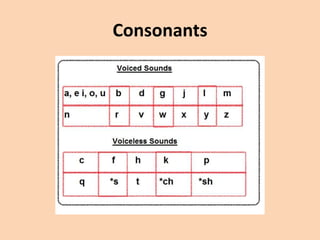
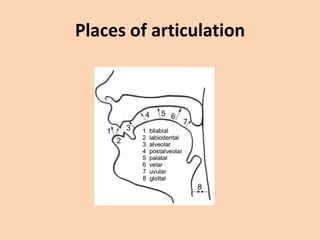
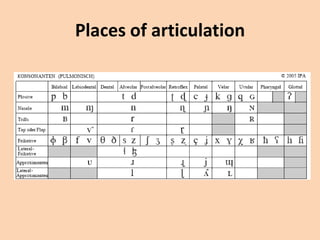
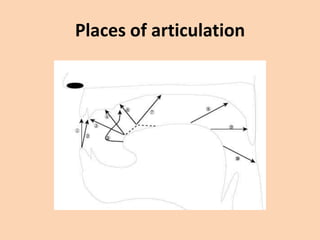
This document discusses the classification of consonant sounds according to their place of articulation in the vocal tract. It explains that consonants are sounds produced with some restriction of airflow, as opposed to vowels. The main places of articulation described are bilabial, labiodental, interdental, alveolar, palatal, velar, uvular, and glottal sounds. Each place is defined by where in the mouth the air flow is obstructed, such as with the lips or tongue touching different areas like the teeth, hard palate, soft palate or uvula.





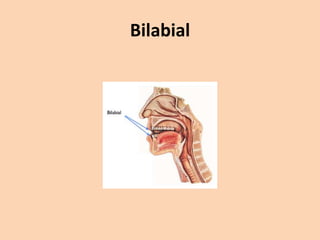
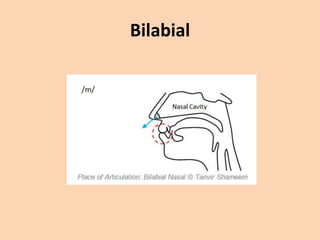
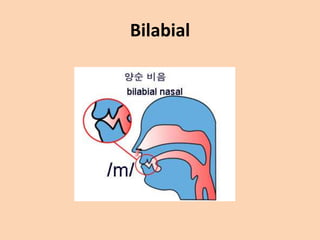
![Bilabial
• When producing a [b], [p] or [m], articulation
is done by bringing both lips together.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/consonants-140226014708-phpapp02/85/Phonetics-Consonants-11-320.jpg)

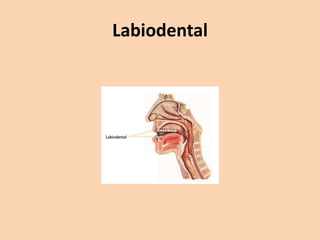
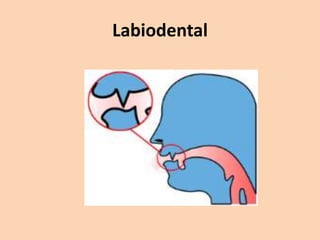
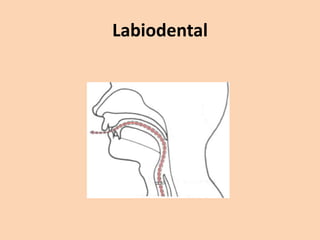
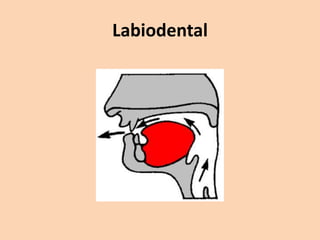
![Labiodental
• [f] and [v] are also used with the lips.
