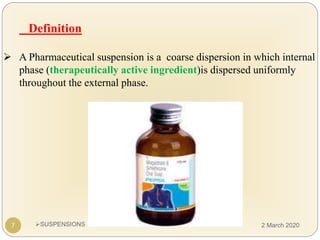
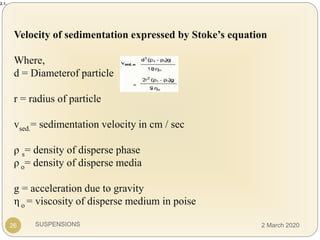
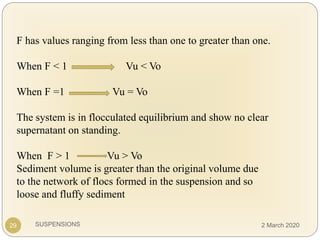
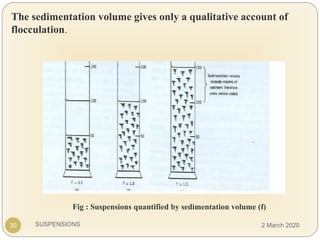
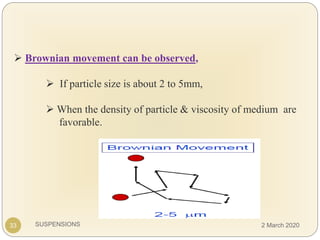
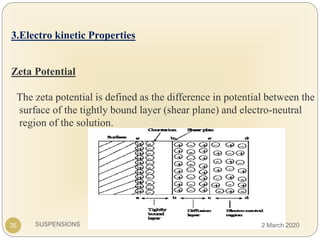
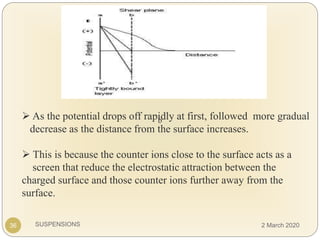
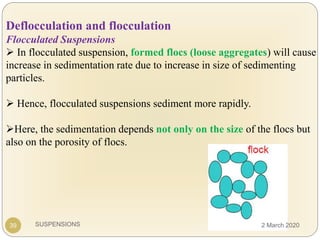
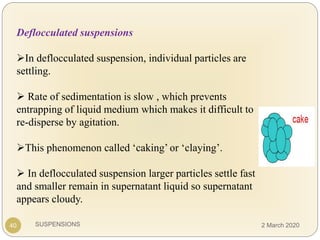
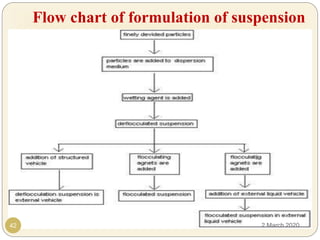
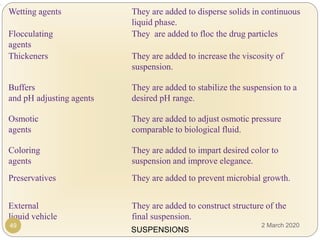
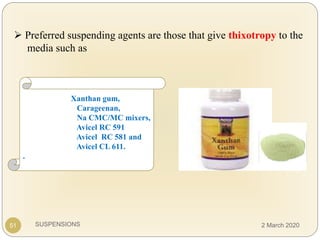
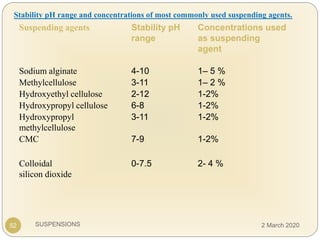
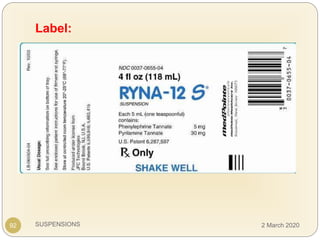
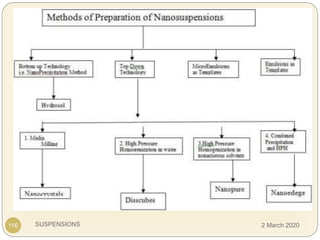
The document discusses pharmaceutical suspensions. It defines a suspension as a coarse dispersion where an insoluble solid drug is uniformly dispersed throughout a liquid medium. Suspensions offer advantages like increased drug stability and controlled drug release. Key considerations in developing suspensions include particle size, sedimentation, wettability, and Brownian motion. Common applications are oral suspensions to mask bitter tastes or for poorly soluble drugs. The document outlines classification, evaluation, stabilization, and manufacturing of pharmaceutical suspensions.