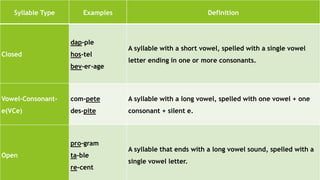
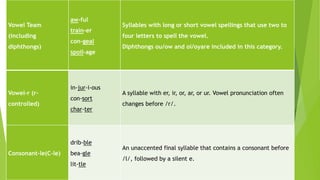
This document defines syllables and different types of syllables such as closed, vowel-consonant-e, open, vowel team, vowel-r, consonant-le, and leftovers. It also discusses types of words according to number of syllables like monosyllabic, disyllabic, trisyllabic, and polysyllabic words. Additionally, it covers topics like stress (emphatic, contrastive, tonic, new information, word, and sentence stress), patterns of stress in syllables (monosyllabic, disyllabic, and multi/polysyllabic words), and degrees of stress (primary, secondary, tertiary, and quatern