• They, however, are also articulated by
touching the bottom lip to the upper teeth.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/consonants-140226014708-phpapp02/85/Phonetics-Consonants-16-320.jpg)
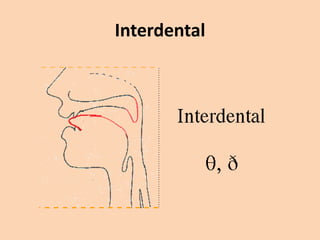
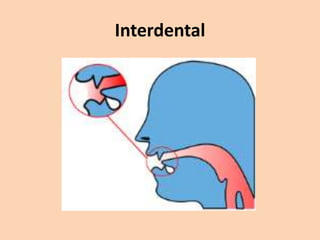
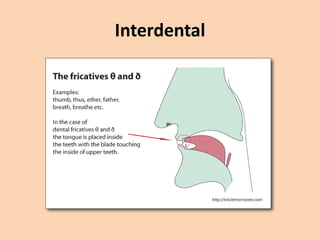
![Interdental
• [θ] and [ð] are both spelled as "th".
• They are pronounced by inserting the tip of
the tongue between the teeth.
• (θ as in think)
• (ð as in the)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/consonants-140226014708-phpapp02/85/Phonetics-Consonants-21-320.jpg)
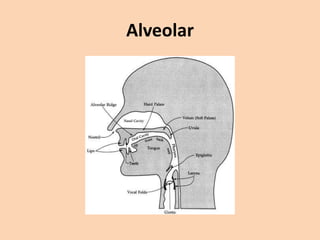
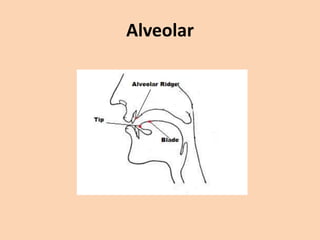
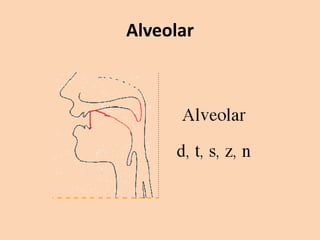
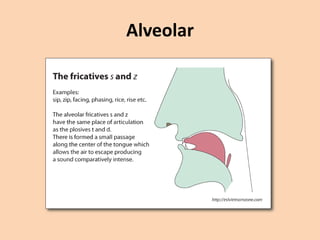
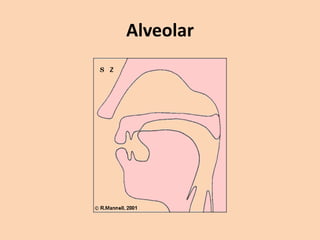
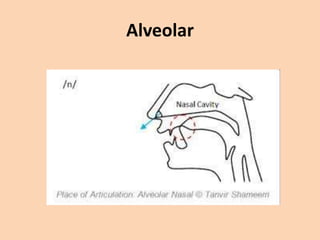
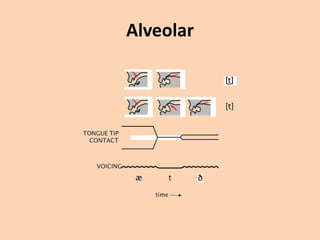
![Alveolar
• [t][d][n][s][z][l][r] are produced in many ways
where the tongue is raised towards the
alveolar ridge.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/consonants-140226014708-phpapp02/85/Phonetics-Consonants-25-320.jpg)
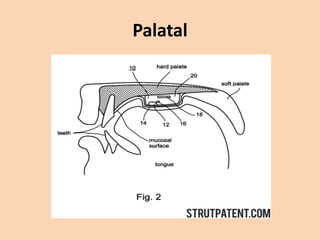
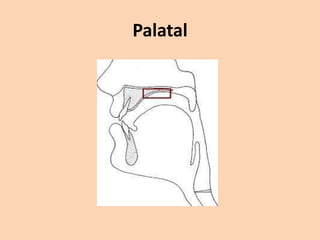
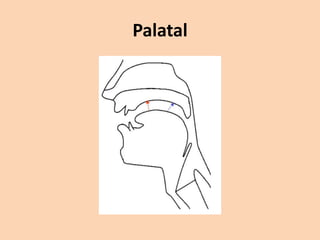
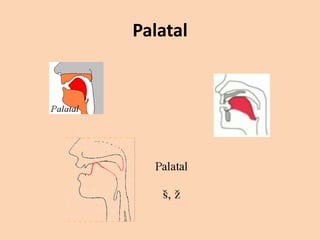
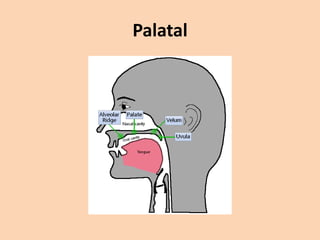
![Palatal
• [ ʃ ] [ ʒ ] [ tʃ ] [ dʒ ] [ j ] are produced by
raising the front part of the tongue to the
