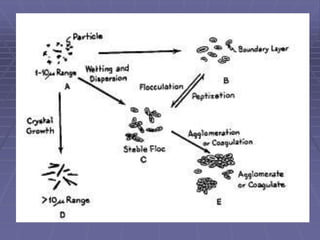
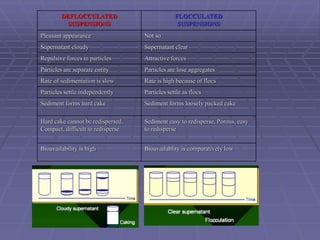
Suspensions are liquid dosage forms containing finely dispersed solid particles. They are used for drugs that are insoluble, unstable, or need to be absorbed slowly. Suspensions can be administered orally, ocularly, otically, rectally, parenterally, or topically. Factors in formulation include the nature and size of particles, viscosity, and physical stability. Structured vehicles and controlled flocculation are used to prepare deflocculated and flocculated suspensions, respectively. Evaluation tests assess properties like sedimentation, redispersibility, and zeta potential. Packaging requires containers with headspace and instructions to shake before use.







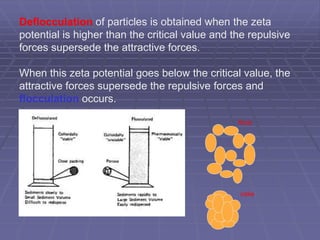



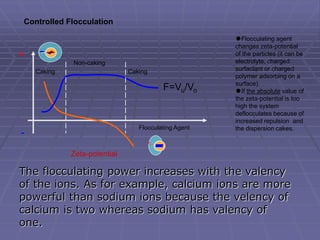
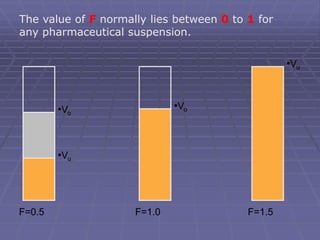
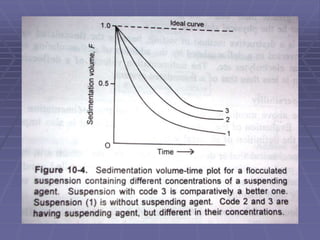
![Sedimentation volume, F, of a suspension is expressed by
the ratio of the equilibrium volume of the sediment, Vsed
[Vu] to the total volume, Vtot [Vo] of the suspension.
Thus, F = Vsed/Vtot = [Vu] / [Vo]
The value of F provides a qualitative knowledge
about the physical stability of the suspension.
Also used as one of the quality control tool- it is
simple to estimate
Higher the F, more stable the suspension is.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/suspensions-230831152223-6a69fb2a/85/SUSPENSIONS-ppt-13-320.jpg)



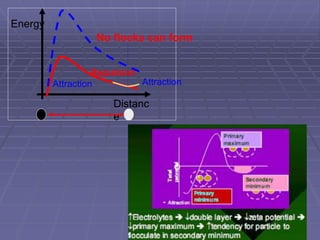
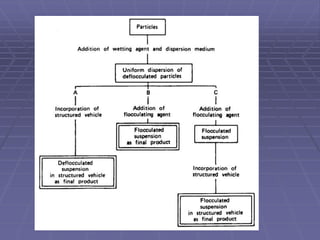
![METHODS OF PREPARATION
Aim is to prepare physically stable suspensions [desired one
is deflocculated or flocculated]. Hence the normal ways of
doing so are
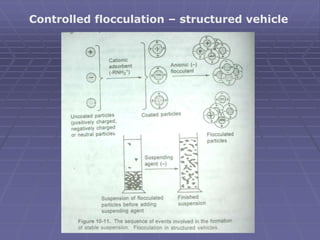
(1) use of structured vehicle – for deflocculated suspension
(2) use of controlled flocculation – for flocculated suspension
- using electrolytes
- using surfactants
- using polymers
and
(3) Controlled flocculation – structured vehicle](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/suspensions-230831152223-6a69fb2a/85/SUSPENSIONS-ppt-19-320.jpg)

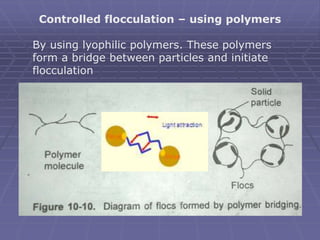
![Structured vehicle – Deflocculated suspension
Structured vehicles are the aqueous solutions of natural and
synthetic gums. – act by entrapping the particles [generally
deflocculated particles]
MC, CMC, sodium CMC, acacia, and tragacanth are the
most commonly used structured vehicle in the
pharmaceutical suspensions. [suspensions will be plastic
and pseudo plastic]
Suspensions of higher solids content are prepared
(e.g. toothpaste) using a combination of a clay and
a gum (e.g. NaCMC)
Hydrocolloids are also used as they hydrate well with water
and swell increasing viscosity.
Eg., Nonionic -- MC, HPMC
Ionic -- Sodium CMC, Cabopol
Clays -- Bentonite](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/suspensions-230831152223-6a69fb2a/85/SUSPENSIONS-ppt-24-320.jpg)
![Structured vehicle – Deflocculated suspension
Hence, these structured vehicles act as suspending
agents
and the concentration depends on
- Viscosity of vehicle – influence stability
- Amount of solids – adding clays calls for use of
preservatives [methyl and propyl parabens]
- Particle size
- Density of solids – density of structured vehicles
increased by including PVPs, PEGs,
sugars, Glycerine](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/suspensions-230831152223-6a69fb2a/85/SUSPENSIONS-ppt-25-320.jpg)