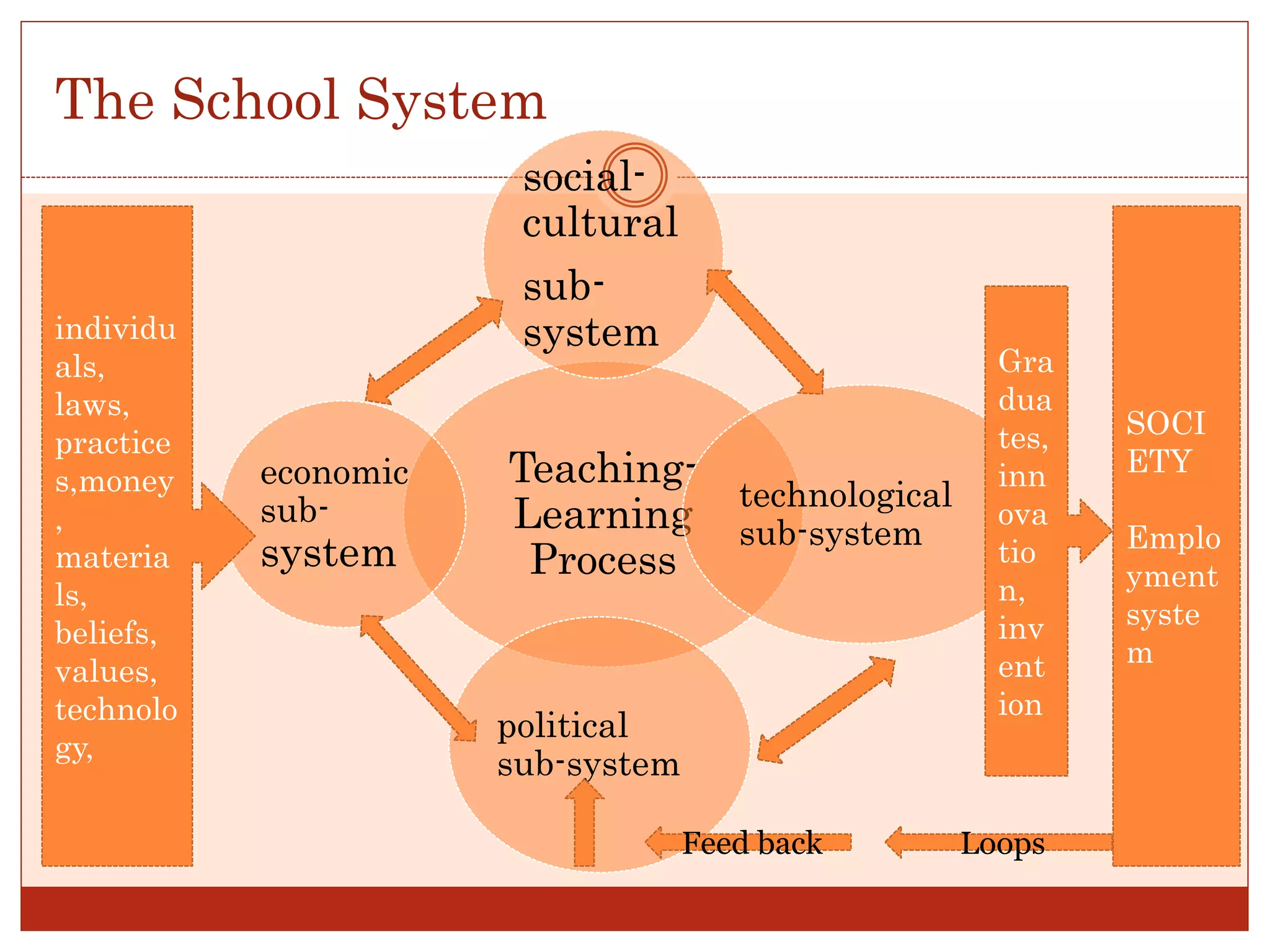
The systems approach views an organization holistically as a system of interrelated parts working together toward common goals. It considers how an organization interacts with and is influenced by its external environment. An organization is seen as an open system that acquires inputs from the environment, transforms them through internal processes, and produces outputs that feedback into the environment. The systems approach aims to understand how all parts of an organization depend on each other so the entire system can function effectively.