palate.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/consonants-140226014708-phpapp02/85/Phonetics-Consonants-35-320.jpg)
![Velar
• [k][g][ŋ] are produced by raising the back part
of the tongue to the soft palate or the velum.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/consonants-140226014708-phpapp02/85/Phonetics-Consonants-40-320.jpg)
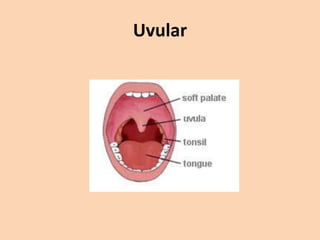
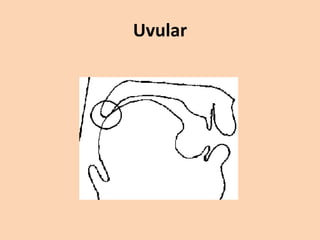
![Uvular
• [ʀ][q][ԍ] these sounds are produced by raising
the back of the tongue to the uvula. The 'r' in
French is often a uvular trill (symbolized by
[ʀ]). The uvular sounds [q] and [ԍ] occur in
Arabic. These do not normally occur in
English.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/consonants-140226014708-phpapp02/85/Phonetics-Consonants-42-320.jpg)

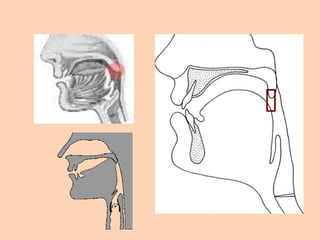
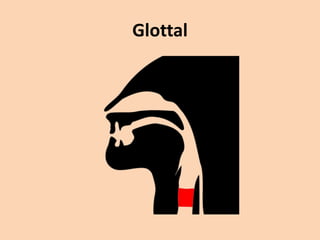
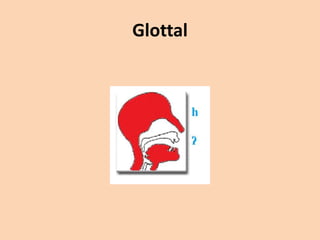
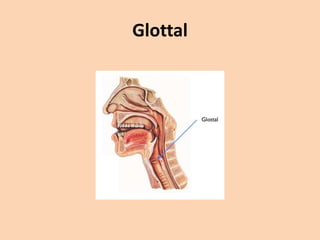
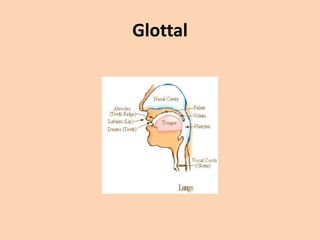
![Glottal
• [h][ʔ] the sound [h] is from the flow of air
coming from an open glottis, past the tongue
and lips as they prepare to pronounce a vowel
sound, which always follows [h].
• if the air is stopped completely at the glottis
by tightly closed vocal chords the sound upon
release of the chords is called a glottal stop
[ʔ].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/consonants-140226014708-phpapp02/85/Phonetics-Consonants-48-320.jpg)