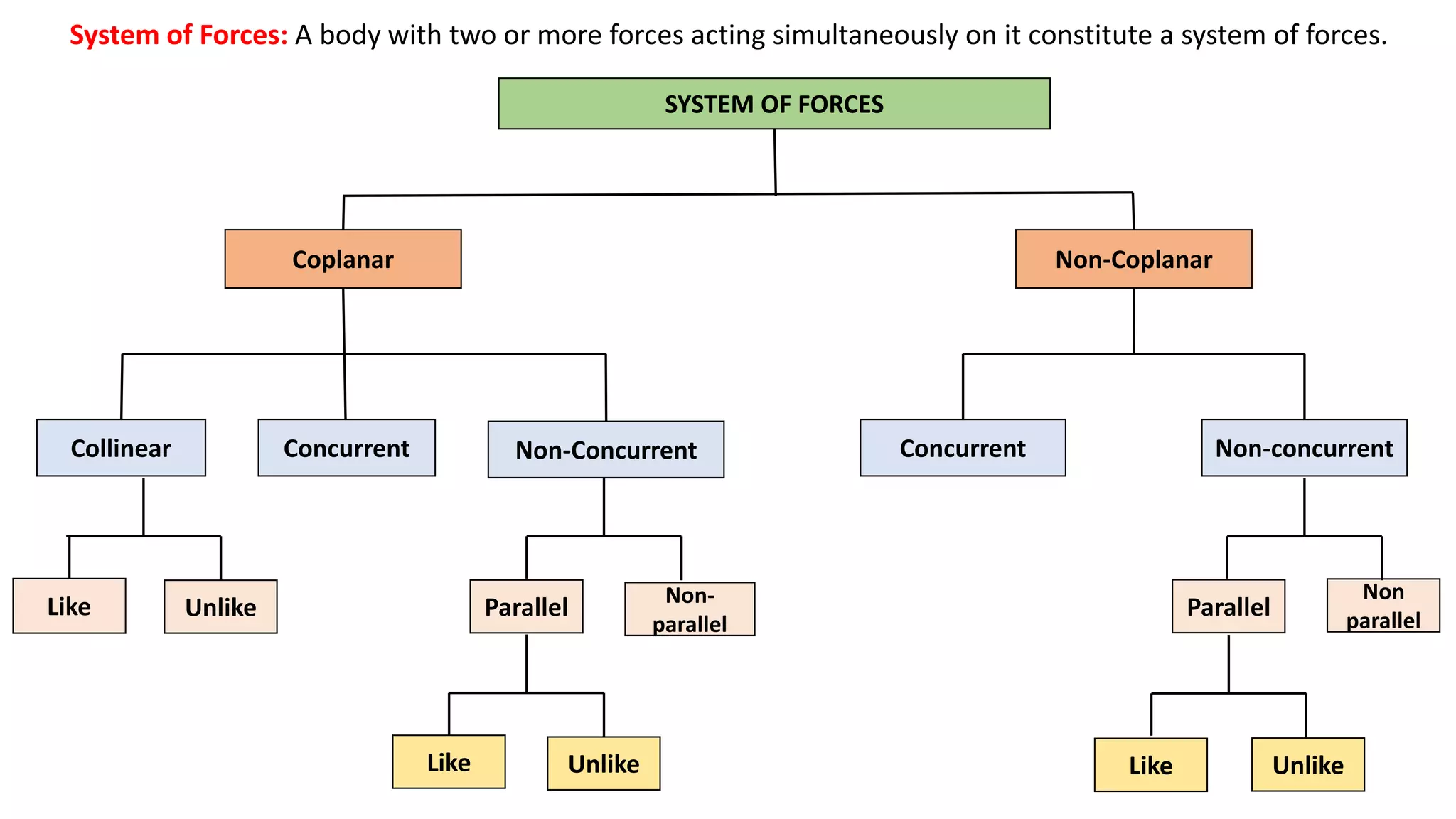
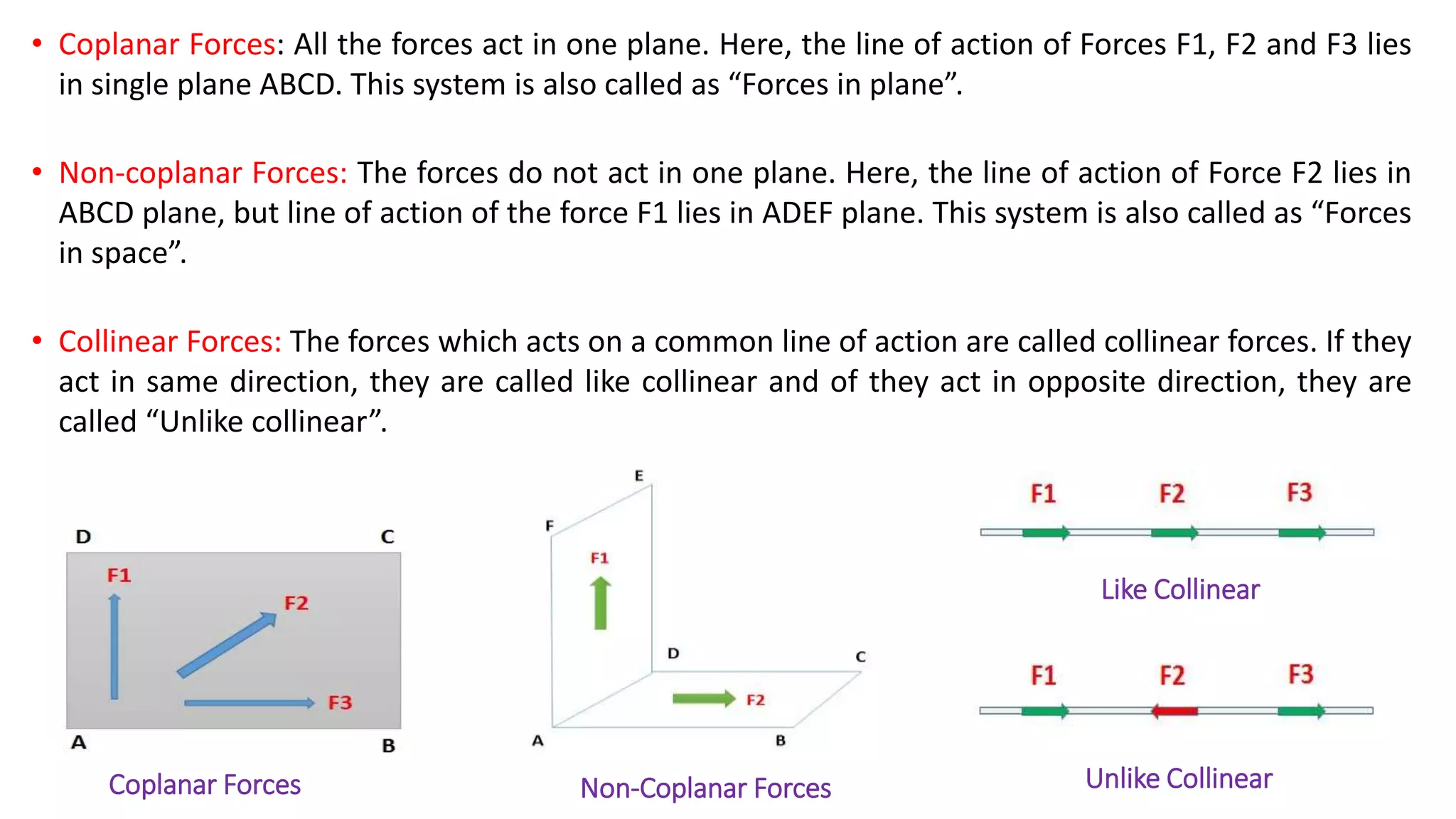
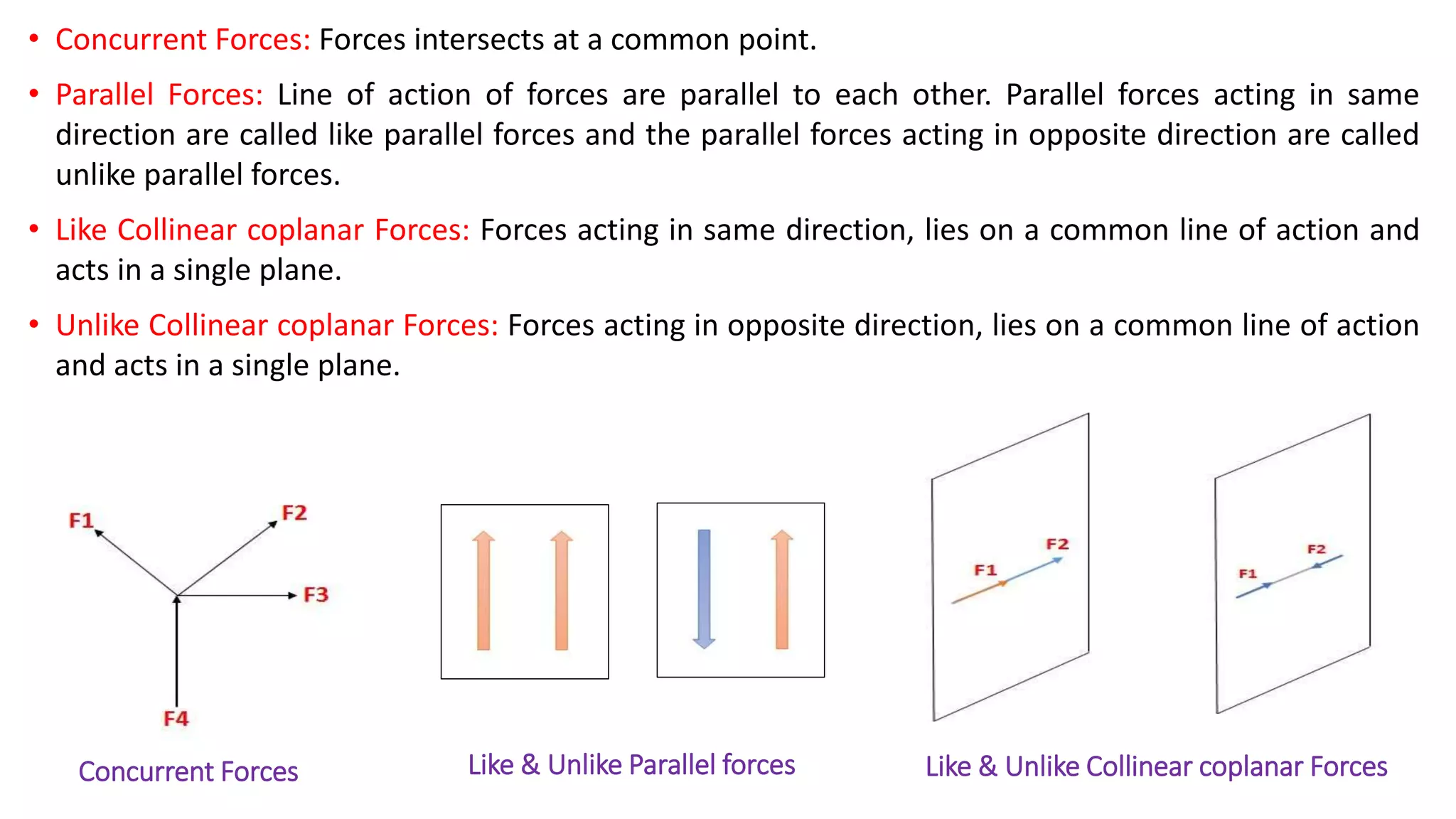
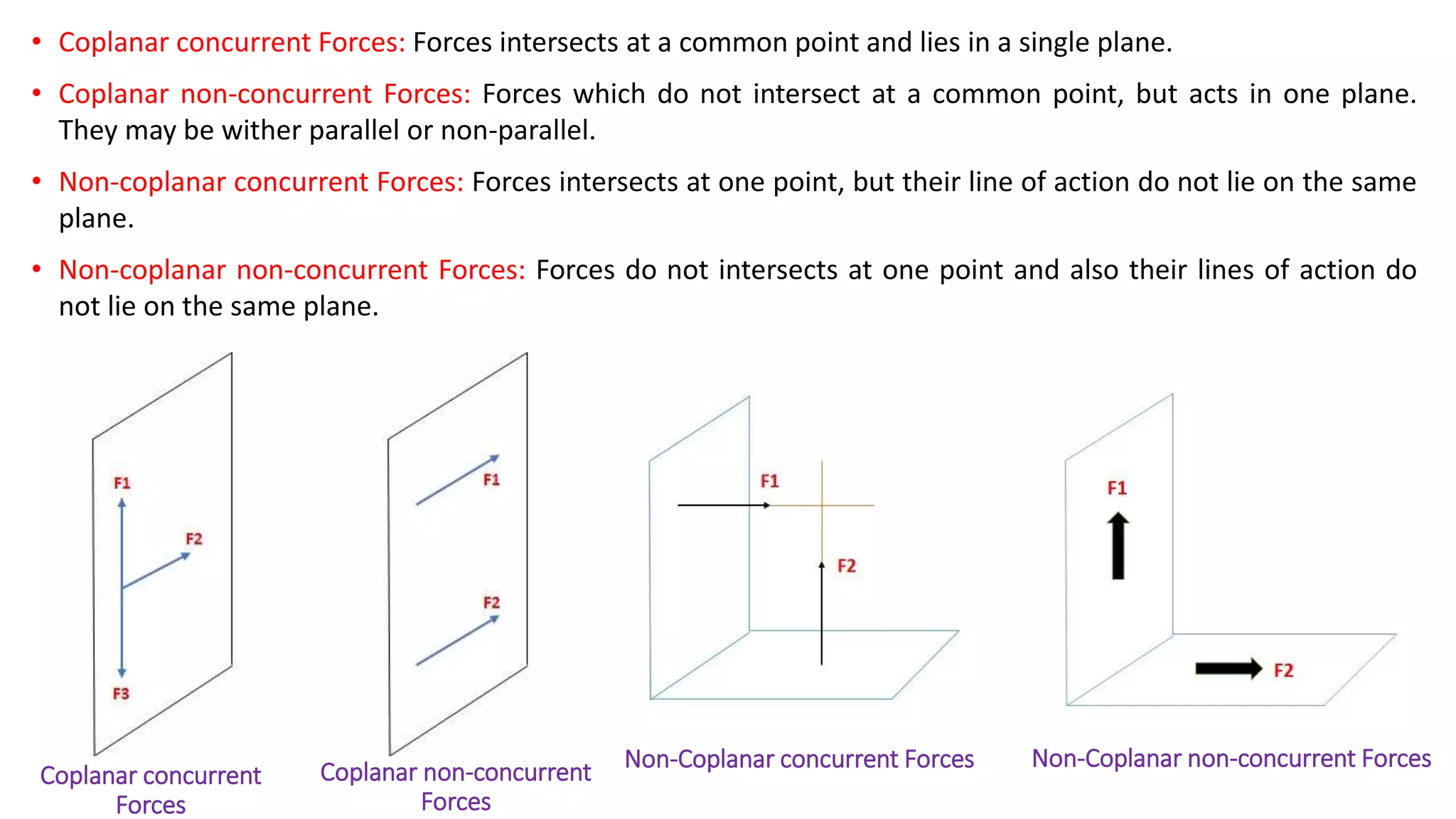
The document discusses systems of forces acting on a body. It defines different types of force systems including coplanar forces that act in the same plane, and non-coplanar forces whose lines of action are not in the same plane. Within these categories, forces can be further classified as collinear if they act along the same line, concurrent if they intersect at a single point, parallel if their lines of action are parallel, and like or unlike based on direction. Examples are provided of different force system configurations such as concurrent coplanar forces intersecting in a plane, and non-concurrent non-coplanar forces that do not intersect and act in different planes.