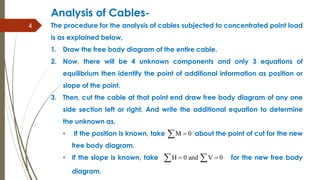
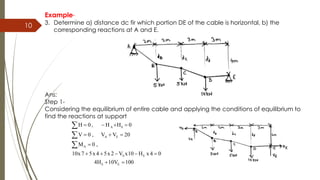
This document provides an overview of cables and their analysis. It defines cables as flexible members that can only withstand tension. It lists some common engineering applications of cables. It then outlines the assumptions made in cable analysis, including that cables are flexible, have negligible self-weight, and experience only tension forces. The document explains the procedure for analyzing cables subjected to concentrated loads, including drawing free body diagrams, applying equilibrium equations, and determining tensions and reactions. It provides examples of solving for cable tensions, reactions, slope, and horizontal forces using this procedure.